HEIDENHAIN ND 1300 VED and Crosshair Systems User Manual
Page 89
5
Probes
69
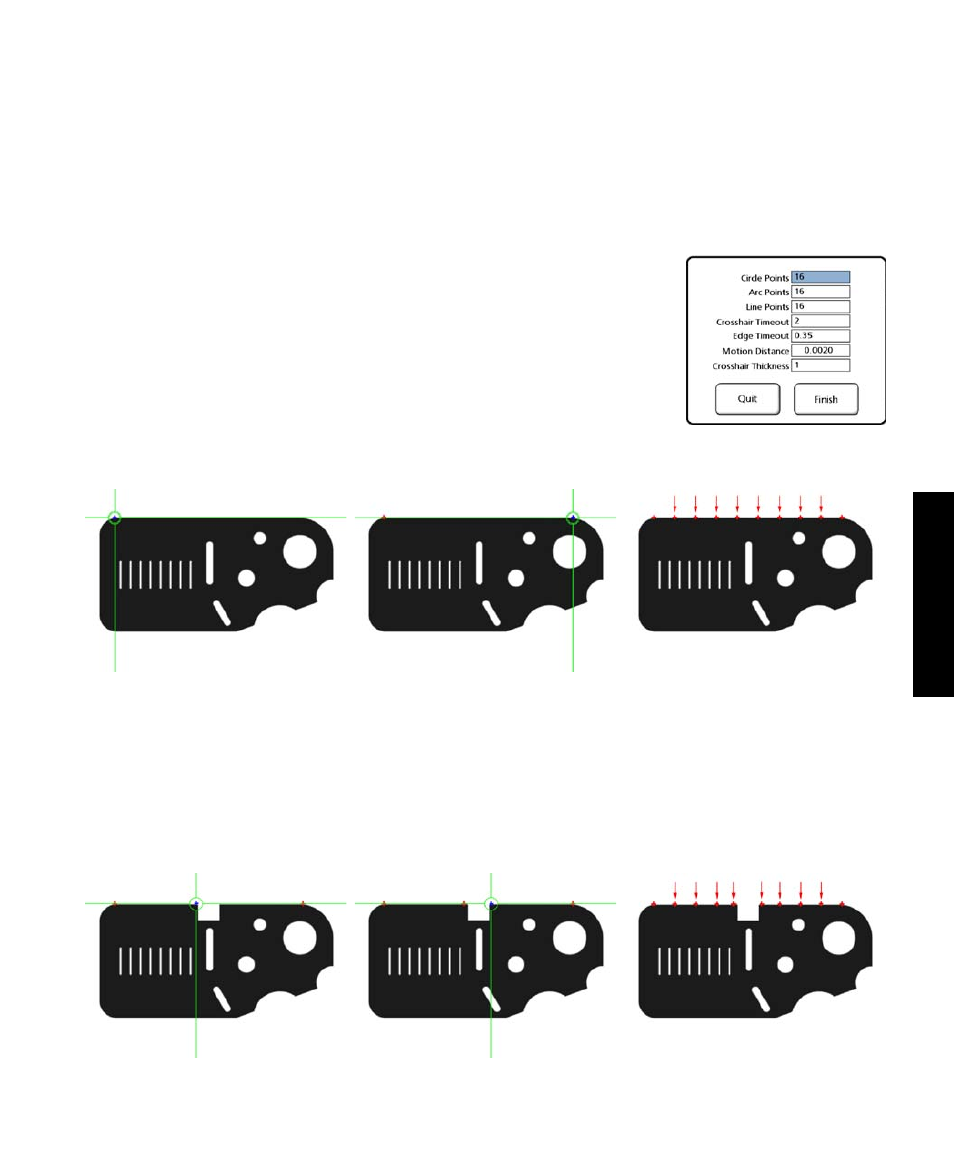
Seeding to avoid erroneous data
The multiple edge probe can be seeded manually using the single edge probe to avoid collecting data over
keyways, protrusions and other feature anomalies. This is accomplished by:
1 Seeding points very close to, and enclosing the area of anomaly using the single edge probe
2 Switching to the multiple edge probe to complete the measurement by probing the reminder
of specified points automatically
Normally, the multiple edge probe attempts to collect the specified number
of points from an even distribution of probed points along the feature edge,
which includes the seed points.
As shown in the example below, when a line without anomalies is probed, the
multiple edge probe is seeded with the two endpoints, and then automatically
probes the remainder of the specified points at locations distributed evenly
between the endpoints.
This process works well when the feature probed includes few or no edge anomalies. However, discon-
tinuous or indistinct edges can lead to data errors if no preventive action is taken.
Since a combination of seeded locations and system-generated locations are used to distribute and probe
points, tightly enclosing any edge anomaly between two seeded points greatly reduces the possibility that
the multiple edge probe will probe the anomaly.
16 Points are specified
for a line
The multiple edge probe is seeded with the endpoints of the line, and evenly distributes the remaining points
The single edge probe seeds the endpoints of the line and then probes additional seed points that enclose the
line anomaly. The multiple edge probe is then selected and the remaining points are probed automatically.
Probing
