Nff classification – Northern Connectors Harting DIN 41 612 Connectors User Manual
Page 23
00
.
17
Gen
er
al
in
fo
rma
tio
n
Railway specific products with NFF Classification: F1 and I2
In addition to the standard demands of connectors, as defined
in IEC 60 603-2, for example, market and application specific
demands and requirements are gaining increasing significance.
In the railway engineering area the demands made on reliability
and safety are particularly high, in order to ensure utmost
passenger safety in all instances. Especially in the case of routes
involving a high share of tunnels that only offer limited escape
route possibilities in the event of fire, the technical demands made
on the materials employed are very stringent.
In addition to the fire load, and/or the flammability of a material,
the so-called smoke gas density is a key characteristic, which is
determined based on the opacity and toxicity of the smoke gas
emissions. The risk posed by the two characteristics can not
be defined in relationship to each other, which means that both
minimal inflammability as well as minimal smoke gas density must
be fulfilled. Materials that meet both requirements are very rare
and in many instances it is only possible to fully meet one of the
two criteria.
The French NFF 16-101 railway standard defines these
requirements precisely and presents a structure of application
groups by way of a matrix.
NFF 16-101 classifies non-metallic materials used in rail vehicles
in terms of fire behavior, opacity and toxicity of smoke gas
emissions in the event that the materials should burn.
In order to enable the classification with regard to the deployment
of connectors, the following values must be applied:
1. Fire behavior class
Classification:
I0
for I.O. ≥ 70
and no inflammation at 960 °C
I1
for I.O. 45 - 69
and no inflammation at 960 °C
I2
for I.O. 32 - 44
and no inflammation at 850 °C
I3
for I.O. 28 - 31
and no afterburning at 850 °C
I4
for I.O. ≥ 20
NC not classified
Note: The values are derived from specified test methods
determining the oxygen value (I.O.) and testing inflammability by
way of a filament.
2. Smoke development classification
Classification:
F0
for I.F. ≤ 5
F1
for I.F. 6 - 20
F2
for I.F. 21 - 40
F3
for I.F. 41 - 80
F4
for I.F. 81 - 120
F5
for I.F. > 120
Note: The values of the smoke index (I.F.) are derived from
specified test methods by determining opacity (specific optical
density, opacity values), toxicity (critical gas concentration of CO,
CO
2
, HCl, HBr, HCN, HF, SO
2
in smoke).
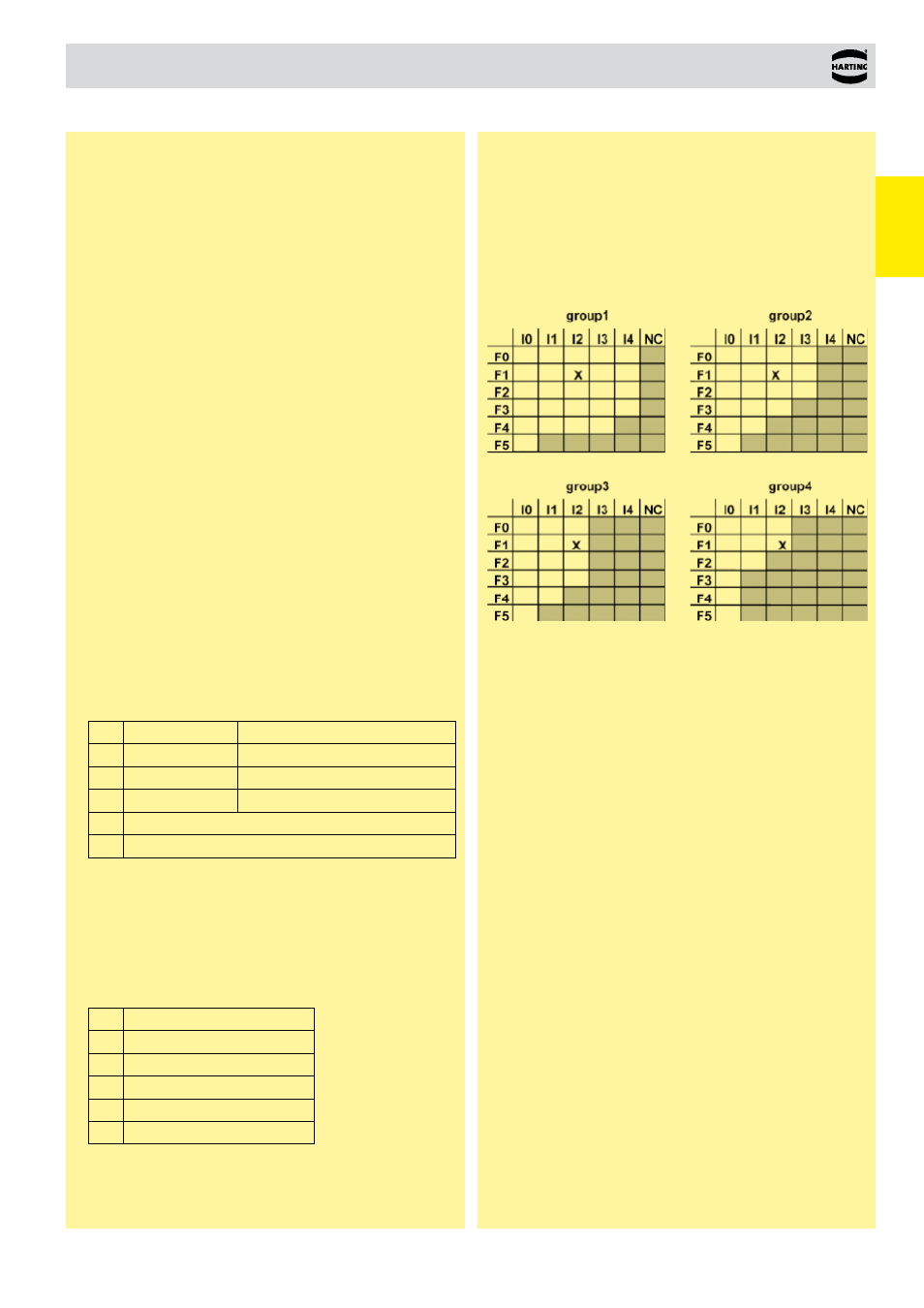
The matrix from NFF 16-102 shows how the combination of both
characteristics results in a classification. This matrix is defined
by the contractor in each project put up for bidding. The matrix
is geared to the type of train and course of the route, whereby
special attention is given to the number of tunnels. By complying
with the high classifications I2 and F1, the designated standards
supplementing connectors according to IEC 60 603-2 can be used
in all four defined groups and for all railway applications. According
to NFF 16-102 the standard DIN connectors (I3, F4) are only
permissible for Group 1.
Diagram: Classification from NFF 16-102, April 1992
The HARTING DIN Power and DIN Signal-Portfolio looks back
on a highly successful track record in the railroad engineering
industry. Typical application areas include – among many others -
control, steering, monitoring components and modules on board
trains, as well as signal technology components or the power
supply of electronic components.
The extended range of connectors complying with the highest
classification according to NFF 16-101 and 16-102 considerably
reduce our customers’ development times: as the selected
connectors are suitable for every stipulated hazard or risk class,
they are ideal for realizing product platforms, and therefore find
use in every conceivable rail vehicle or railroad engineering
project. This dispenses with the need for complex, product specific
development work, at least in terms of selecting passive PCB
interfaces, while the technical approval process is streamlined
considerably.
In order to facilitate rapid identification the additional, railway
specific articles are designated accordingly on the product pages.
