5 marker operations – GW Instek APS-1102 Control Software User Manual User Manual
Page 58
APS-1102 Control Software User Manual
7-6
7.5.5 Marker
operations
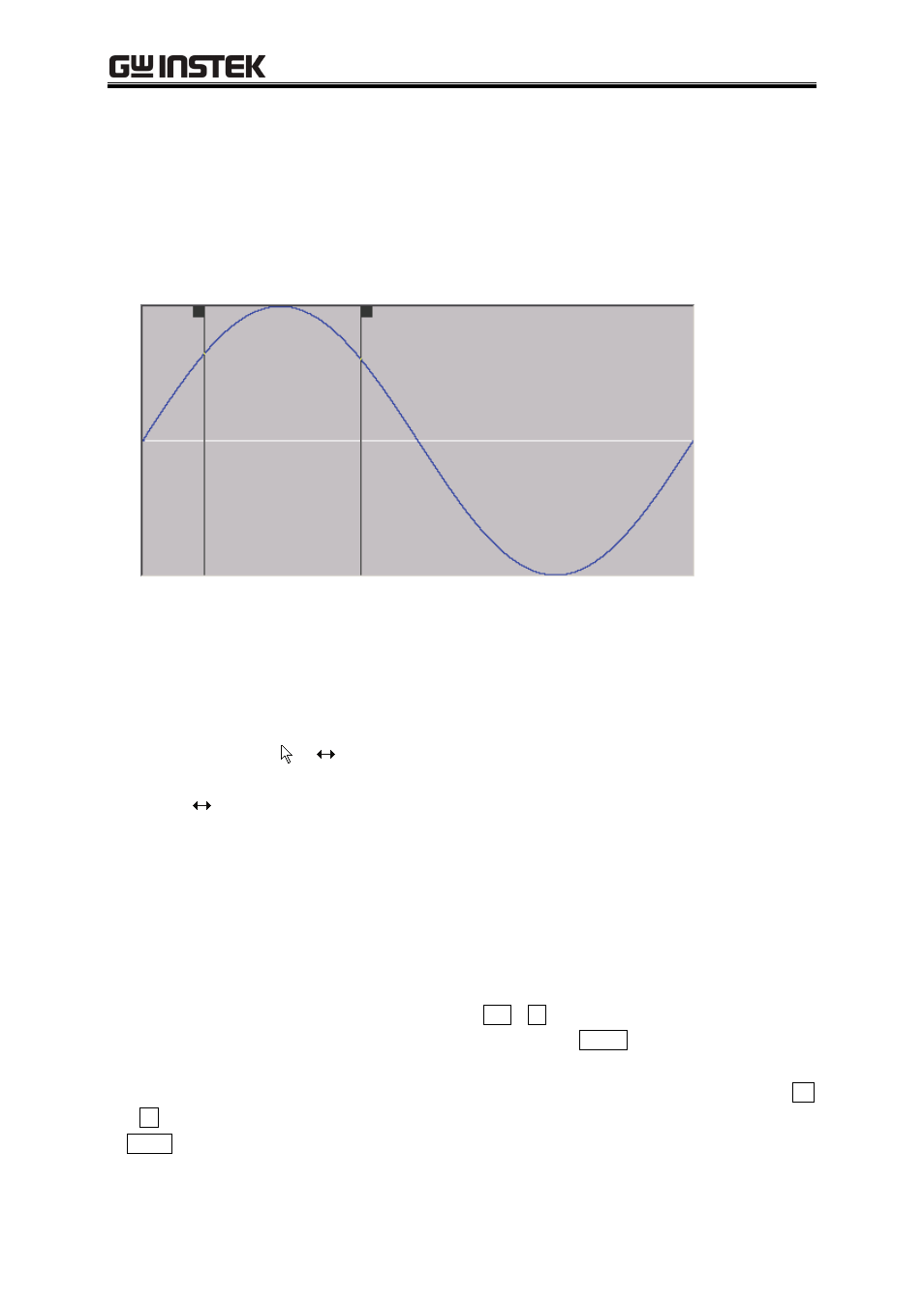
a) Marker types
There are two markers used in the ARB: marker A and marker B.
Marker A cannot be set to the right of marker B. marker A must be always to the left of or at the same
position as marker B.
Marker
A
Marker
B
The position of each marker is displayed to the right of [MrkA(X)] and [MrkB(X)].
The waveform value to the marker position is displayed to the right of [A(Y)] and [B(Y)].
b) Moving the marker (mouse dragging)
The marker can be moved in two ways: mouse dragging and numerical value specification.
Moving the mouse cursor to the same horizontal position as the marker, the shape of the mouse
cursor changes from to . Dragging the mouse in this status moves the marker. Though the
marker is difficult to see to the right or left edge, moving the mouse cursor to either edges makes the
cursor to .
When the marker is moved by mouse dragging, the waveform data address is used as the moving unit.
When one dot on the display corresponds to multiple addresses due to the display magnification
ratio, the address corresponding to one dot on the display is used as the moving step.
c) Marker moving (numerical value setting)
For marker position specification with a higher resolution, directly input the marker position with a
numerical value.
Clicking the right space to [MrkA(X)] or pressing
Alt
+
A
selects the position display section of
marker A. Inputting a numerical value followed by pressing the
Enter
key jump marker A to the
specified position.
Likewise, to jump marker B to the specified position, click the right space to [MrkB(X)] or press Alt
+
B
and input a numerical value in the marker B position display section, and then press the press
Enter
key.
