IAI America RCM-GW-DV User Manual
Page 26
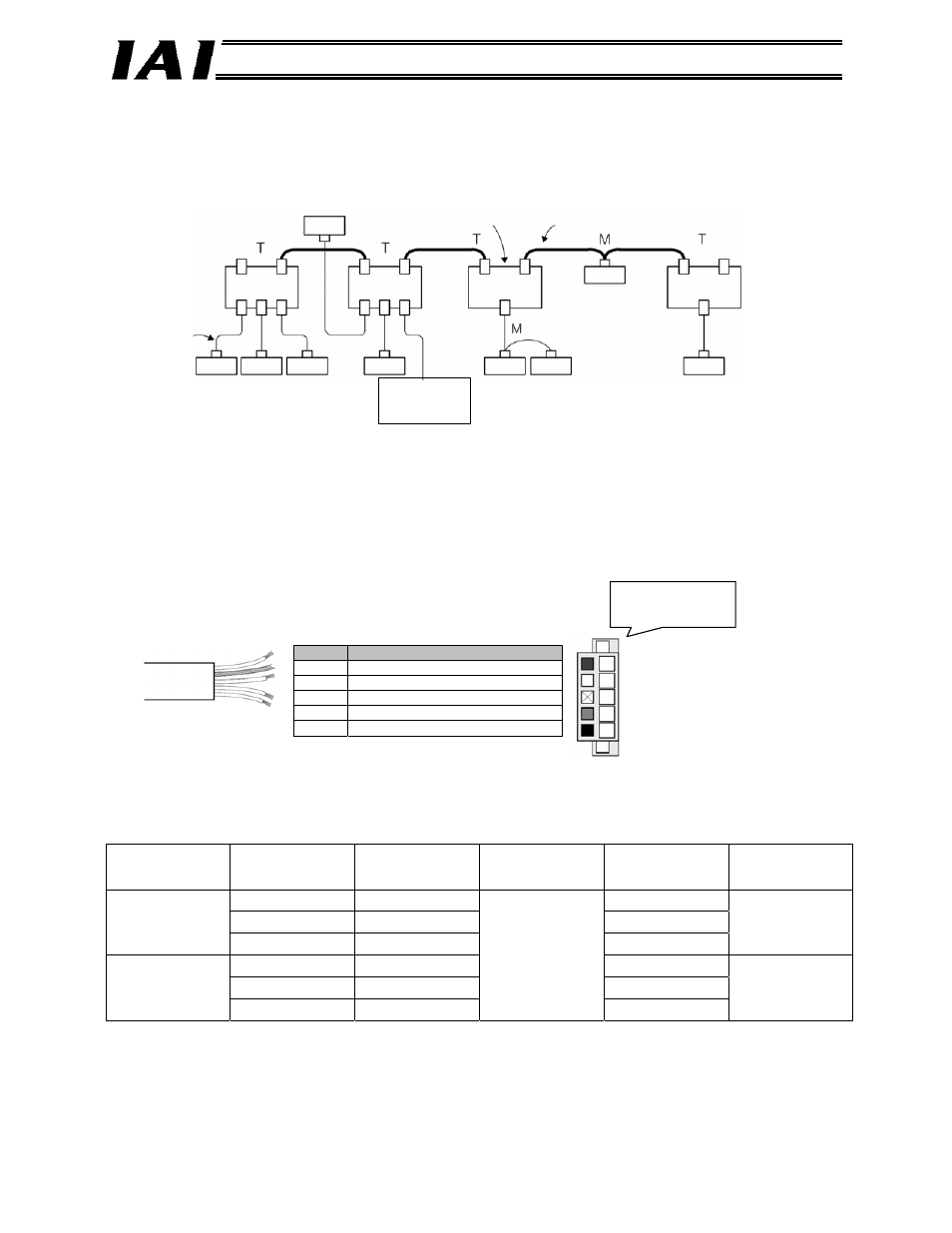
DeviceNet Gateway
DeviceNet unit (master)
Node
Terminal
resistors are
installed.
Branch line
T-junction tap
Main line
24-VDC
communication
power supply
Terminal
resistors are
installed.
Node
Node
Node
Node
Node
Node
Node
Node
DeviceNet network wiring is shown below.
For details on DeviceNet, refer to the operation manual for the master (PLC).
Shown below is an example of the DeviceNet network.
(1) A device with an address connected to the network is called “node.” A node may be a master
(DeviceNet unit in the figure above) that manages DeviceNet, or a slave that connects an
external I/O. Masters and slaves can be arranged in any positions.
(2) A cable having a terminal resistor installed on both ends is called “main line” (thick line in the
figure), while a cable branching from a main line is called “branch line” (thin line in the figure).
Both cables use the dedicated five-lead DeviceNet cable. Either the thick cable or thin cable is
used depending on the supplied current.
You can learn more about this dedicated cable on the ODVA website.
The dedicated cable is shown below.
Color
Signal type
Red
Power-supply cable + (V+)
White
Communication data high (CAN H)
- Shield
Blue
Communication data low (CAN L)
Black
Power-supply cable - (V-)
How to Determine Which Cable to Use
The table below summarizes the differences between thick and thin cables.
Type Baud
rate
Maximum
network length
Branch length
Total branch
length
Current capacity
500 kbps
100 m
39 m
250 kbps
250 m
78 m
Thick cable
125 kbps
500 m
156 m
8 A
500 kbps
100 m
39 m
250 kbps
100 m
78 m
Thin cable
125 kbps
100 m
6 m
156 m
3 A
The wire colors are
also printed on the
dedicated connector.
