AMETEK ReFlex Programming Manual User Manual
Page 53
Controller Module Remote Programming
ReFlex Power™ Programming Manual
M380056-03 Rev L
49
2.13.8
S
ETTING THE
SRQ
BIT IN THE
STB,
AN EXAMPLE
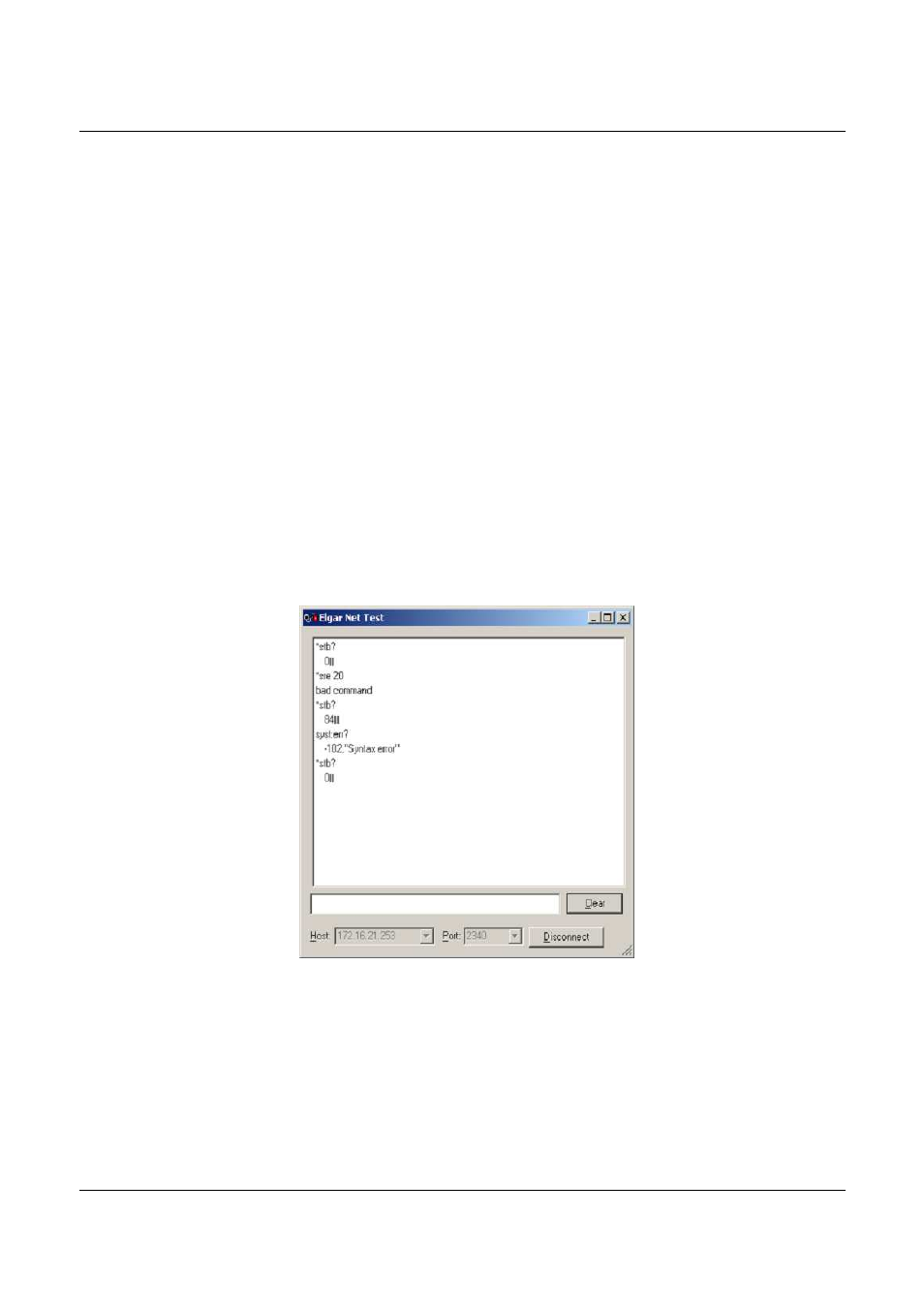
The following example shows the STB is initially zero. The SRE is enabled to
set SRQ if Message AVailable / Error Event Queue is asserted. A ‘bad
command’ is sent to the RFP system, which causes the Error Queue to have
an entry, which sets status bits in the STB. The setting of the bits in the STB
that match bits set in the SRE, will then cause bit 6 (SRQ) to be set, which
will generate the SRQ response if enabled by the host IVI-driver. To clear an
SRQ, the cause of the SRQ must be cleared. In the example below, reading
the Error Queue will cause the Message AVailable / Error Event Queue bits
to clear, if the Error Queue is empty, and if there are no other matching bits
between the STB and SRE or STB and PE registers, the STB SRQ bit will
clear, signaling the end of the SRQ event. The RFP system is now ready to
generate another SRQ event. If the SRQ bit does not clear, then there is
another pending SRQ event and the cause will need to be cleared before the
SRQ event will end. If there is a pending but not enabled SRQ event pending
and the corresponding bits in the ESE or PE registers are then set, this will
then generate an immediate SRQ and the client will need to issue commands
to clear these events before any other SRQ’s will be recognized.
