Key netstream technologies, Flow aging, Netstream data export – H3C Technologies H3C MSR 5600 User Manual
Page 191: Netstream traditional data export
178
•
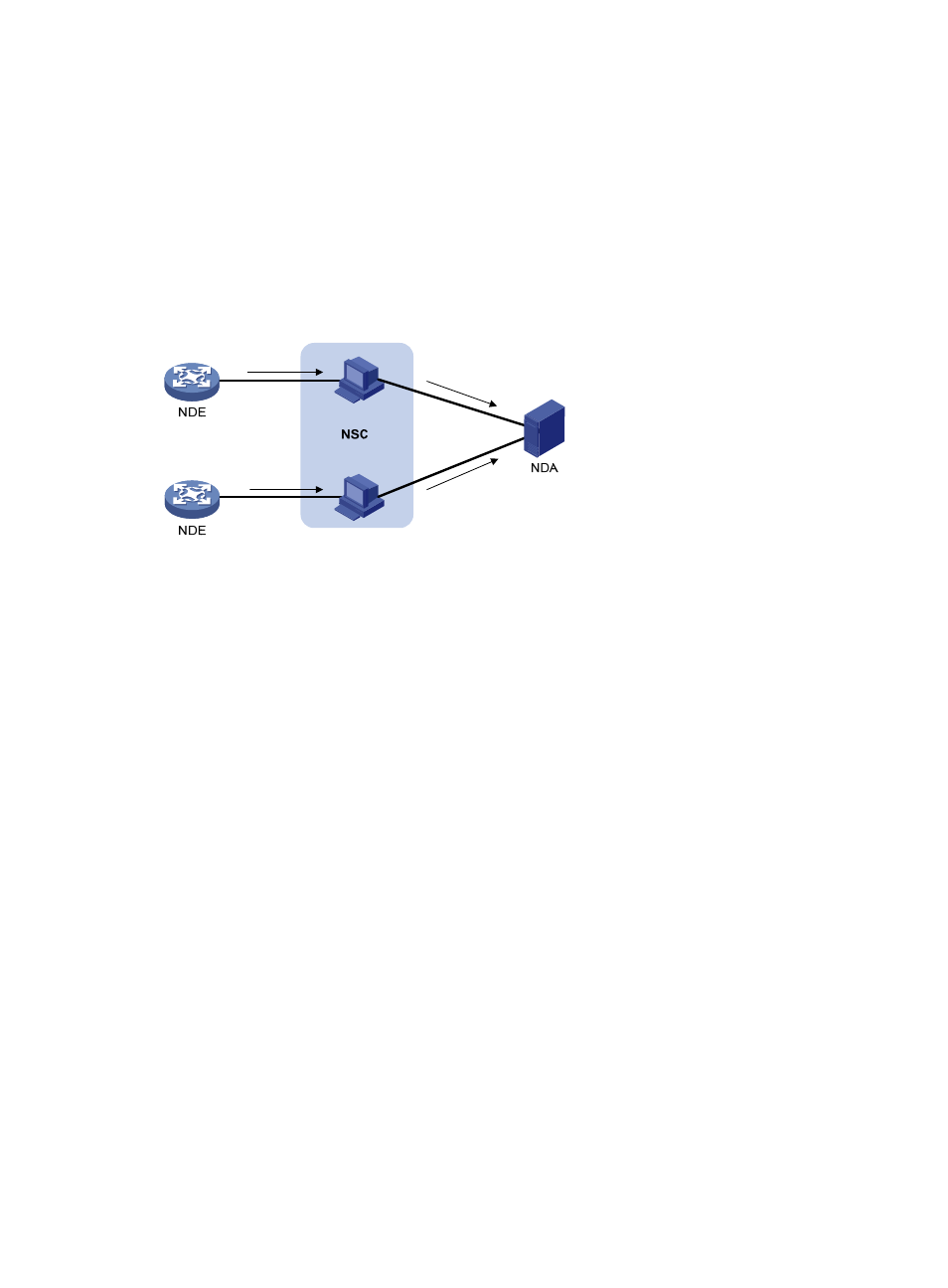
NetStream collector—The NSC is usually a program running in an operation system. It parses the
packets received from the NDE, and then it stores the statistics to the database for the NDA. The
NSC can gather data from multiple NDEs.
•
NetStream data analyzer—The NDA analyzes network traffic. It collects statistics from the NSC,
performs further process for the statistics, and generates various reports for traffic billing, network
planning, and attack detection and monitoring. The NDA can collect statistics from multiple NSCs.
Typically, the NDA features a Web-based system for users to easily obtain, view, and gather the
data.
NSC and NDA are usually integrated into a NetStream server.
Figure 52 NetStream system
As shown in
, NetStream collects and analyzes data as follows:
1.
The NDE, the device configured with NetStream, periodically delivers the collected statistics to the
NSC.
2.
The NSC processes the statistics, and then it sends the results to the NDA.
3.
The NDA analyzes the statistics for accounting, network planning, and the like.
This document focuses on the description and configuration of the NDE.
Key NetStream technologies
Flow aging
NetStream uses the flow aging to enable the NDE to export NetStream data to the NetStream server.
NetStream creates a NetStream entry for each flow to store the flow statistics in the cache. When the
timer of the entry expires, the NDE exports the summarized data to the NetStream server in a specific
NetStream export format, and clears NetStream entry information in the cache. For more information
about flow aging types and configurations, see "
Configuring NetStream flow aging
NetStream data export
NetStream traditional data export
Traditional NetStream collects the statistics of each flow. When an entry ages out, NetStream exports the
data in the entry to the NetStream server.
The data includes the statistics of each flow. However, this method consumes more bandwidth and CPU
than the aggregation method, and it requires a large cache size.
