Setting the error log file size -78 – HP XP7 Storage User Manual
Page 146
Value
Description
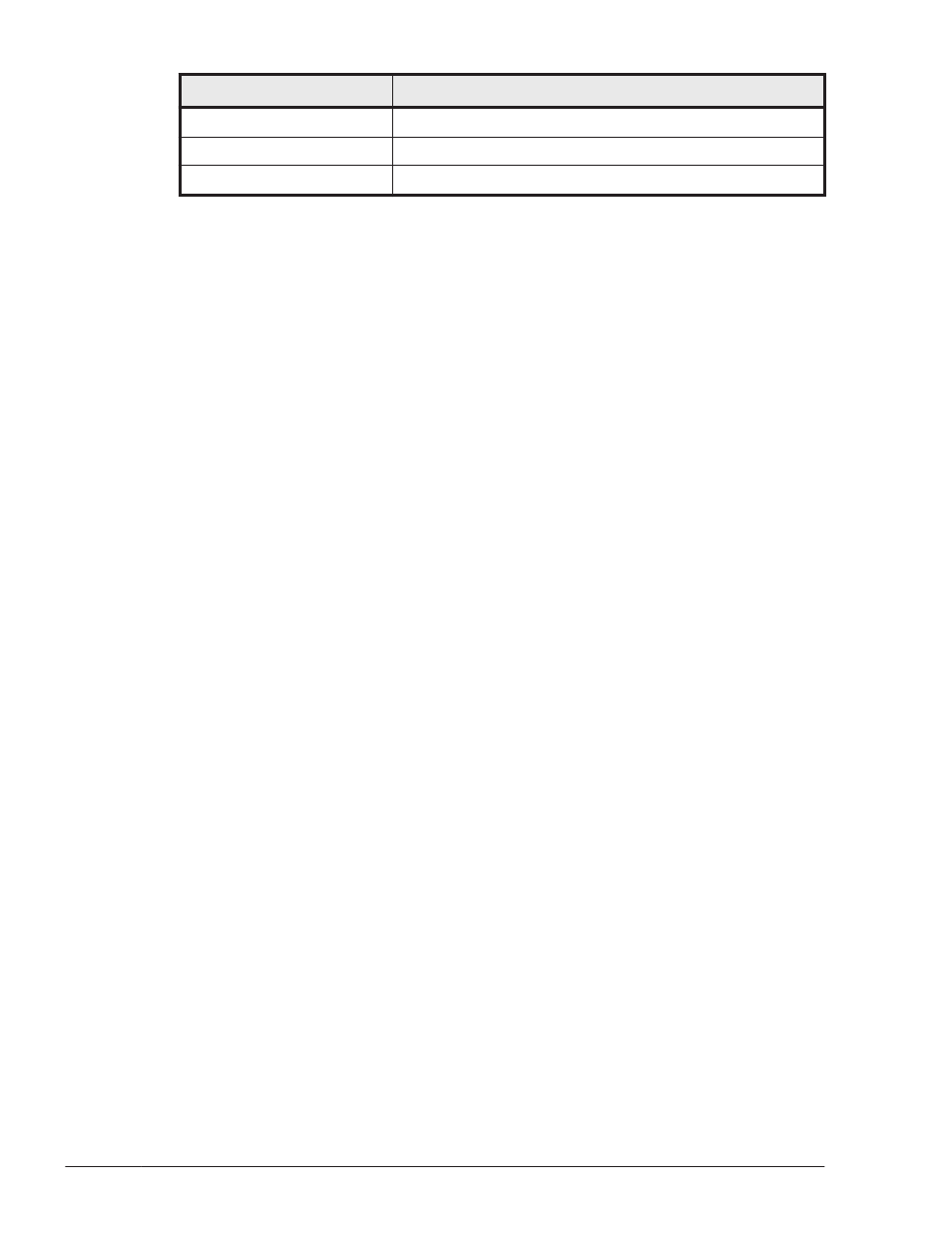
2
Program operation summaries are output.
3
Program operation details are output.
4
All information is output.
If an error occurs, you might have to set the trace level to 1 or higher to
collect any trace information.
The higher this value is set, the more information that will be output. As the
amount of trace information to be output increases, it will take less time to
overwrite the old trace information with the new information.
For normal operation, we recommend that you set the trace level to 0. If you
set the trace level to a value higher than necessary, HDLM performance
might decrease, or trace information required to analyze the cause of an
error might be overwritten.
•
Setting up the trace level by using the set operation
The following is an example of setting up the trace level by using a
command:
dlnkmgr set -systflv 1
Specify the trace level as a number.
Setting the Error Log File Size
There are two error logs: the HDLM manager log file dlmmgrn.log (n
indicates a file number from 1 to 16) and the HDLM GUI log file dlmguin.log
(n indicates a file number of 1 or 2).
You can specify a value (in kilobytes) from 100 to 2000000 for the error log
file size. For HDLM GUI logs, file sizes range from 100 to 9900. If you specify
a value over 9901, 9900 will be used. For HDLM manager logs, the specified
value will be applied as it is without being limited by the above.
When an error log file reaches its maximum size, the information in the oldest
error log file will be overwritten with new information. By specifying both the
log file size and the number of log files, you can collect up to 32000000KB
(approximately 30GB) of error log information.
•
Setting up the error log file size by using the set operation
The following is an example of setting up the error log file size by using a
command:
dlnkmgr set -elfs 1000
Specify the size of the error log file in kilobytes.
3-78
Creating an HDLM Environment
Hitachi Dynamic Link Manager (for Windows®) User Guide
