3 examples of servo system configurations, 1 single-phase, 200 v main circuit, 3 examples of servo system configurations -8 – Yaskawa SGDH Linear Sigma Series User Manual
Page 30: 1 single-phase, 200 v main circuit -8, Sgdh-ae servopack
1 Outline
1.3.1 Single-phase, 200 V Main Circuit
1-8
1.3 Examples of Servo System Configurations
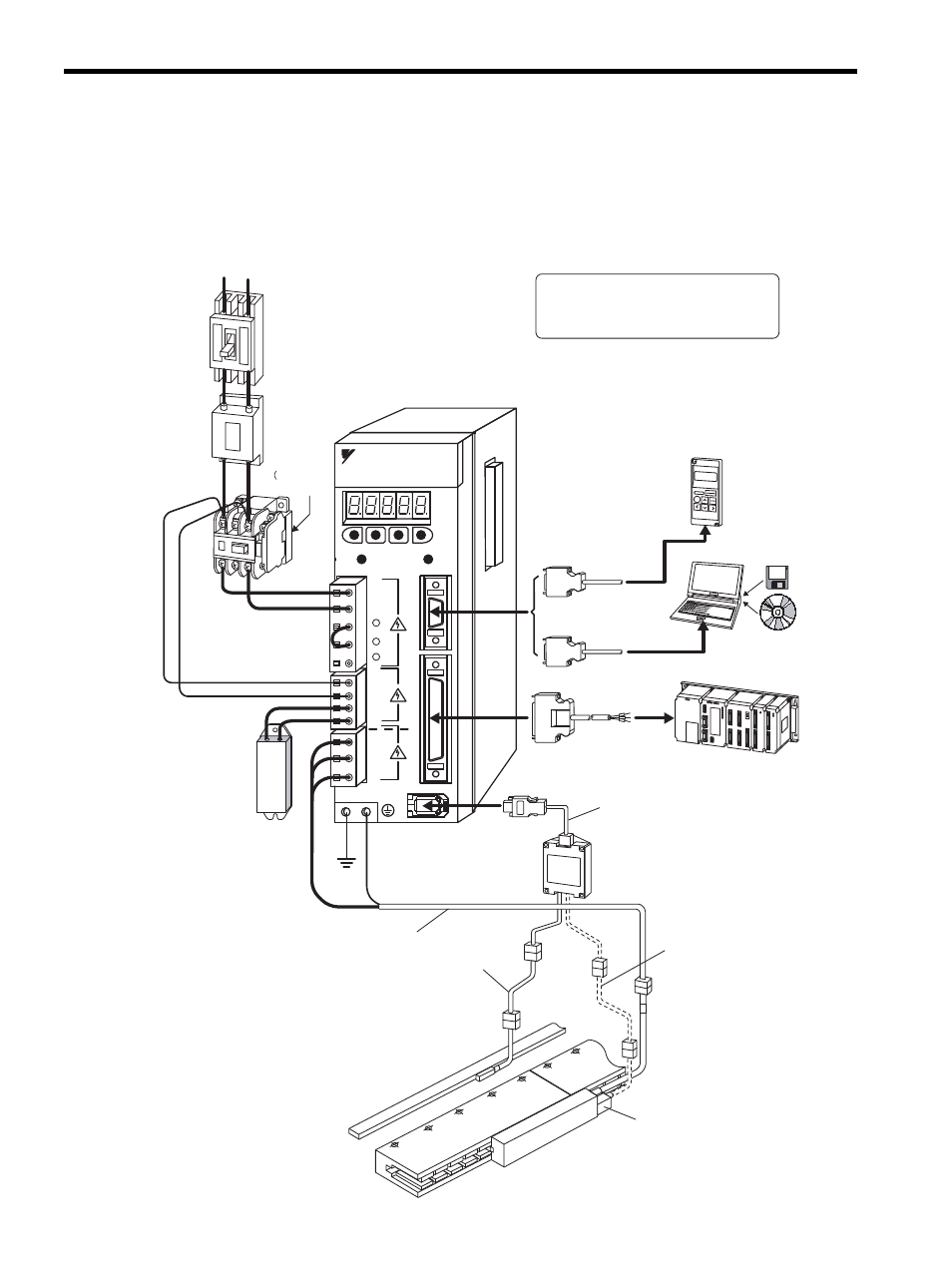
This section describes examples of basic servo system configuration.
1.3.1 Single-phase, 200 V Main Circuit
Regenerative
resistor
Noise filter
Molded-case
circuit breaker
(MCCB)
Magnetic
contactor
Digital
operator
Personal computer
Host controller
Connection cable
for digital operator
Connection cable
for personal computer
(Refer to 2.6.1.)
(Refer to 2.6.1.)
(Refer to 2.6.1.)
(Refer to 2.6.4.)
(Refer to 2.6.5.)
Refer to
2.6.3)
(Refer to 2.6.3)
(Refer to 2.6.2)
I/O signal cable
Note : To connect a DC reactor, refer to
7.5.5 DC Reactor for Harmonic
Suppression.
SGDH-AE
SERVOPACK
Power supply
Single-phase 200 VAC
Protects the power supply
line by shutting the circuit
OFF when an overcurrent
is detected.
Eliminates external
noise from the power
line.
Connect an external
regenerative resistor
to terminals B1 and B2
if the regenerative
capacity is insufficient.
Turns the servo ON
and OFF.
Install a surge
suppressor.
Linear scale
(To be provided by
users.)
Hall sensor unit
Connection cable
for hall sensor
Encoder
cable
Main circuit cable for
linear servomotor
Serial converter unit
Connection cable
for serial converter unit
(Refer to 2.5.)
(Refer to 2.5.)
(Refer to 2.5.)
(Refer to 2.5.)
(Refer to 2.4.)
R T
C
N
3
C
N
1
L1C
L2C
B1
B2
U
V
W
L1
L2
+
1
MODE/SET
DATA/
CHARGE
POWER
C
N
SGDH-
SERVOPACK
200V
YASKAWA
+
2
-
Coreless Linear Servomotor
