Index, Explanaton – Yokogawa PC-Based MX100 User Manual
Page 69
2-55
IM MX180-01E
Integrat
on Mon
tor
3
2
1
4
5
App
Index
Explanaton
Alarm Types
Alarm level settings and operation differ depending on the hardware style number of the
MX100. See the table below.
Connectable module types or settng tems
MX100 Hardware Style Number
*
S3
S2
S1
Alarm level setting (alarm 3 to alarm 4)
Yes
No
No
Yes: Setting and operation allowed, No: Setting and operation not allowed
* The style number is printed on the MX100 main module name plate.
There are six types of alarms.
When not using difference input on measurement channels, select OFF, High, or Low.
When using difference input, select OFF, dHigh, or dLow.
On computation channels, select OFF, High, Low, rHigh, or rLow.
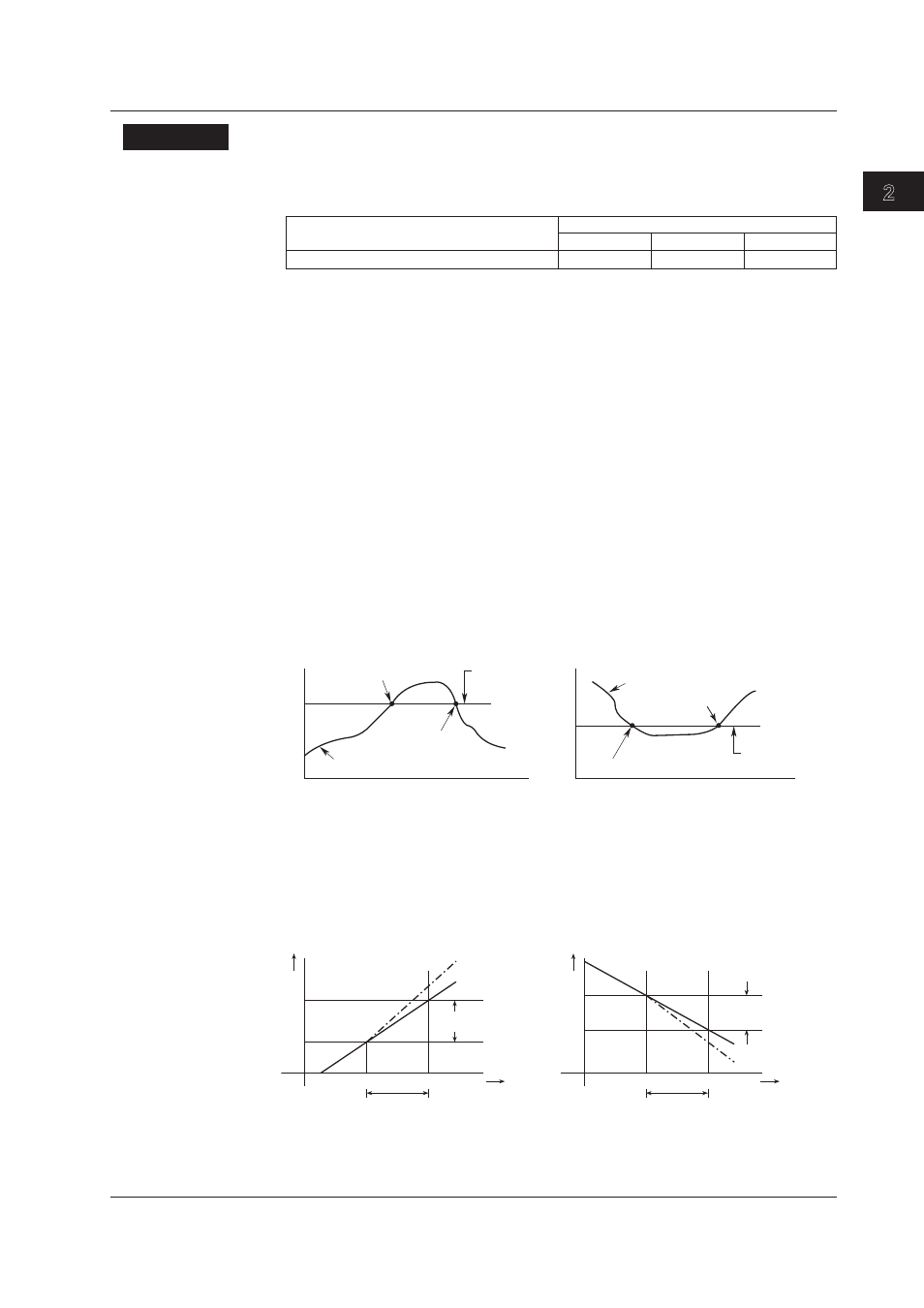
• Upper lmt alarm (Hgh)
An alarm occurs when the measured/computed value exceeds the alarm value.
• Lower lmt alarm (Low)
An alarm occurs when the measured/computed value falls below the alarm value.
• Dfference upper lmt alarm (dHgh)
An alarm occurs when the difference input (difference between the measured value of
its own channel and that of the reference channel) exceeds the alarm value.
• Dfference lower lmt alarm (dLow)
An alarm occurs when the difference input (difference between the measured value of
its own channel and that of the reference channel) falls below the alarm value.
Alarm value
Alarm reset
Measured value
or computed value
Alarm occurrence
Upper-limit alarm
Difference upper limit alarm
Lower-limit alarm
Difference lower limit alarm
Measured value
or computed value
Alarm reset
Alarm value
Alarm occurrence
•
Upper lmt on rate-of-change alarm (rHgh)
An alarm occurs if the amount of change in the computed value in the rising direction
exceeds the alarm setting value within the rate-of-change detection interval.
•
Lower lmt on rate-of-change alarm (rLow)
An alarm occurs if the amount of change in the computed value in the falling direction
exceeds the alarm setting value within the rate-of-change detection interval.
Computed value
Change in the
computed value
T
1
Time
Interval
T
2
t
1
t
2
T
2
Time
T
1
t
1
t
2
Change in the
computed value
Interval
t
2
–t
1
Amount of change
in the setting |T
2
–T
1
|
Upper limit on rate-of-change alarm
Lower limit on rate-of-change alarm
Computed value
t
2
–t
1
Amount of change
in the setting |T
1
–T
2
|
The rate-of-change detection interval is equal to measurement interval × measurement
count. Select the measurement count (1 to 15) using the Interval of rate-of-change alarm
box.
2.9 Settng Alarms and Alarm Indcatons
