Table2.8 raid 10 overview, Figure2.5 raid 10 logical drive, Raid 10 logical drive – Avago Technologies MegaRAID SATA 150-4 (523) User Manual
Page 39: Raid 10 overview
RAID Levels
2-17
Copyright © 2003–2006 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
provides an overview of RAID 10.
In
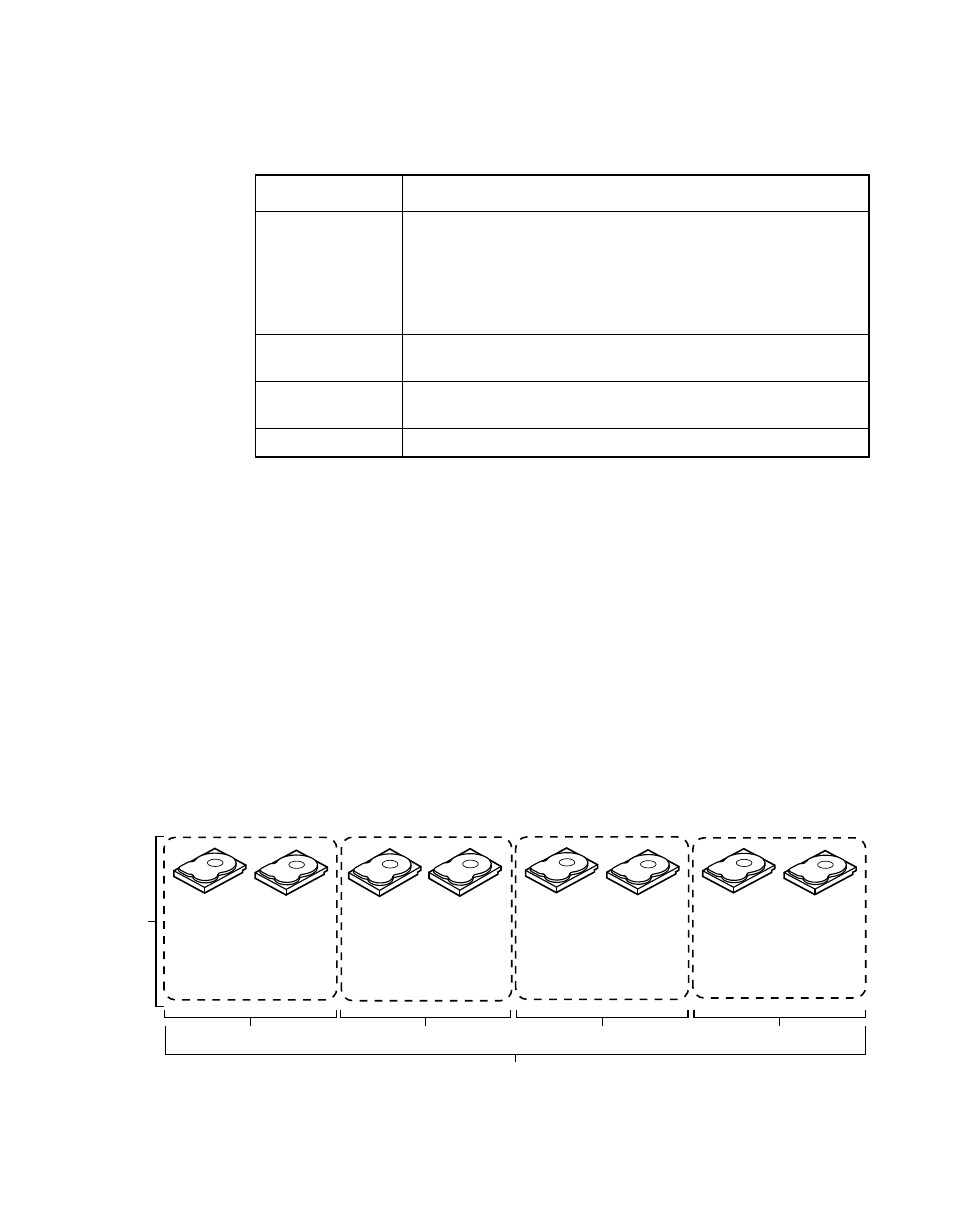
, logical drive 0 is created by distributing data across four
arrays (arrays 0 through 3). Spanning is used because one logical drive
is defined across more than one array. Logical drives defined across
multiple RAID 1 level arrays are referred to as RAID 10 logical drives. To
increase performance, data is striped across arrays, which enables
access to multiple arrays simultaneously.
Using RAID level 10, rather than a simple RAID set, up to 8 spans can
be supported, and up to 8 drive failures can be tolerated, though less
than total disk drive capacity is available. Though multiple drive failures
can be tolerated, only one drive failure can be tolerated in each RAID 1
level array.
Figure 2.5
RAID 10 Logical Drive
Table 2.8
RAID 10 Overview
Feature
Description
Uses
Appropriate when used with data storage that needs 100%
redundancy of mirrored arrays and that also needs the
enhanced I/O performance of RAID 0 (striped arrays.) RAID
10 works well for medium-sized databases or any
environment that requires a higher degree of fault tolerance
and moderate to medium capacity.
Strong Points
Provides both high data transfer rates and complete data
redundancy.
Weak Points
Requires twice as many drives as all other RAID levels
except RAID 1.
Drives
2n, where n is greater than 1.
Segment 1
Segment 1
Duplicate
Segment 2
Segment 3
Duplicate
Segment 4
Duplicate
Segment 3
Segment 4
Segment 5
Segment 6
Segment 7
Segment 8
Segment 5
Duplicate
Segment 6
Duplicate
Segment 7
Duplicate
Segment 8
Duplicate
Segment 2
Duplicate
...
RAID 1
RAID 1
RAID 1
RAID 1
RAID 10
RAID 0
...
...
...
