Critical paths view – Achronix ACE Version 5.0 User Manual
Page 156
Views
Chapter 3. Concepts
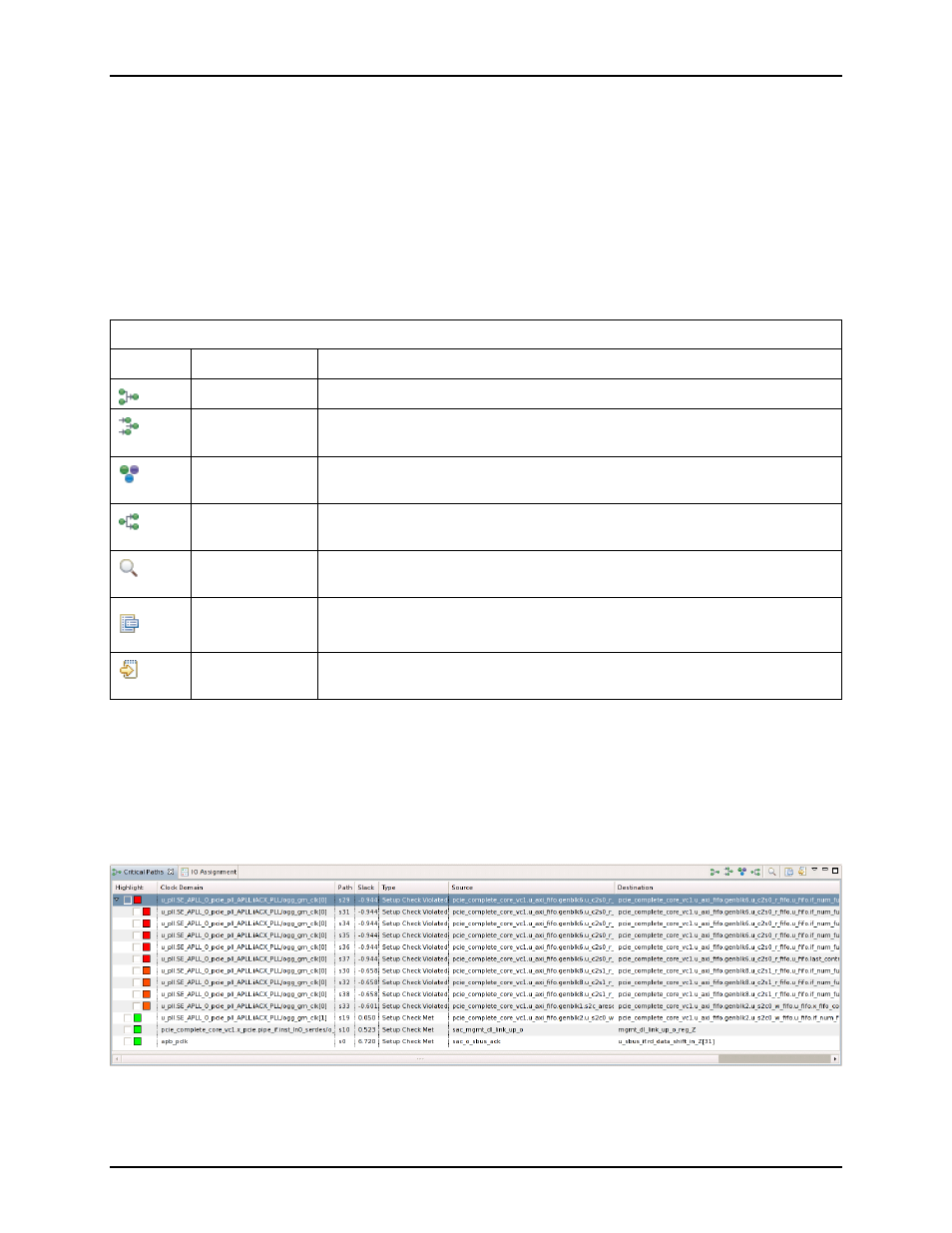
Critical Paths View
The Critical Paths view provides a table of critical paths resulting from running timing analysis. This view
displays critical path details, manages selection of objects on critical paths, and highlights critical paths in
the
. The information shown in the view will differ slightly based upon whether the target
device is synchronous (the 22iHD family) or asynchronous (the 22iHP family).
Clicking on a row in the table enables the toolbar buttons for analyzing the associated critical path, and
causes a graphical diagram of the associated critical path to be displayed in the
Clicking on a column header sorts the table according to that column’s data.
By default, the Critical Paths view is included in the
. To add it to the current
perspective, select Window → Show View → Critical Paths.
Critical Paths View Toolbar Buttons
Icon
Action
Description
Select path
Adds the selected critical path in the table to the current ACE selection set.
Select pins
Adds pins on the selected critical path in the table to the current ACE
selection set.
Select instances
Adds instances on the selected critical path in the table to the current ACE
selection set.
Select nets
Adds nets on the selected critical path in the table to the current ACE
selection set.
Zoom to path
Zooms the Floorplanner view to a region containing the selected critical
path in the table.
Print Path
Details
Prints a detailed report of the selected critical path in the table to the text
output in the TCL Console view.
Save Script File
Displays the Save Script File dialog, allowing the user to save a TCL script
of find commands for use in the schematic viewer of the synthesis tool.
Synchronous Target Devices
For synchronous parts, the view will show a tree table, with each branch of the tree representing a separate
clock domain. The most critical path of each clock domain will be the branch node, with all other paths
from that clock domain acting as leaves for that branch. Setup violations are considered ”worse” than hold
violations, thus any setup violation will take precedence over hold violations as the branch node, regardless
of relative slack values.
Figure 3.75: Critical Paths View for 22iHD devices
Entries in the table are always grouped by clock domain, with individual paths sorted within a clock
UG001 Rev. 5.0 - 5th December 2012
144
