Altera RapidIO II MegaCore Function User Manual
Page 132
5–8
Chapter 5: Signals
Physical Layer Signals
RapidIO II MegaCore Function
August 2014
Altera Corporation
User Guide
To control the transceivers, you must implement the following blocks in your design:
■
For Arria V, Arria V GZ, Cyclone V, and Stratix V variations: Dynamic
reconfiguration block. Refer to
The dynamic reconfiguration block lets you reconfigure the following PMA
settings:
■
Pre-emphasis
■
Equalization
■
Offset cancellation
■
V
OD
on a per channel basis
■
For all variations: Reset controller block. Refer to
“Reset for RapidIO II IP Cores”
f
For more information about the Altera dynamic reconfiguration and PHY reset
controller IP cores, refer to the
.
f
For information about the Arria 10 PHY reset controller IP core and the Arria 10
dynamic reconfiguration interface, refer to the
.
f
For more information about offset cancellation, refer to the relevant device handbook.
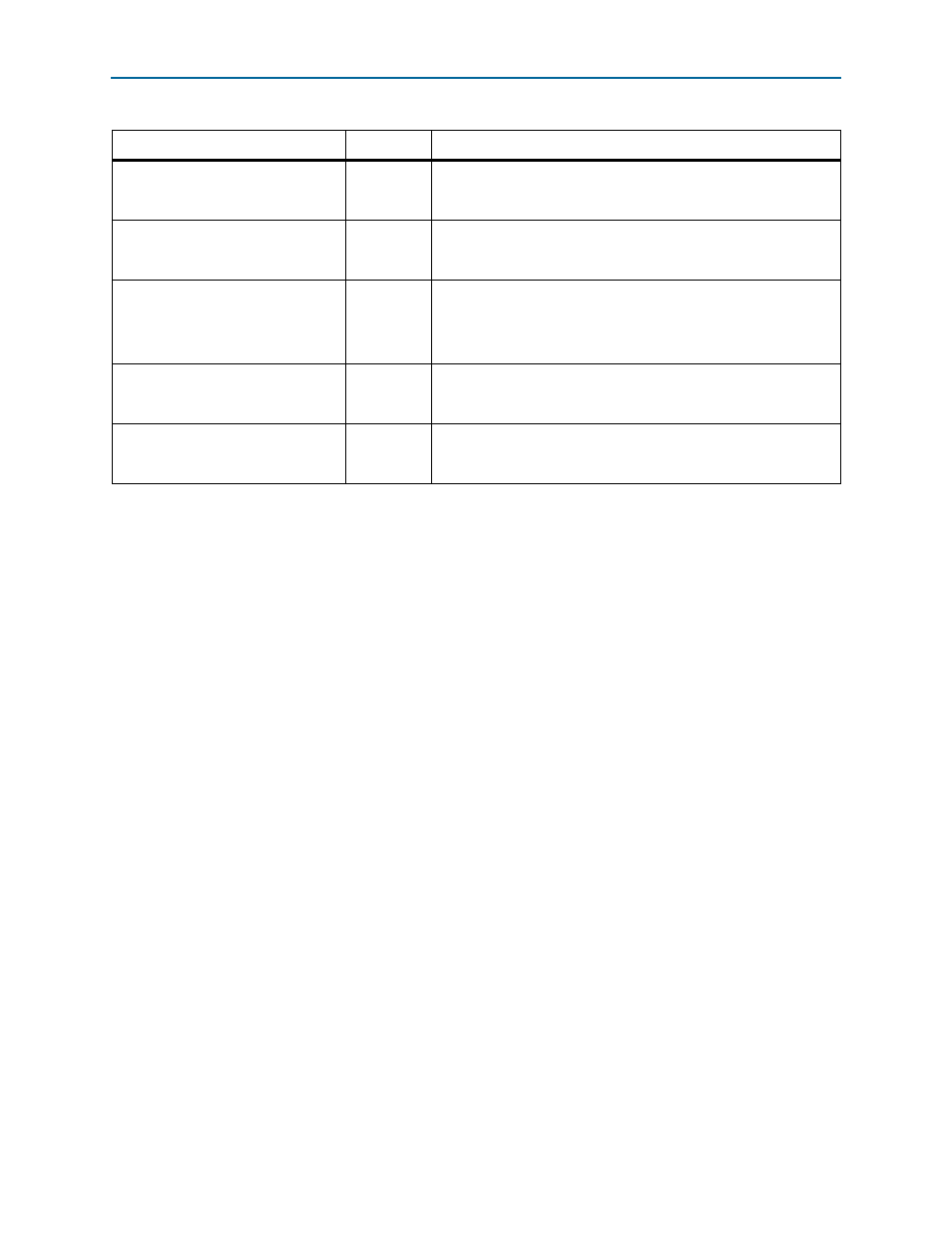
reconfig_read_ch3
Input
Arria 10 dynamic reconfiguration slave read request for the
transceiver channel configured for RapidIO lane 3. This signal is
available only in 4x variations.
reconfig_write_ch3
Input
Arria 10 dynamic reconfiguration slave write request for the
transceiver channel configured for RapidIO lane 3. This signal is
available only in 4x variations.
reconfig_address_ch3[9:0]
Input
Arria 10 dynamic reconfiguration slave address bus for the
transceiver channel configured for RapidIO lane 3. The address is a
word address, not a byte address.
This signal is available only in 4x variations.
reconfig_writedata_ch3[31:0]
Input
Arria 10 dynamic reconfiguration slave write data bus for the
transceiver channel configured for RapidIO lane 3. This signal is
available only in 4x variations.
reconfig_readdata_ch3[31:0]
Output
Arria 10 dynamic reconfiguration slave read data bus for the
transceiver channel configured for RapidIO lane 3. This signal is
available only in 4x variations.
Table 5–8. Arria 10 Transceiver Dynamic Reconfiguration Avalon-MM Interface Signals (Part 3 of 3) (Part 3 of 3)
Signal
Direction
Description
