14 bpdu tunneling configuration, Introduction to bpdu tunneling, Background – H3C Technologies H3C S7500E Series Switches User Manual
Page 201: Bpdu tunneling configuration
14-1
14
BPDU Tunneling Configuration
When configuring BPDU tunneling, go to these sections for information you are interested in:
Introduction to BPDU Tunneling
BPDU Tunneling Configuration Examples
Introduction to BPDU Tunneling
As a Layer 2 tunneling technology, BPDU tunneling enables Layer 2 protocol packets from
geographically dispersed customer networks to be transparently transmitted over specific channels
across a service provider network.
Background
Customers usually use dedicated lines in a service provider network to build their own Layer 2
networks. As a result, very often, a customer network is broken down into parts located at different
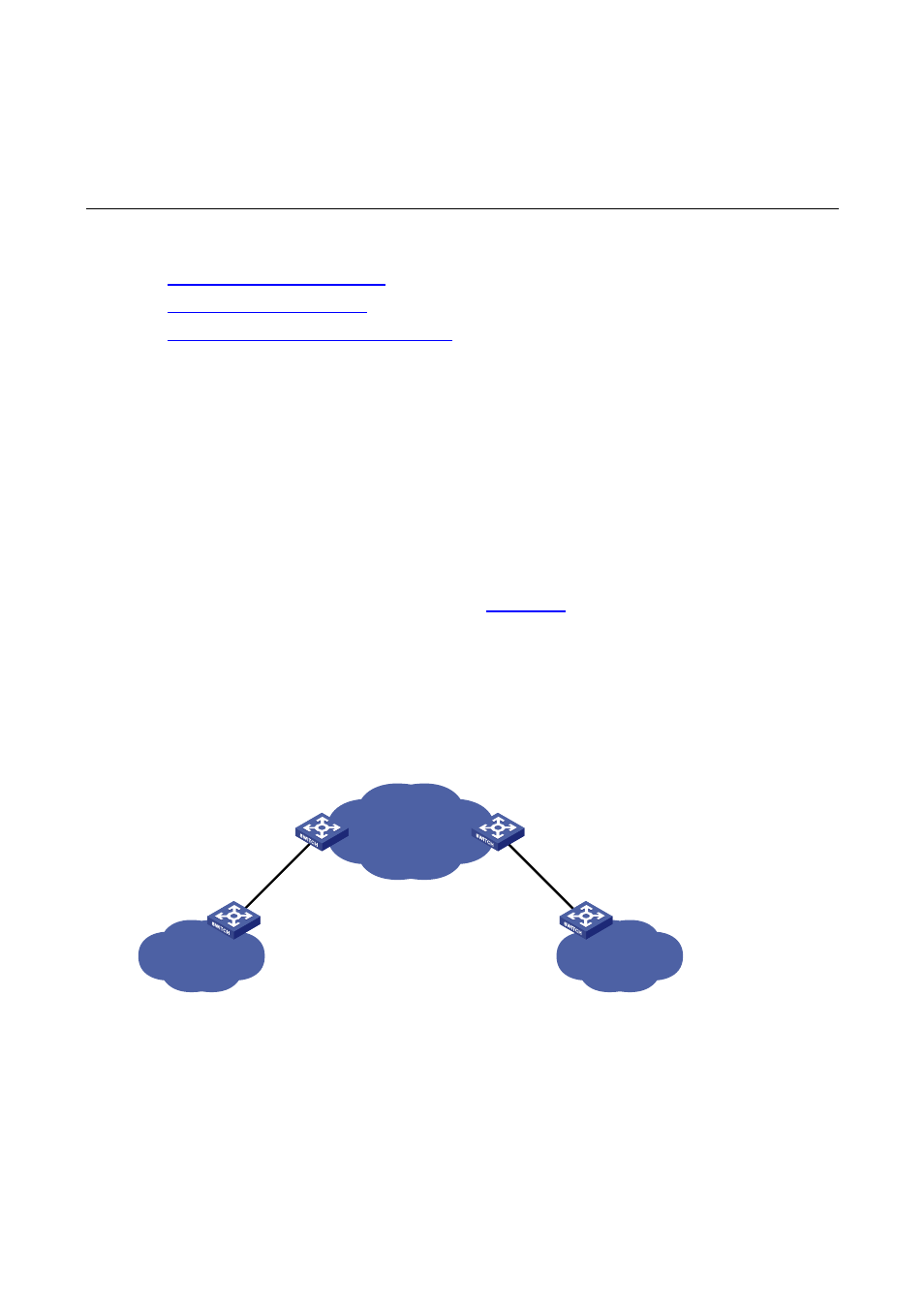
sides of the service provider network. As shown in
, User A has two devices: CE 1 and CE
2, both of which belong to VLAN 100. User A’s network is divided into network 1 and network 2, which
are connected by the service provider network. When Layer 2 protocol packets cannot be
transparently transmitted in the service provider network, User A’s network cannot implement
independent Layer 2 protocol calculation (for example, STP spanning tree calculation). In this case,
the Layer 2 protocol calculation in User A’s network is mixed with that in the service provider network.
Figure 14-1
BPDU tunneling application scenario
ISP network
User A network 1
VLAN 100
User A network 2
VLAN 100
CE 1
CE 2
PE 1
PE 2
With BPDU tunneling, Layer 2 protocol packets from customer networks can be transparently
transmitted in the service provider network:
1) After receiving a Layer 2 protocol packet from User A network 1, PE 1 in the service provider
network encapsulates the packet, replaces its destination MAC address with a specific multicast
MAC address, and then forwards the packet in the service provider network;
