Physical explanations, Cn c – Ocean Optics NanoCalc User Manual
Page 71
Ocean Optics Germany GmbH Thin Film Metrology
70
11
Physical explanations
11.1
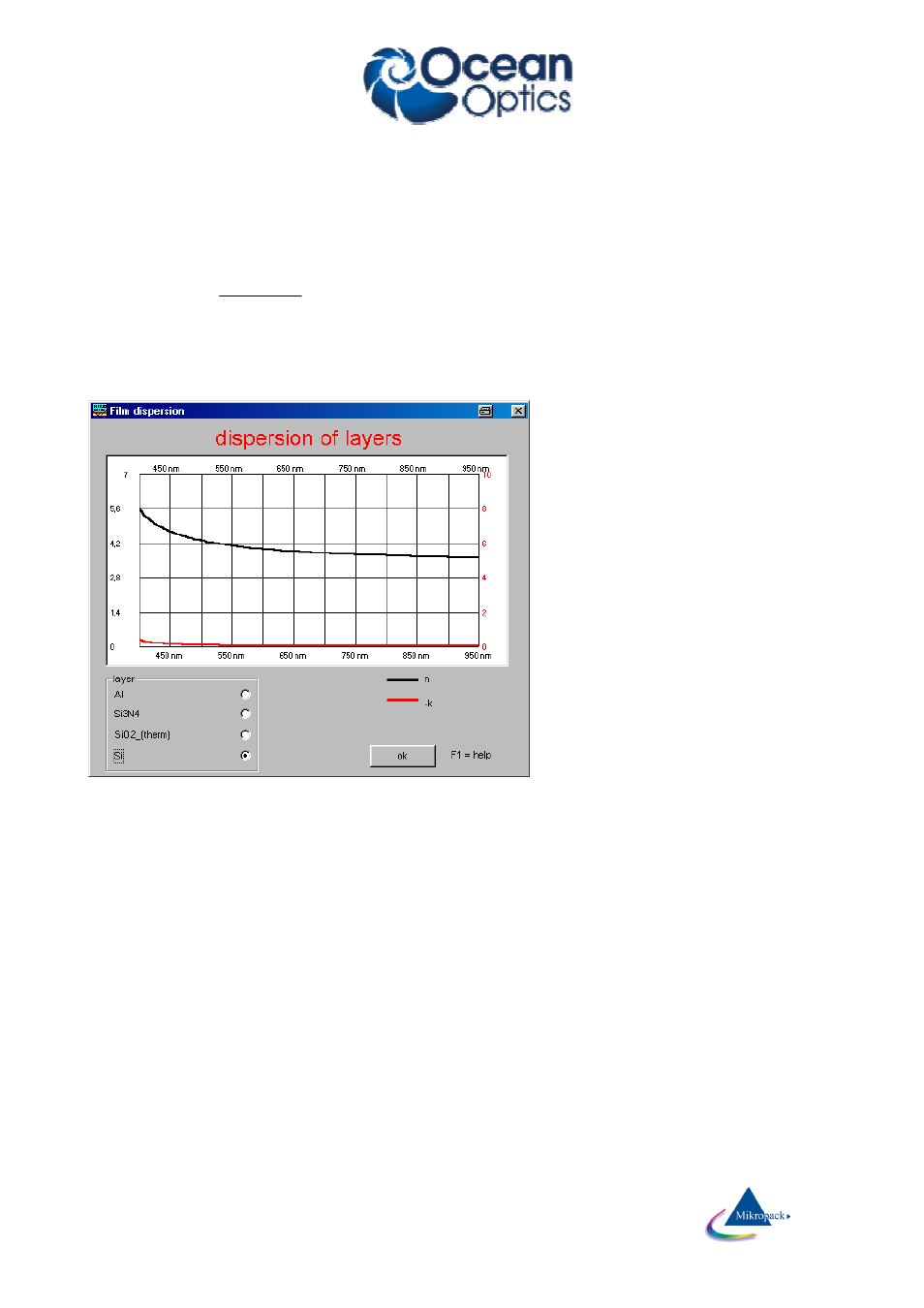
Refraction index and absorption indices
The refraction index n of a substance is defined as
with c = speed of light
The absorption index k of a substance
describes the absorption behavior of
materials. Glasses and photoresists have
negligible absorption in the visible range.
n and k are a function of the wavelength
lambda: n = n(λ). This phenomenon is
called „dispersion“.
n(λ) and k(λ) are closely interrelated via
the dielectric function ε(λ).
11.2
Cauchy coefficients
These coefficients empirically describe the dispersion functions of n(λ) and k(λ).
In many cases the 6 Cauchy coefficients are sufficient to describe the spectral behavior of resists, glasses
etc. Normally NanoCalc uses „nanometers“ as a unit dimension. If you add your own cauchy parameters in a
.DAT-file, pay attention on the correct dimension !! It is possible to use other dimensions within the software
but not in the .DAT-files.
Structure of a .DAT-file:
SiO2_(therm)
name of the material
# this is my own comment 1 arbritrary comment (beginning with #)
# this is my own comment 2
633,1.4570,0
lambda, n and k at 633 nm
150,900
measured data between these limits
Table (or CAUCHY)
150,1.5510,0
n and k at 150 nm
151,1.5504,0
n and k at 151 nm
152,1.5491,0
n and k at 152 nm
v a c u u m
m a t e r i a l
c
n
c
=
