Specify your linear load mechanism, Mechanism type – Rockwell Automation Motion Analyzer Software User Manual
Page 178
178
Rockwell Automation Publication MOTION-UM004B-EN-P - October 2012
Chapter 2
Sizing Your System
2.3. Specify Your Linear Load
Mechanism
A linear load mechanism is used to convert rotary motor torque to linear motion
through a transmission (belt drive, lead screw, chain and sprocket, or rack and
pinion), where thrust from a linear motor, electric cylinder, or linear stage
produces linear motion directly.
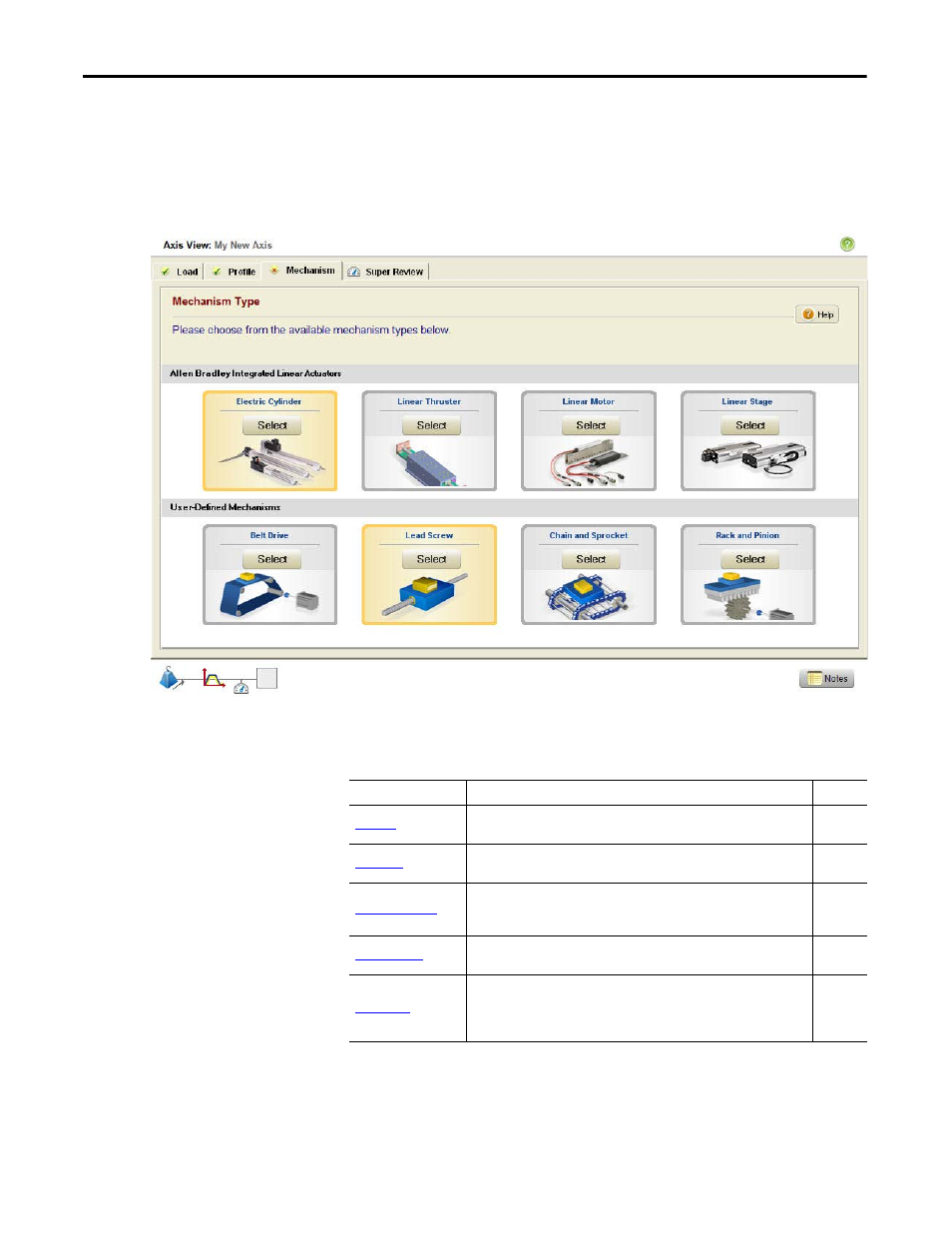
Figure 130 - Mechanism Type
The following mechanisms are available in Motion Analyzer software.
Table 101 - Mechanism Types
Type
Description
Page
A rotary motor coupled to a timing pulley that drives a flexible toothed belt,
with its coupled load, back and forth between two idler pulley guides.
A lead screw is coupled to a rotary motor and causes relative linear motion
between a rotating screw and its non-rotating nut.
A chain and sprocket is a rotary motor coupled to a sprocket wheel that drives a
linked chain, with its coupled load, back and forth between idler sprocket
guides.
A rack and pinion is a rotary motor coupled to a toothed pinion wheel that
engages a toothed rack to create relative motion between the two elements.
Linear motors are either iron-core and ironless motors that directly create
linear thrust. Their separate sections (coil and magnet channel) produce
relative motion between a carriage and its base along the user-supplied linear
bearing guides.
