Epon system reliability, S7500e series switches and epon system – H3C Technologies H3C S7500E Series Switches User Manual
Page 40
2-7
EPON System Reliability
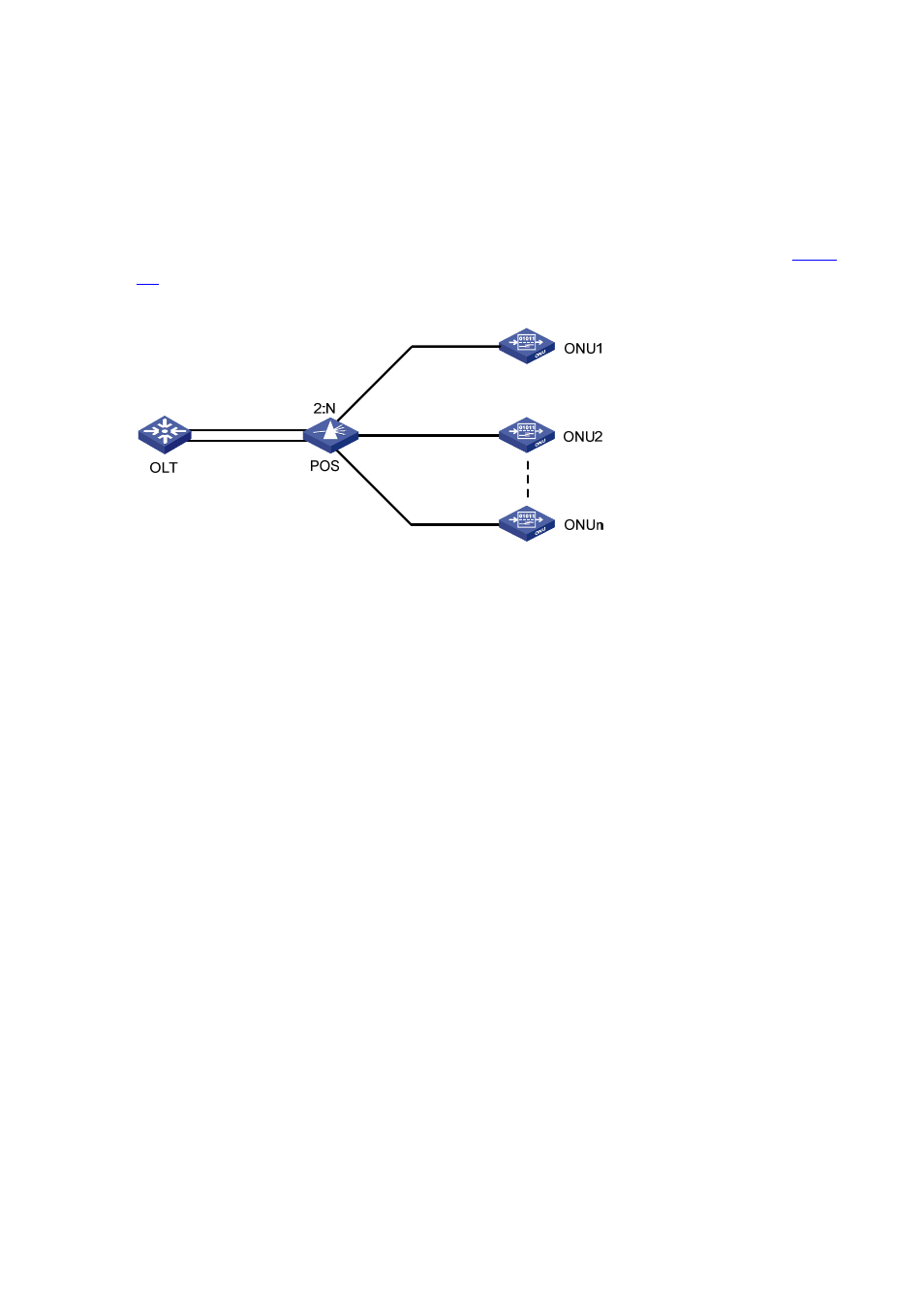
To ensure high reliability for the trunk fibers and OLTs in an EPON system, you can add two OLT ports
on one EPON card or on two different EPON cards to a fiber backup group. When a system fault
occurs, for example, when a trunk fiber is broken or an OLT port becomes abnormal, a switchover is
performed automatically between the two OLTs, which act as backup for each other. You can also
perform a manual switchover between two OLT ports added to the backup group as needed.
depicts a fiber backup group, where POS is a 2:N optical splitter.
Figure 2-5
Network diagram for a fiber backup group
S7500E Series Switches and EPON System
Features of an S7500E Switch Working as an OLT Device
With an EPON card installed, an S7500E switch can work as an OLT device in an EPON system. In
such a case, the S7500E switch has the following features:
Compliance with EPON interoperation standards: Interoperable with other vendors' ONUs that
support China Telecom Technical Requirements for EPON Devices.
Integrating access and convergence: Each EPON card in an S7500E switch has multiple physical
OLT ports, and each OLT port has 64 logical ports, namely, ONU ports, each of which can
correspond with an ONU. Thus, one EPON card can work as multiple OLT devices. This reduces
users' equipment purchase costs, and the management costs and fault ratio caused by
interconnection between multiple device ports.
Powerful ONU remote management capabilities: You can centrally manage and configure
different services on ONUs and ONU UNI (User Network Interface) ports through OLTs. This
greatly lowers subsequent maintenance costs.
Excellent security protection: OLTs can protect network devices in terms of control, management,
and forwarding against illegal access or abnormal traffic.
Powerful access control list (ACL) and QoS functions: OLTs support standard and extended ACLs,
and support traffic policing, traffic shaping, packet priority, multiple queue scheduling mechanisms,
multiple congestion avoidance mechanisms, and other QoS assurance functions.
