Caution – IAI America RCM-GW-DV User Manual
Page 27
DeviceNet Gateway
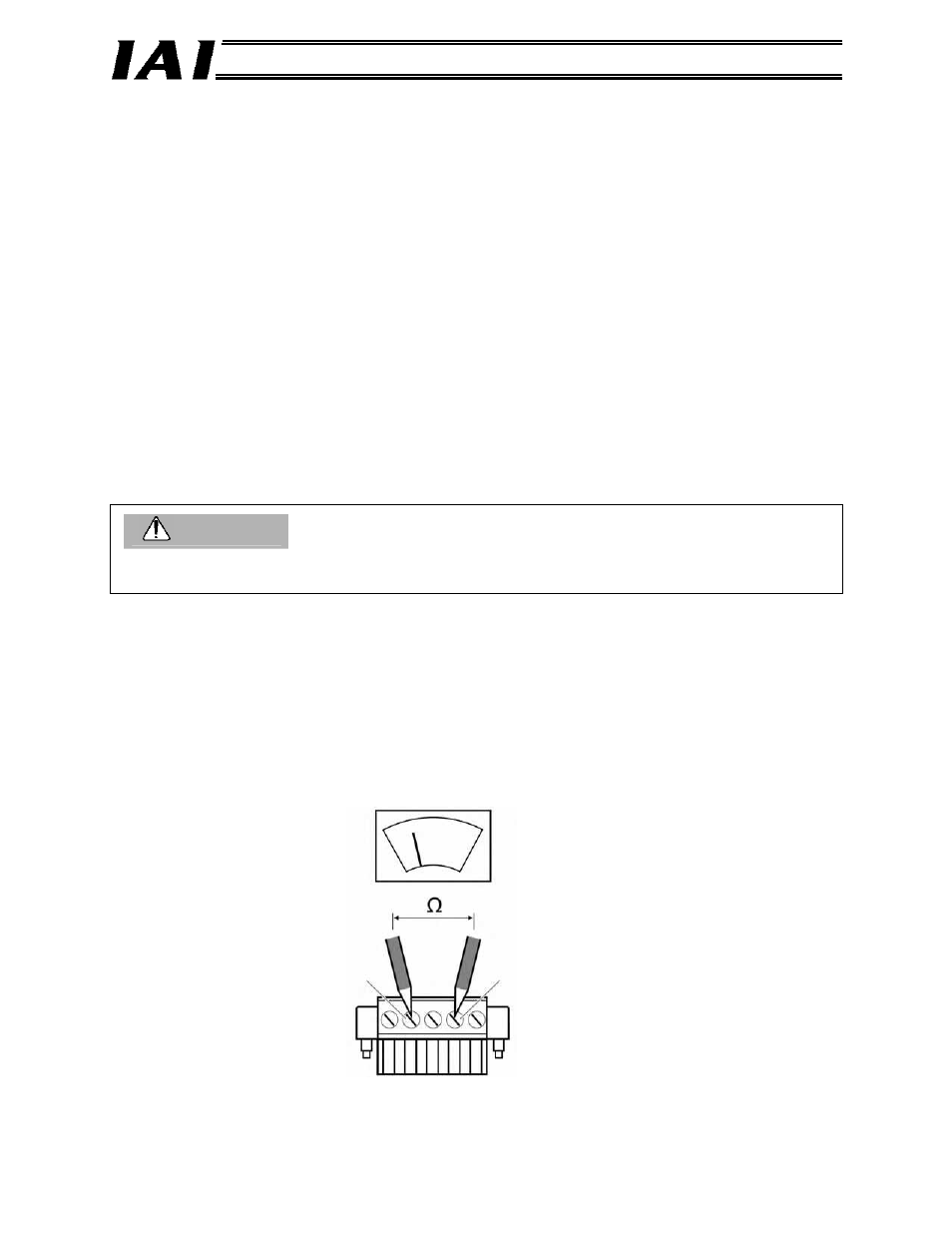
Tester
Use a tester to measure the
resistance between the signal lines.
White (CAN H)
Blue (CAN L)
About Grounding
• Do not ground the shield wires at multiple locations on the network. Always ground the shield wires at
one location.
• Provide dedicated grounding separately from the inverters for drive systems, etc.
(3) Nodes can be connected in one of two ways. Both methods can be employed together in a
single network.
[1] T-junction method --- A T-junction tap, etc., is used (Indicated by “T” in the network
diagram on p. 20)
[2] Multi-drop method --- A multi-drop connector is used to directly branch the cable at a node
(Indicated by “M” in the network diagram on p. 20)
(4) The communication power (24 VDC) must be supplied to each node via a five-lead cable.
With a DeviceNet system, the communication power (24 VDC) must be supplied to the network.
(5) A terminal resistor must be installed on both ends of a main line.
The gateway unit does not come with a terminal resistor.
Use a terminal-block type terminal resistor (121
Ω ±1%, 1/4 W) or T-branch tap with terminal
resistor (121
Ω ±1%, 1/4 W) by Omron, or connect other resistor of the same specification
directly between the white and blue terminals on the communication connector.
(6) The baud rate is limited in accordance with the network lengths (total branch line length and
maximum network length).
Caution
Align the ground potential level of the power supply of each controller connected to the Gateway Unit
with the ground potential level of the power supply of the Gateway Unit.
(7) When the wiring is complete, turn off the power and use a tester to measure the resistance
between the signal lines CAN H (white) and CAN L (blue) at any node.
• If the measured resistance is between 50 and 70 Ω, the connection is appropriate.
• If the measured resistance is 70 Ω or higher, the signal wires are open at some point or
there are not enough terminal resistors. This situation is classified as follows. If the
measured resistance is around 100
Ω, there is only one terminal resistance on the network.
If the measured resistor is 300
Ω or more, there is no terminal resistor on the network.
• If the measured resistance is less than 50 Ω, on the other hand, there are too many terminal
resistors. To be specific, there are at least three terminal resistors on the network.
Do not measure resistance while the system is operating, because it may cause communication data
errors, resulting in an unexpected accident.
