Dns servers, Configuring a management interface, Configuring management interface parameters – H3C Technologies H3C SecBlade IPS Cards User Manual
Page 62: Configuring management interface parameters -2
5-2
DNS Servers
Domain name system (DNS) is a distributed database used by TCP/IP applications to translate domain
names into corresponding IP addresses. With DNS, you can use easy-to-remember domain names in
some applications and let the DNS server translate them into correct IP addresses.
Domain name resolution is implemented by querying the DNS server. The resolution procedure is as
follows:
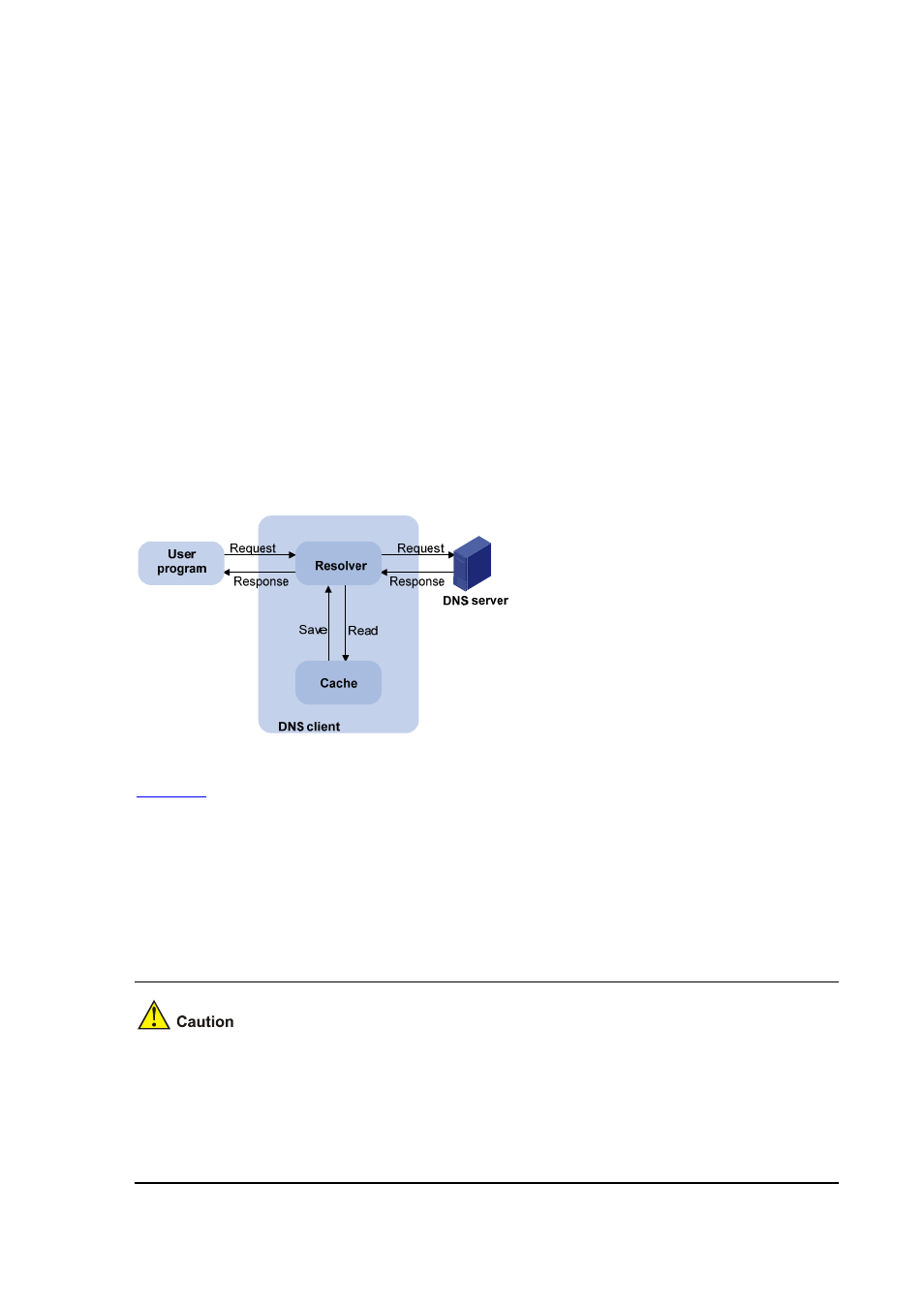
1) A user program sends a name query to the resolver of the DNS client.
2) The DNS resolver looks up the local domain name cache for a match. If a match is found, it sends
the corresponding IP address back. If not, it sends a query to the DNS server.
3) The DNS server looks up the corresponding IP address of the domain name in its DNS database. If
no match is found, it sends a query to a higher DNS server. This process continues until a result,
whether successful or not, is returned.
4) The DNS client returns the resolution result to the application after receiving a response from the
DNS server.
Figure 5-1 Dynamic domain name resolution
shows the relationship between the user program, DNS client, and DNS server. The resolver
and cache comprise the DNS client. The user program and DNS client can run on the same device or
different devices, while the DNS server and the DNS client usually run on different devices.
Configuring a Management Interface
Configuring Management Interface Parameters
z
After the IP address of a management interface is changed, Web users that have already logged in
to the management interface cannot perform operations in IE any more. They need to log in to the
interface again by using the new IP address.
z
If a device has multiple management interfaces, you are recommended to use one of them, and
configure others as standby interfaces.
