Multicast mode, Multiple instances of ntp – H3C Technologies H3C S7500E Series Switches User Manual
Page 71
3-7
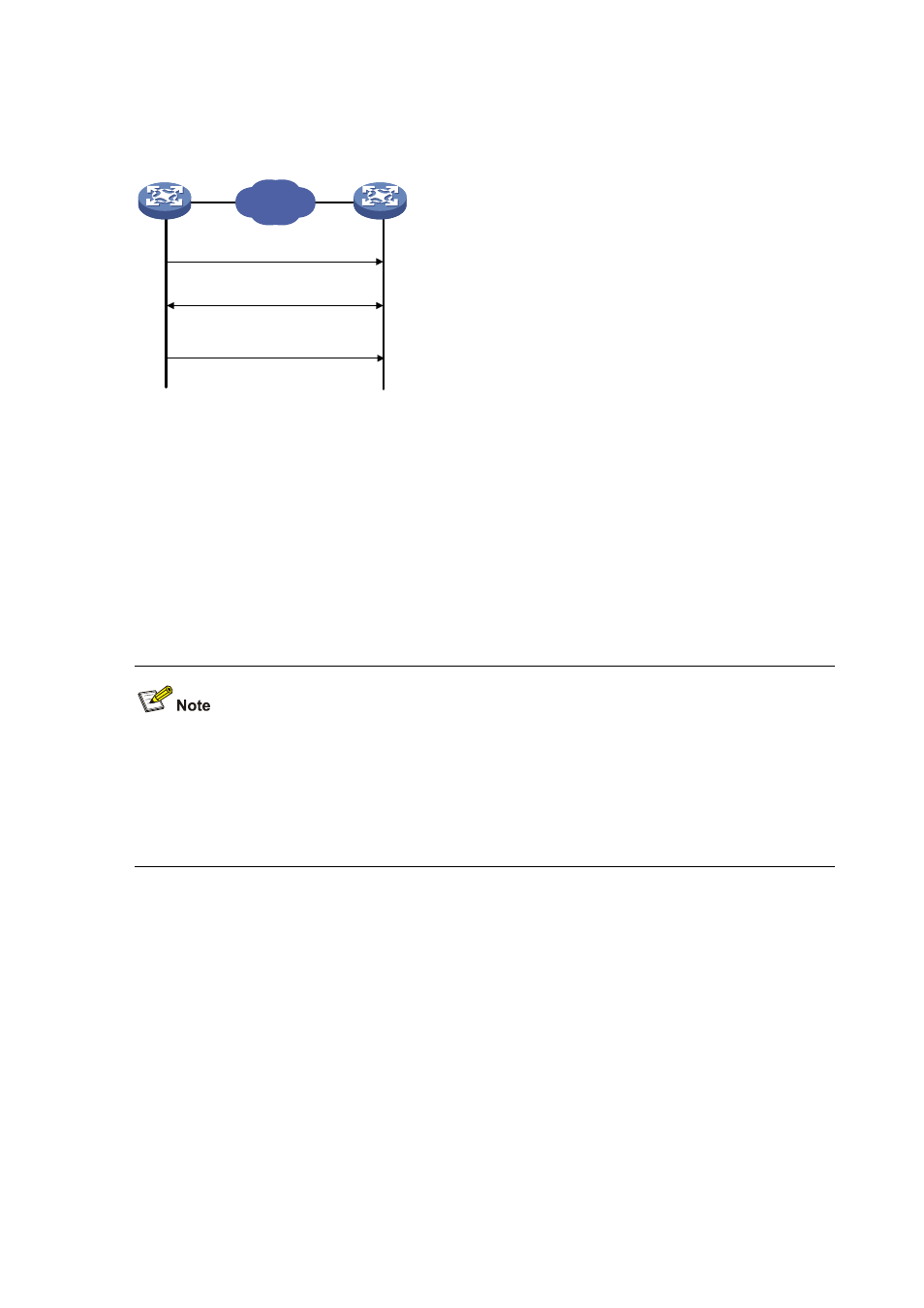
Multicast mode
Figure 3-6 Multicast mode
Network
Client
Server
After receiving the first
multicast message, the
client sends a request
Clock synchronization message
exchange (Mode 3 and Mode 4)
Periodically multicasts clock
synchronization messages (Mode 5)
Calculates the network delay
between client and the server
and enters the multicast
client mode
Periodically multicasts clock
synchronization messages (Mode 5)
Receives multicast
messages and synchronizes
its local clock
In the multicast mode, a server periodically sends clock synchronization messages to the
user-configured multicast address, or, if no multicast address is configured, to the default NTP
multicast address 224.0.1.1, with the Mode field in the messages set to 5 (multicast mode).
Clients listen to the multicast messages from servers. After a client receives the first multicast
message, the client and the server start to exchange messages, with the Mode field set to 3
(client mode) and 4 (server mode) to calculate the network delay between client and the server.
Then, the client enters the multicast client mode and continues listening to multicast messages,
and synchronizes its local clock based on the received multicast messages.
In symmetric peers mode, broadcast mode and multicast mode, the client (or the symmetric
active peer) and the server (the symmetric passive peer) can work in the specified NTP working
mode only after they exchange NTP messages with the Mode field being 3 (client mode) and
the Mode field being 4 (server mode). During this message exchange process, NTP clock
synchronization can be implemented.
Multiple Instances of NTP
The client/server mode and symmetric mode support multiple instances of NTP and thus
support clock synchronization within an MPLS VPN network. Namely, network devices (CEs
and PEs) at different physical location can get their clocks synchronized through NTP, as long
as they are in the same VPN. The specific functions are as follows:
z
The NTP client on a customer edge device (CE) can be synchronized to the NTP server on
another CE.
z
The NTP client on a CE can be synchronized to the NTP server on a provider edge device
(PE).
z
The NTP client on a PE can be synchronized to the NTP server on a CE through a
designated VPN instance.
