Symmetric peers mode, Broadcast mode – H3C Technologies H3C S7500E Series Switches User Manual
Page 70
3-6
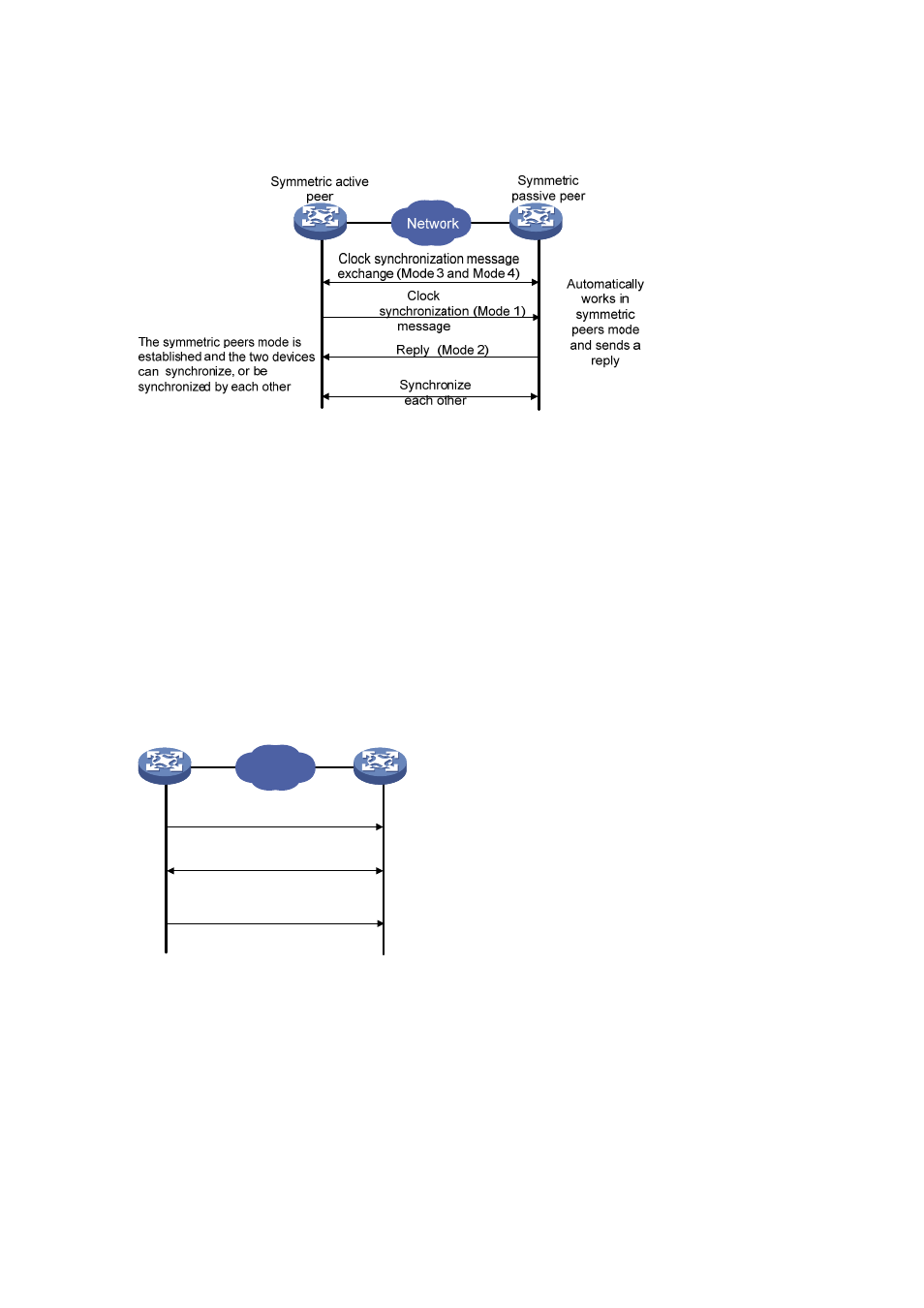
Symmetric peers mode
Figure 3-4 Symmetric peers mode
A device working in the symmetric active mode periodically sends clock synchronization
messages, with the Mode field in the message set to 1 (symmetric active); the device that
receives this message automatically enters the symmetric passive mode and sends a reply,
with the Mode field in the message set to 2 (symmetric passive). By exchanging messages, the
symmetric peers mode is established between the two devices. Then, the two devices can
synchronize, or be synchronized by each other. If the clocks of both devices have been already
synchronized, the device whose local clock has a lower stratum level will synchronize the clock
of the other device.
Broadcast mode
Figure 3-5 Broadcast mode
Network
Client
Server
After receiving the first
broadcast message, the
client sends a request
Clock synchronization message
exchange (Mode 3 and Mode 4)
Periodically broadcasts clock
synchronization messages (Mode 5)
Calculates the network delay
between client and the server
and enters the broadcast
client mode
Periodically broadcasts clock
synchronization messages (Mode 5)
Receives broadcast
messages and synchronizes
its local clock
In the broadcast mode, a server periodically sends clock synchronization messages to the
broadcast address 255.255.255.255, with the Mode field in the messages set to 5 (broadcast
mode). Clients listen to the broadcast messages from servers. After a client receives the first
broadcast message, the client and the server start to exchange messages, with the Mode field
set to 3 (client mode) and 4 (server mode) to calculate the network delay between client and the
server. Then, the client enters the broadcast client mode and continues listening to broadcast
messages, and synchronizes its local clock based on the received broadcast messages.
