Compuprint 4247-Z03 Programmer Manual User Manual
Page 202
Decimal
Hex
Content
Description
4-5
4-5
8000 - 7FFF
X Coordinate of Origin of Bar Code Block
6-7
6-7
8000 - 7FFF
Y Coordinate of Origin of Bar Code Block
8-9
8-9
0000
When you use the X,Y coordinate system or the I,B coordinate
system with the inline orientation equal to 0 degrees, you must
use the 0 or 90 degree orientation for bar codes.
2D00
Note (2)
5A00
When you use the I,B reference system and the inline
orientation is 180 degrees, you must use the 180 or 270 degree
orientation for bar codes.
8700
10
A
00
Absolute I, Absolute B
20
Absolute I, Relative B
40
Relative I, Absolute B
60
Relative I, Relative B
A0
Absolute X, Absolute Y
11-x
B-x
Reserved
Notes:
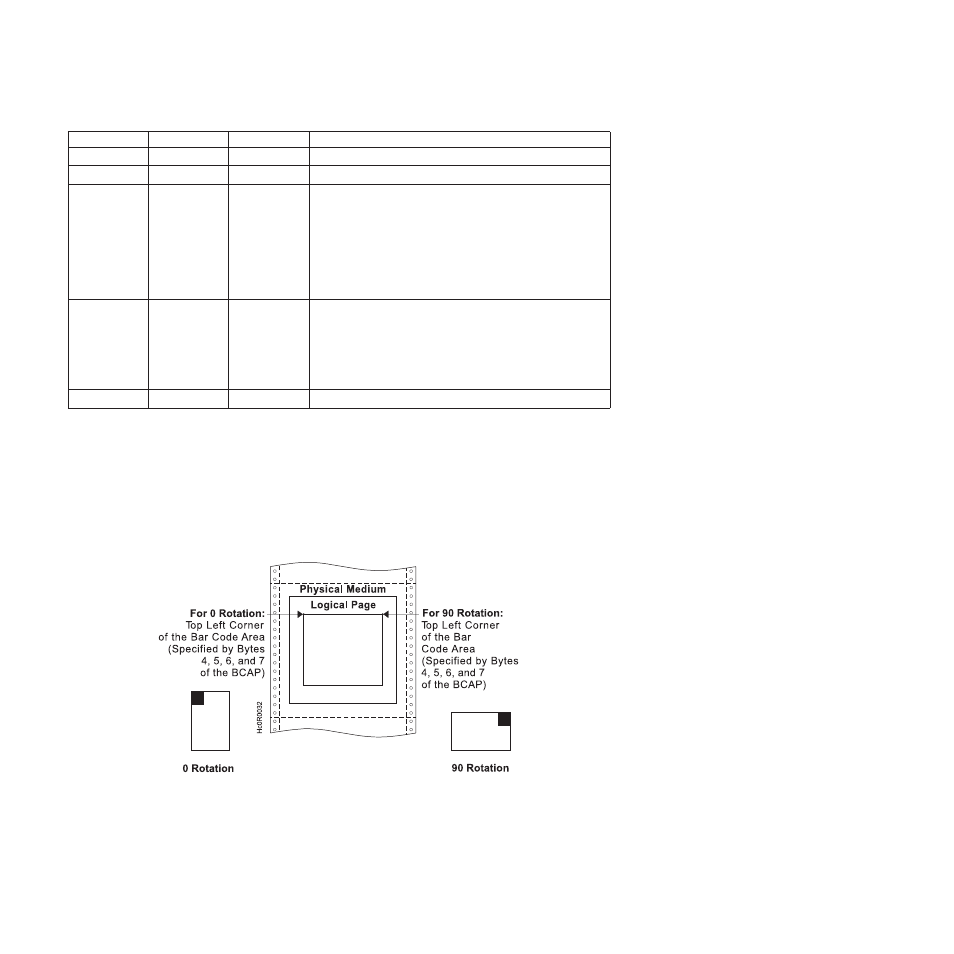
1. Any positive or negative value fitting in the two byte field is allowable. Negative values are in
twos-complement form. Figure 6-38 shows the BCAP field specifying the top left reference point, or
origin, for the bar code block, relative to the logical page.
2. Bar codes with a unit/module width of 0.533 mm (0.021 in.) cannot be printed in high speed mode. Bar
codes with a unit/module width of 0.356 mm (0.014 in.) and a wide-to-narrow ratio of 2.5:1 cannot be
printed in high speed mode.
Byte A of the BCAP specifies the reference coordinate system. The reference coordinate system for
determining the top left corner of the bar code area can be either the X,Y or the I,B coordinate system.
If byte A equals X'00', the absolute I and B coordinates determine the top left corner. BCAP bytes 4 and 5
specify the text inline coordinate. BCAP bytes 6 and 7 specify the text baseline coordinate.
Figure 26. Specifying the Bar Code Block Using the Bar Code Area Position Field
182
Programmer Manual
