Actions of yvp110 during operation, 1 block modes, Actions of yvp110 during operation -1 – Yokogawa YVP110 User Manual
Page 63: Block modes -1
<10. Actions of YVP110 During Operation>
10-1
IM 21B04C01-01E
10. Actions of YVP110 During Operation
10.1 Block Modes
All function blocks have modes. All blocks have
their mode, expressed by MODE_BLK parameter.
It is a structure of four components; Target,
Actual, Permitted and Normal. Target is the mode
into which an operator wants to bring this block.
This component is writable. Actual shows the
actual mode of the block and is read-only. When
necessary condition is satisfied, actual mode
becomes same to target. There is a chance that
actual mode says different from target by some
reason. Permitted mode shows which mode is
allowed in this Function Block. Normal mode is a
memo for operator to record mode that an operator
expects in normal conditions.
The table below shows the modes supported by
each function block contained in a YVP110.
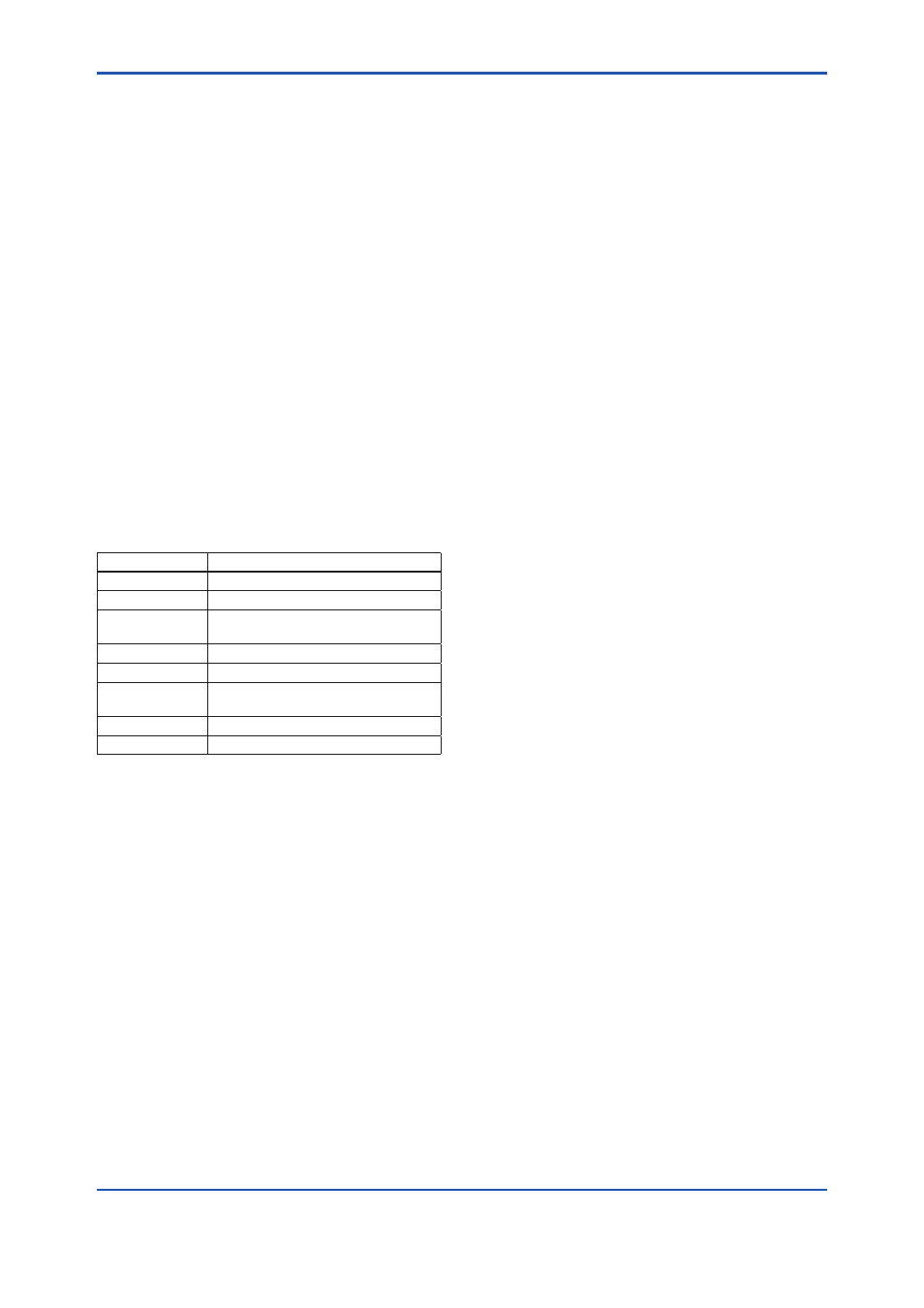
Table 10.1
Block Modes
Function Block
Modes
Resource
Auto, O/S
Transducer
Auto, O/S
AO
RCas, Cas, Auto, Man, (LO), (IMan),
O/S
DI
Auto, Man, O/S
OS
Auto, Cas, (IMan), O/S
PID
Rout, RCas, Cas, Auto, Man, (LO),
(IMan), O/S
IS
Auto, Man, O/S
AR
Auto, Man, O/S
Modes marked with ( ) in the above table cannot be
specified as “target”.
The following are outlines of each mode.
O/S mode
Means Out of Service mode, in which the block
does not run, and its output and setpoint maintain
their previous values.
IMan mode
Means Initialization Manual mode. Only the AO and
PID blocks in the YVP110 support this mode. When
one of these blocks detects a loss of a correct
path to the downstream block (such as when the
downstream block is in the O/S, Man, Auto or LO
mode), it enters IMan mode. For example, when
the data status of BKCAL_IN in a PID block is “bad”
or “good: not invited”, the PID block enters IMan
mode.
LO mode
Means Local Override mode. If the PID block
enters LO mode, the block output follows the
tracking value (TRK_VAL). In AO block, the block
enters LO mode when the block detects the fault
status. In this case, the block holds the output or
outputs the pre-configured value (FSTATE_VALUE)
according to the setting of options.
Man mode
Means Manual mode. If the data status of a
function block’s input is bad or its target mode is
Man, the block enters Man mode. In Man mode,
the function block does not update its OUT value.
If the target is also Man, it allows the user to write a
desired value to it.
Auto mode
In Auto mode, the function block performs the
specified calculations based on the setpoint
and outputs the result, independently without
interlocking with another function block. The user
can write the setpoint of a function block in this
mode if the target is Auto. If the target mode of
a function block is Auto, or if both of the following
conditions are met for a function bock, the block
enters Auto mode:
• The target mode is Cas or RCas.
• There is an error in communication with the
upstream function block.
Cas mode
Means Cascade mode. In Cas mode, the function
block performs the specified calculations based on
the setpoint that is input from a different function
block via the cascade input parameter and outputs
the result.
ROut mode
Means Remote Output mode. In ROut mode, the
output of the function block is set to the value of the
remote output parameter that is written by a host
computer or others. To prevent a sudden change in
output, the block’s calculations are initialized when
a change in mode occurs.
