Using active directory with ldap id mapping, Required attributes for templates – HP StoreAll Storage User Manual
Page 66
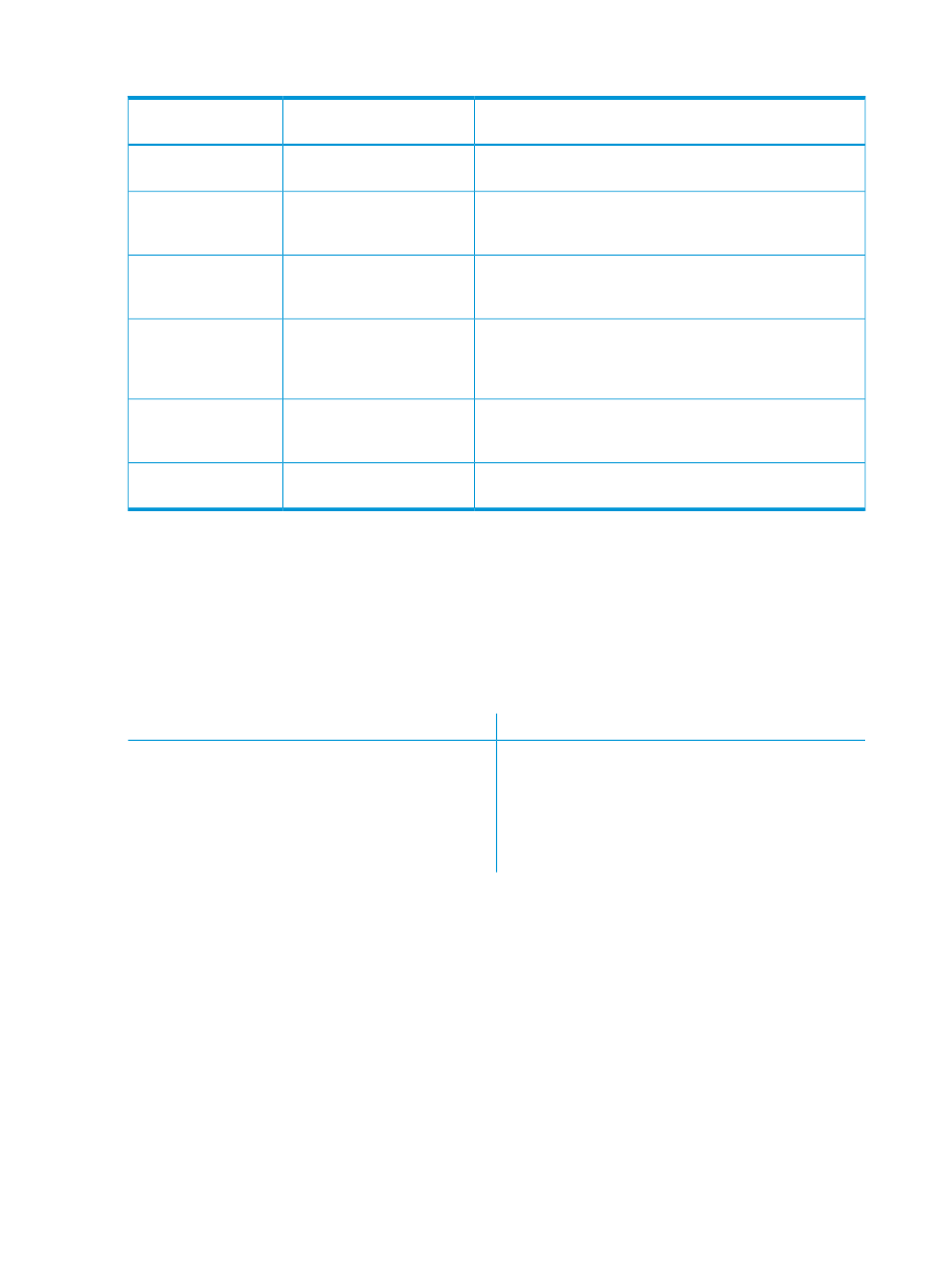
Required attributes for templates
Description
Value
Nonvirtual attribute
name
Helps identify the configuration version uploaded. Potentially
used for reports, audit history, and troubleshooting.
Any arbitrary string
VERSION
A FQDN or IP. Typically, it is a front-ended switch or an IP
LDAP proxy/balancer name/address for multiple backend
high-availability LDAP servers.
Host name or IP
LDAPServerHost
The LDAP OU (organizational unit) to which configuration
entries can be written. This OU must exist on the server and
must be readable and writable using LDAPWriteDN.
Writable OU name string
LdapConfigurationOU
Limited write DN credentials. HP recommends that you do not
use cn=Manager credentials. Instead, use an account DN with
DN name string
LdapWriteDN
very restricted write permissions to the LdapConfigurationOU
and beneath.
Password for the LdapWriteDN account.
Unencrypted password string.
LDAP encrypts the string on
storage.
LDAPWritePassword
Supported schema for the OpenLDAP server.
Samba, posix, or user defined
schema
schematype
Using Active Directory with LDAP ID mapping
When LDAP ID mapping is a secondary lookup method, the system reads SMB client UIDs and
GIDs from LDAP if it cannot locate the needed ID in an AD entry. The name in LDAP must match
the name in AD without respect for case or pre-appended domain.
If the user configuration differs in LDAP and Windows AD, the LDAP ID mapping feature uses the
AD configuration. For example, the following AD configuration specifies that the primary group
for user1 is Domain Users, but in LDAP, the primary group is group1.
LDAP Configuration
AD configuration
user1
uid:
user1
user:
1010
uidNumber:
Domain Users
primary group:
1001 (group1)
gidNumber:
not specified
UNIX uid:
Domain Users
cn:
not specified
UNIX gid:
1111
gidNumber:
The Linux id command returns the primary group specified in LDAP:
user: user1
primary group: group1 (1001)
LDAP ID mapping uses AD as the primary source for identifying the primary group and all
supplemental groups. If AD does not specify a UNIX GID for a user, LDAP ID mapping looks up
the GID for the primary group assigned in AD. In the example, the primary group assigned in AD
is Domain Users, and LDAP ID mapping looks up the GID of that group in LDAP. The lookup
operation returns:
user: user1
primary group: Domain Users (1111)
AD does not force the supplied primary group to match the supplied UNIX GID.
The supplemental groups assigned in AD do not need to match the members assigned in LDAP.
LDAP ID mapping uses the members list assigned in AD and ignores the members list configured
in LDAP.
66
Configuring authentication for SMB, FTP, and HTTP
