Siemens S5-135U/155U User Manual
Page 30
3-4
System Manual
C79000-G8576-C199-06
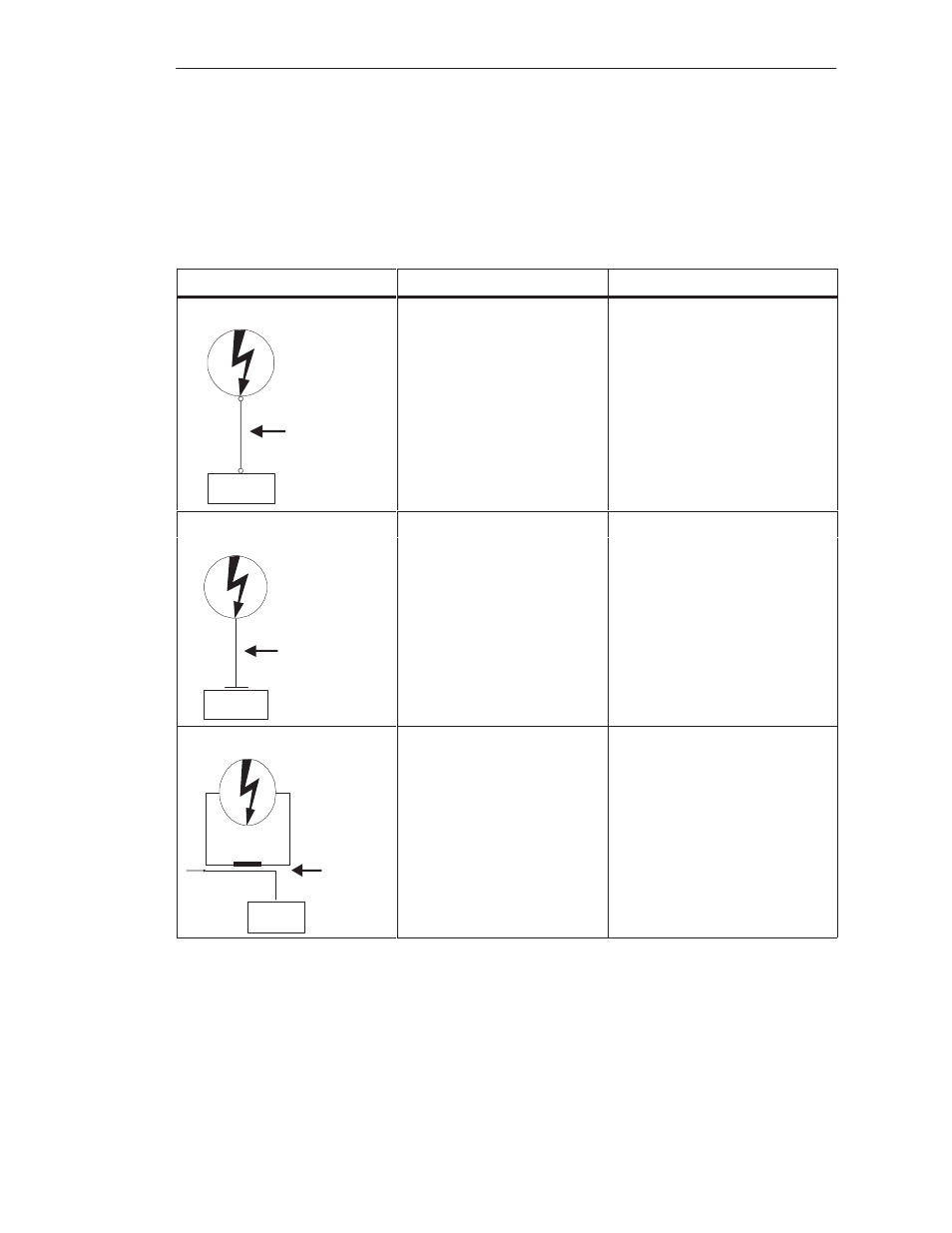
Shown in the following table are the four different coupling mechanisms,
their causes, and possible interference sources.
Coupling Mechanism
Cause
Typical Interference Sources
S
Direct Coupling
Direct or metallic coupling
l
h
i
i
S
Switched devices (supply
ff
d b i
d
SIMATIC S5
Interference
Direct Coupling
Path
always occurs when two circuits
have a common conductor
affected by inverters and
external power supply units)
S
Motors being started
S
Different potentials of
component cases with a
common power supplys
S
Static discharges
S
Capacitive Coupling
Capacitive or electrical coupling
b
d
S
Interference pickup via
ll l i
l
bl
SIMATIC S5
Interference
Capacitive Coupling
Path
occurs between conductors
which are at different potentials.
The degree of coupling is
proportional to the voltage
variation as a function of time.
parallel signal cables
S
Static discharge of the
operator
S
Contactors
S
Inductive Coupling
Inductive or magnetic coupling
b
d
S
Transformers, motors,
l
i
ld
SIMATIC S5
Interference
Inductive
Coupling Path
Signal
occurs between two conductor
loops through which current is
flowing. Interference voltages
are induced by the magnetic
fluxes associated with the
currents. The degree of coupling
is proportional to the current
variation as a function of time.
electric welders
S
Parallel AC supply cables
S
Cables whose currents are
switched⁄
S
Signal cables with a high
frequency
S
Unconnected coils
Coupling
Mechanisms and
Typical
Interference
Sources at a
Glance
Installation Guidelines
