Aggregating links in static mode, Selecting a reference port, Setting the aggregation state of each member port – H3C Technologies H3C S7500E Series Switches User Manual
Page 129: Table 11-4
11-5
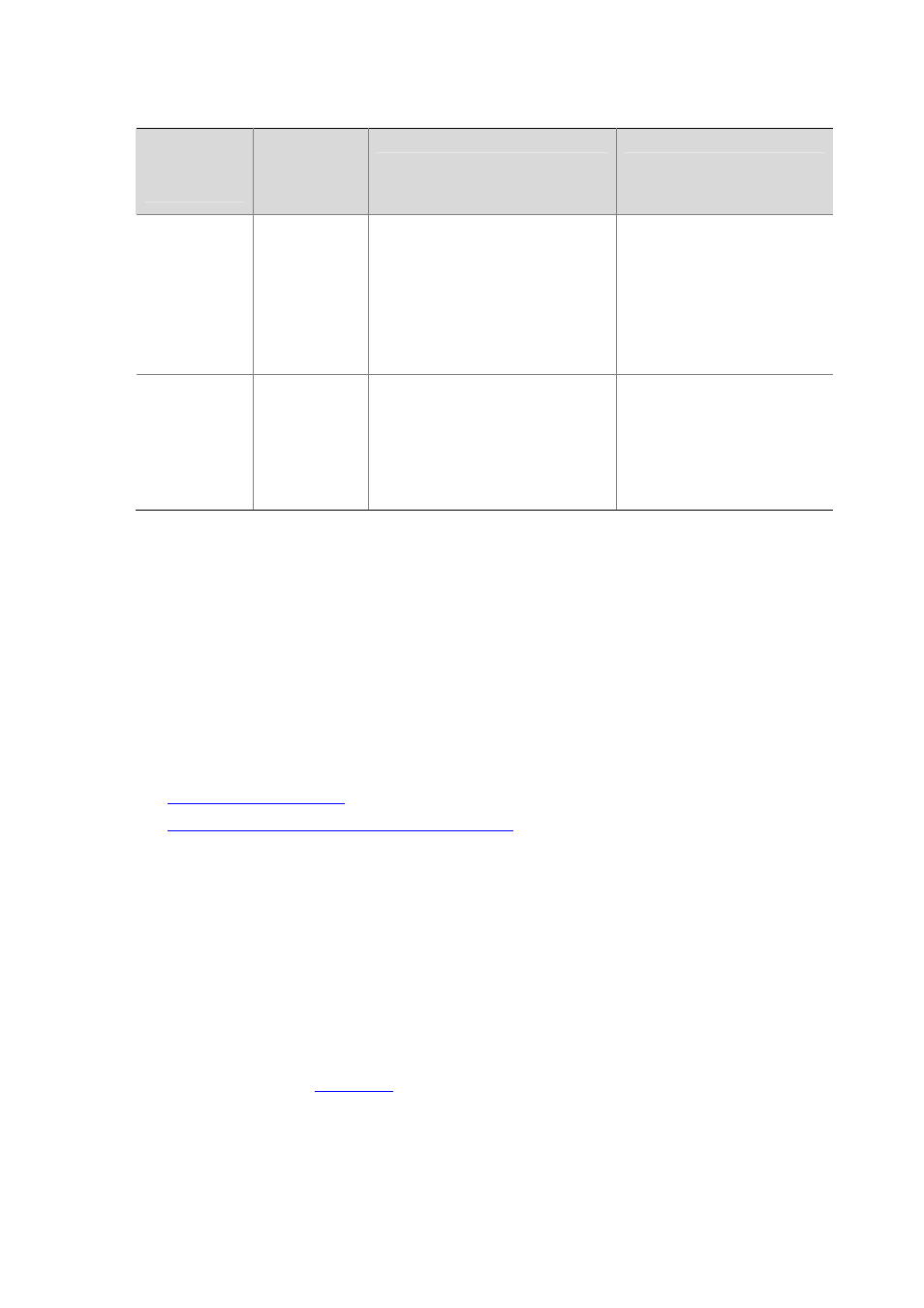
Table 11-4
A comparison between static and dynamic aggregation modes
Aggregation
mode
LACP status
on member
ports
Pros
Cons
Static Disabled
Aggregation is stable. The
aggregation state of the member
ports is not affected by their peers.
The member ports cannot
change their aggregation state
in consistent with their peers.
The administrator needs to
manually maintain link
aggregations.
Dynamic Enabled
The administrator does not need to
maintain link aggregations. The peer
systems maintain the aggregation
state of the member ports
automatically.
The aggregation state of
member ports is easily affected
by the network environment,
which makes dynamic
aggregation instable.
In a dynamic link aggregation group:
A selected port can receive and send LACPDUs.
An unselected port can receive and send LACPDUs only if it is up and have the same class-two
configurations as the aggregate interface.
Aggregating Links in Static Mode
LACP is disabled on the member ports in a static aggregation group. The aggregation state of the
member ports must be maintained manually.
Static link aggregation comprises:
Setting the aggregation state of each member port
Selecting a reference port
The system selects a reference port from the member ports that are in the up state and have the same
class-two configurations as the aggregate interface.
The candidate ports are sorted by aggregation priority, duplex, and speed in this order: lowest
aggregation priority, full duplex/high speed, full duplex/low speed, half duplex/high speed, and half
duplex/low speed. The one at the top is selected as the reference port. If two ports have the same
aggregation priority, duplex mode, and speed, the one with the lower port number wins out.
Setting the aggregation state of each member port
After selecting the reference port, the static aggregation group sets the aggregation state of each
member port as shown in
.
