Program-address generation, 1 program-address generation – Texas Instruments TMS320C2XX User Manual
Page 101
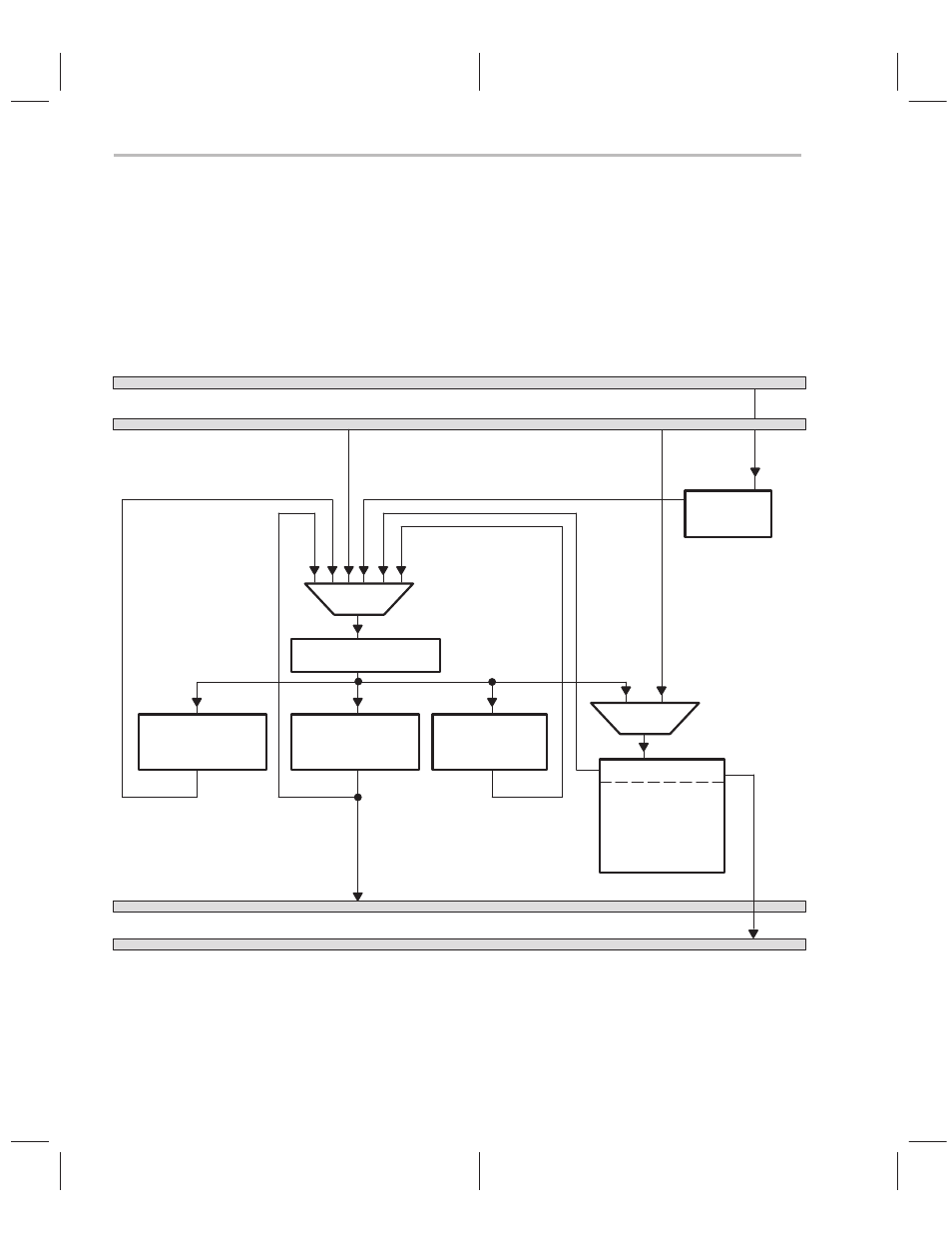
Program-Address Generation
5-2
5.1
Program-Address Generation
Program flow requires the processor to generate the next program address
(sequential or nonsequential) while executing the current instruction. Pro-
gram-address generation is illustrated in Figure 5–1 and summarized in
Table 5–1.
Figure 5–1. Program-Address Generation Block Diagram
Interrupt,
branch, or call
ББББББ
ББББББ
ББББББ
ББББББ
ББББББ
ББББББ
ББББББ
ББББББ
БББББ
БББББ
БББББ
БББББ
БББББББ
БББББББ
БББББББ
БББББББ
ББББББ
ББББББ
ББББББ
ББББББ
БББББББ
БББББББ
БББББББ
ББББББ
ББББББ
MUX
Next program address
register (NPAR)
Program counter
(PC/NPAR+1)
Sequential operation
Program address
register (PAR)
Dummy cycle
Micro stack
(MSTACK)
Table/block move
MUX
Program read bus (PRDB)
Data read bus (DRDB)
Top of stack (TOS)
Program-address
stack
8
16
Program address bus (PAB)
Data write bus (DWEB)
PSHD
instruction
Return
from
subroutine
POPD
instruction
Program
control
BACC or CALA
instruction
