Cg32 – KROHNE OPTIMASS with MFC 300 EN User Manual
Page 80
80
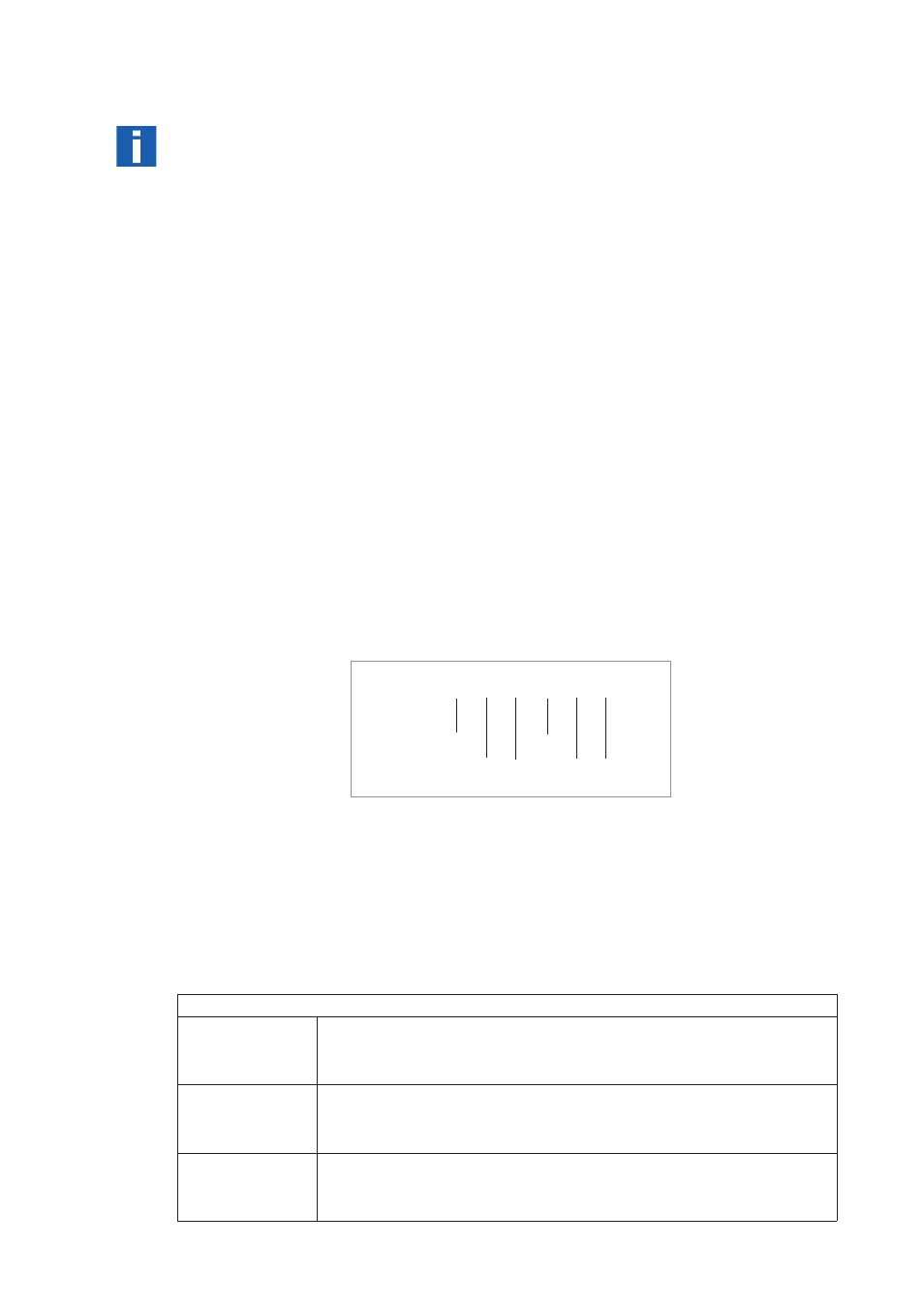
CG32* _ _ 4 _ _
1
Converter type designation
2
Power
3
Display Version
4
I/O Version
5
First option module for terminal A
6
Second option module for terminal B
CG No. examples
CG 320 11 100
100...230 V AC & Standard Display / Basic I/O: Ia or Ip & Sp/Cp & Sp &
Pp/Sp (see table on page 81)
CG 320 11 7FK
100...230 V AC & Standard Display / Modular I/O: Ia & Pn/Sn and option
module PN/SN & CN (see table on page 81)
CG 320 81 4EB
24 V DC & Standard Display / Modular I/O: Ia & Pa/Sa and option module
Pp/Sp & Ip (see tables on page 81)
9.7 I/ O Assemblies for the Inputs and Outputs
Important information for outputs and inputs
PLEASE NOTE
•
The output / input groups are galvanically separated from each other and from all other
input and output circuits.
•
Active mode: the signal converter supplies the power for operation (activation) of receiver
instruments; observe max. operating data.
•
Passive mode: operation (activation) of receiver instruments requires an external power
supply (Uext); observe max. operating data.
•
Connection diagrams of outputs and inputs are shown in section 9.9.
•
For operating data of outputs and inputs, refer to section 9.8
•
The MFC 300 is available with a choice of output/input assemblies:
•
Basic I/O has one mA, one pulse and 2 status outputs. The pulse output can be set as a sta-
tus output, and one of the status outputs as a control input (see Basic I/O table).
•
Modular I/O can be equipped with different output modules, depending on the task (see
Modular I/O table).
•
For hazardous areas, all I/O variants are available for the MFC 300 C (compact) and MFC
300 F (remote) with terminal compartment in EEx - d (flameproof enclosure) or EEx - e
(increased safety) protection.
•
The Bus - System I/O allows intrinsically safe and non-intrinsically safe bus interfaces in
combination with further modules (see Bus - System I/O table).
•
The last 3 places of the CG No. indicate the assigned terminals, see examples below.
•
Abbreviations used are explained in the table on page 82.
Examples of CG No. to identify the electronic module and the I/O variants:
1 2 3 4
5 6
