8 disk striping, Figure2.1 disk striping (raid 0) example, Disk striping – Avago Technologies MegaRAID SATA 150-4 (523) User Manual
Page 28: Disk striping (raid 0) example
2-6
Introduction to RAID
Copyright © 2003–2006 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Step 6.
Select Patrol Read Status to display the number of iterations
completed, the current state of the patrol read (active or stopped),
and the schedule for the next execution of patrol read.
2.4.8
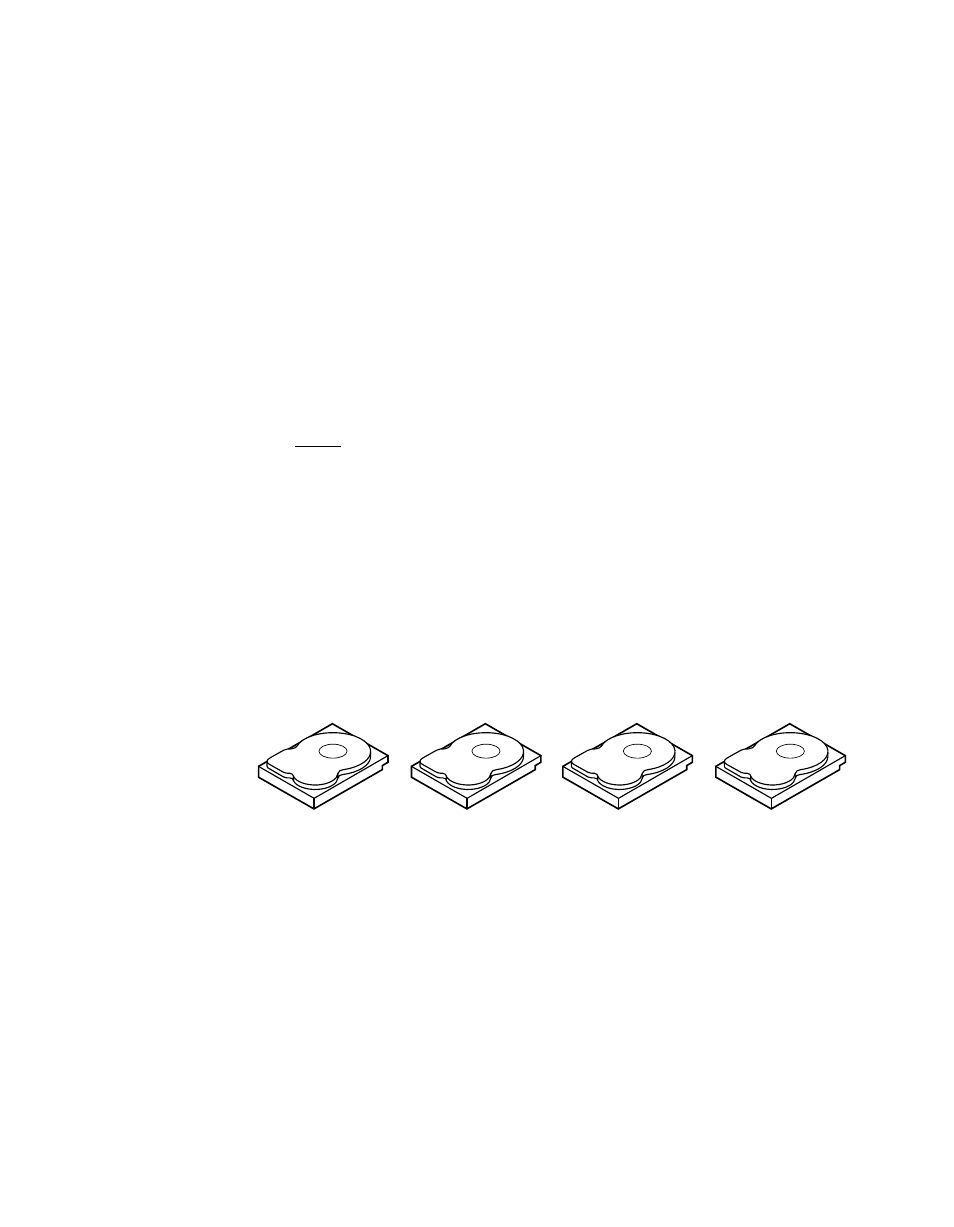
Disk Striping
Disk striping allows you to write data across multiple physical disks
instead of just one physical disk. Disk striping involves partitioning each
drive storage space into stripes that can vary in size from 8 Kbytes to
128 Kbytes. These stripes are interleaved in a repeated sequential
manner. The combined storage space is composed of stripes from each
drive. It is recommended that you keep stripe sizes the same across
RAID arrays.
Note:
Do not install an operating system on a logical drive with
less than a 16 Kbyte stripe size.
For example, in a four-disk system using only disk striping (used in RAID
level 0), segment 1 is written to disk 1, segment 2 is written to disk 2,
and so on. Disk striping enhances performance because multiple drives
are accessed simultaneously, but disk striping does not provide data
redundancy.
shows an example of disk striping.
Figure 2.1
Disk Striping (RAID 0) Example
2.4.8.1
Stripe Width
Stripe width is the number of disks involved in an array where striping is
implemented. For example, a four-disk array with disk striping has a
stripe width of four.
Segment 1
Segment 5
Segment 9
Segment 2
Segment 6
Segment 10
Segment 3
Segment 7
Segment 11
Segment 4
Segment 8
Segment 12
