Configuring sflow, Protocols and standards, Sflow configuration task list – H3C Technologies H3C MSR 5600 User Manual
Page 208
195
Configuring sFlow
Sampled Flow (sFlow) is a traffic monitoring technology.
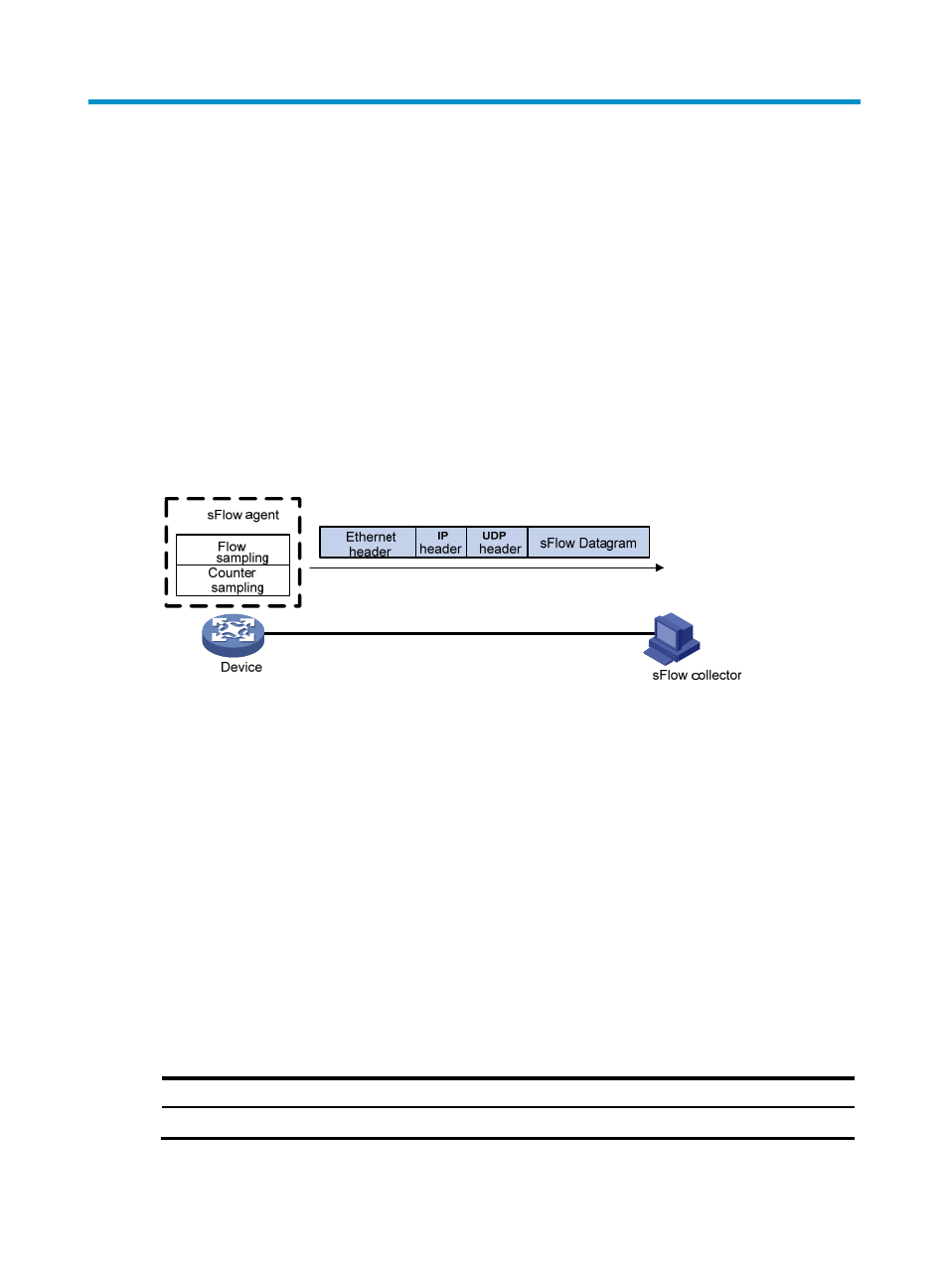
As shown in
, the sFlow system involves an sFlow agent embedded in a device and a remote
sFlow collector. The sFlow agent collects interface counter information and packet information and
encapsulates the sampled information in sFlow packets. When the sFlow packet buffer is full, or the
aging timer (fixed to 1 second) of sFlow packets expires, the sFlow agent sends the sFlow packets in UDP
datagrams to the specified sFlow collector. The sFlow collector analyzes the information and displays the
results.
sFlow provides the following sampling mechanisms:
•
Flow sampling—Obtains packet information.
•
Counter sampling—Obtains interface counter information.
Figure 57 sFlow system
As a traffic monitoring technology, sFlow has the following advantages:
•
Supports traffic monitoring on Gigabit and higher-speed networks.
•
Provides good scalability to allow one sFlow collector to monitor multiple sFlow agents.
•
Saves money by embedding the sFlow agent in a device, instead of using a dedicated sFlow agent
device.
Protocols and standards
•
RFC 3176, InMon Corporation's sFlow: A Method for Monitoring Traffic in Switched and Routed
Networks
•
sFlow.org, sFlow Version 5
sFlow configuration task list
Tasks at a glance
