Why uefi over legacy bios, Key characteristics of uefi – HP Unified Extensible Firmware Interface User Manual
Page 8
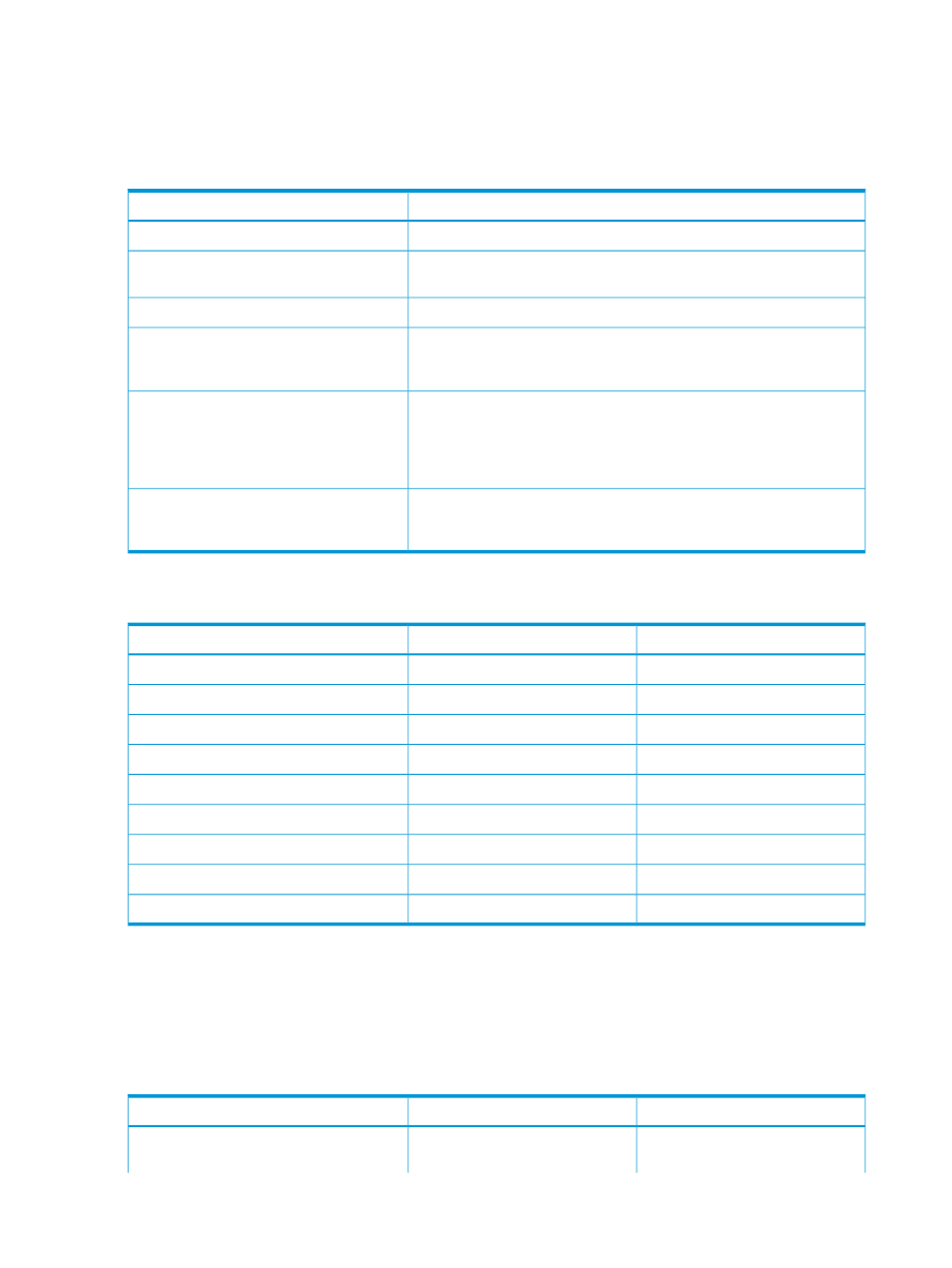
Why UEFI over Legacy BIOS?
ProLiant DL580 Gen8 servers transition to UEFI as the limitations of Legacy BIOS prevent the
adoption of new technologies.
provides details of how UEFI provides more
functionality than Legacy BIOS.
Table 1 UEFI versus Legacy BIOS
Description
Functionality
BIOS cannot boot from hard disks with more than 2.1 TB.
BIOS limitation
UEFI provides an enhanced networking API that enables network
authentication in a pre-boot environment. UEFI also supports Secure Boot.
Pre-boot security
UEFI supports PXE booting IPv6 addresses.
IPv6 PXE boot support
UEFI supports the multi-casting of a single image. A central image server
in UEFI Boot Mode can send an image to multiple listeners at the same
time.
PXE Multi-cast boot
UEFI provides functional pre-boot environment. You can remotely manage
systems with UEFI without booting into Windows or other operating
Pre-boot manageability
systems. UEFI provides a graphical interface that provides full access to
the server hardware, NIC, graphics card, USB, audio, and full x86 and
x64 support.
Includes an embedded UEFI Shell on the ROM. Based on the UEFI Shell
Specification, Revision 2.0, the shell environment provides an API, a
command prompt, and a set of commands.
UEFI Shell
lists major features with advantages of UEFI versus BIOS:
Table 2 Advantages of UEFI versus BIOS
Legacy BIOS
UEFI
Feature
X86/X64 only
Agnostic
Architecture
16 bit (real mode)
32/64 bit
Mode
MBR (2.2 TB limit)
GPT (9.4 ZB limit)
Boot Partition
No
Yes
Runtime Services
No
Yes
Driver Model
No
Yes
App Model
VGA
Graphics Output Protocol (GOP)
POST Graphics
PC-AT ‘de-facto’
Industry standard
Standard
INTx extensions
GUID’d protocols
Modularity
Key Characteristics of UEFI
UEFI is adaptable to both complex instruction set computing (CISC) and reduced instruction set
computing (RISC) architectures. Using standardized protocols, APIs, and drivers, UEFI has access
to processor, storage, and video components providing a stand-alone capability that Legacy BIOS
does not provide.
compares key characteristics of UEFI with Legacy BIOS.
Table 3 Comparison of UEFI versus Legacy BIOS
Legacy BIOS
UEFI
Characteristic
With future ACPI specs under UEFI
forum control, compliancy by future
ACPI specification 5.0a is
incorporated into the UEFI portfolio.
Advanced Configuration and Power
Interface (ACPI) support
8
Introduction
