Programming interface, 1 features, 2 overview – Rainbow Electronics ATtiny10 User Manual
Page 96: 3 physical layer of tiny programming interface
96
8127B–AVR–08/09
ATtiny4/5/9/10
14. Programming interface
14.1
Features
•
Physical Layer:
– Synchronous Data Transfer
– Bi-directional, Half-duplex Receiver And Transmitter
– Fixed Frame Format With One Start Bit, 8 Data Bits, One Parity Bit And 2 Stop Bits
– Parity Error Detection, Frame Error Detection And Break Character Detection
– Parity Generation And Collision Detection
– Automatic Guard Time Insertion Between Data Reception And Transmission
•
Access Layer:
– Communication Based On Messages
– Automatic Exception Handling Mechanism
– Compact Instruction Set
– NVM Programming Access Control
– Tiny Programming Interface Control And Status Space Access Control
– Data Space Access Control
14.2
Overview
The Tiny Programming Interface (TPI) supports external programming of all Non-Volatile Memo-
ries (NVM). Memory programming is done via the NVM Controller, by executing NVM controller
commands as described in
“Memory Programming” on page 107
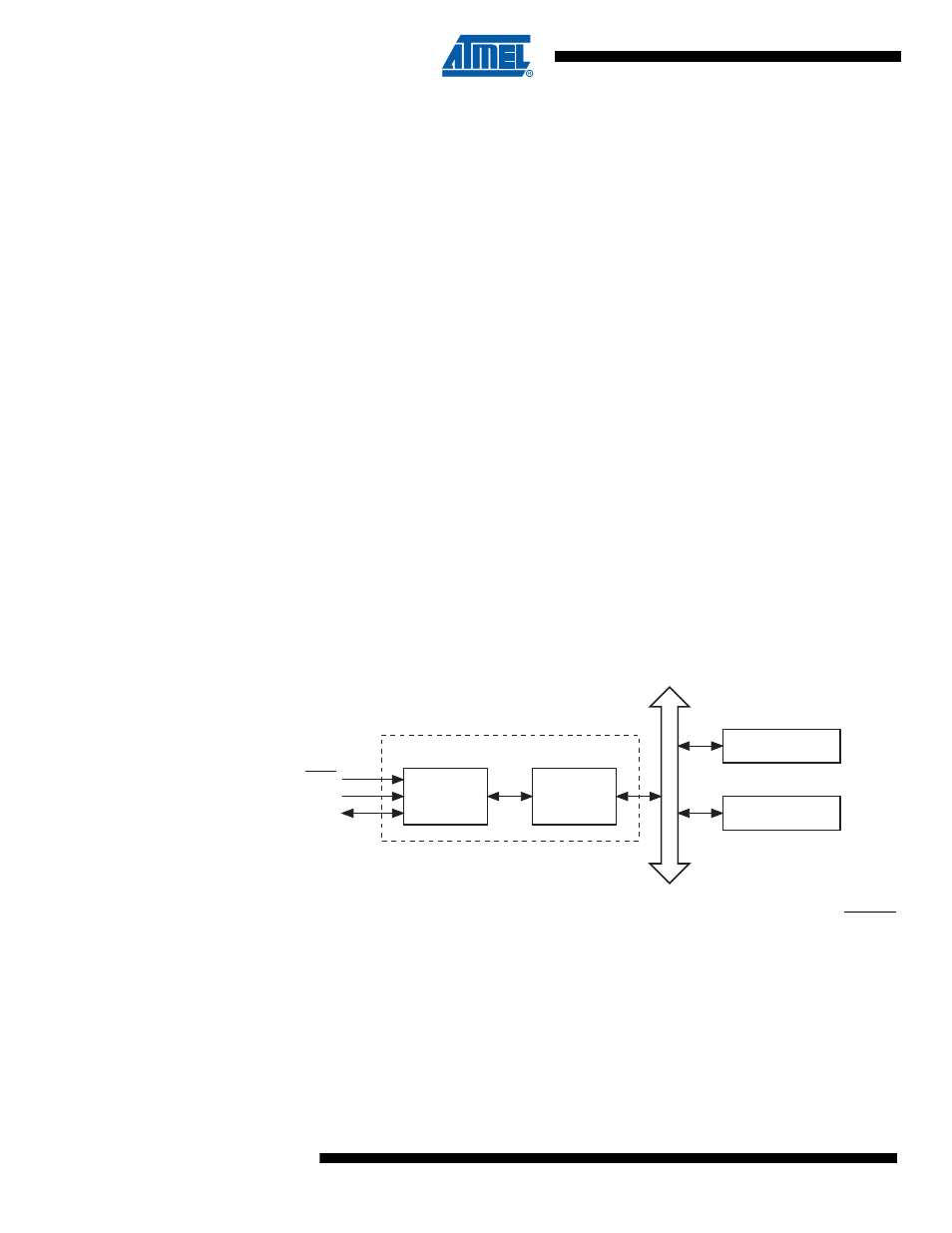
The Tiny Programming Interface (TPI) provides access to the programming facilities. The inter-
face consists of two layers: the access layer and the physical layer. The layers are illustrated in
.
Figure 14-1. The Tiny Programming Interface and Related Internal Interfaces
Programming is done via the physical interface. This is a 3-pin interface, which uses the RESET
pin as enable, the TPICLK pin as the clock input, and the TPIDATA pin as data input and output.
NVM can be programmed at 5V, only.
14.3
Physical Layer of Tiny Programming Interface
The TPI physical layer handles the basic low-level serial communication. The TPI physical layer
uses a bi-directional, half-duplex serial receiver and transmitter. The physical layer includes
serial-to-parallel and parallel-to-serial data conversion, start-of-frame detection, frame error
detection, parity error detection, parity generation and collision detection.
ACCESS
LAYER
PHYSICAL
LAYER
NVM
CONTROLLER
NON-VOLATILE
MEMORIES
TPICLK
RESET
TPIDATA
TINY PROGRAMMING INTERFACE (TPI)
DATA BUS
