Yokogawa Integral Oxygen Analyzer ZR202 User Manual
Page 41
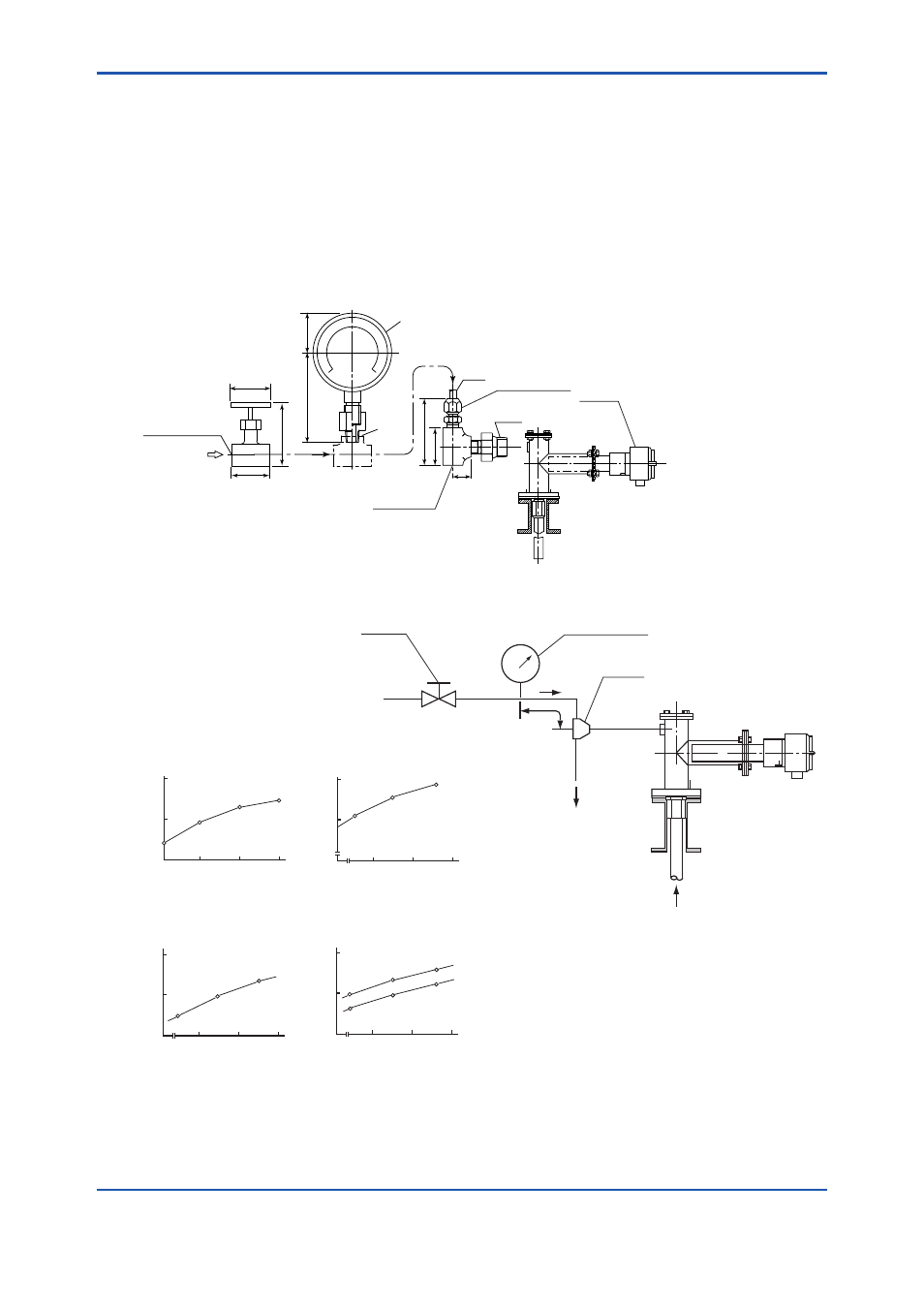
<2. Specifications>
2-23
IM 11M12A01-02E
8th Edition : Jan.13,2012-00
Graph explanation
1) Graph 1 is to compensate for pressure loss in piping between the ejector and the pressure
gauge, and find Po (pressure setting).
2) Graph 2 shows correlation between P (drive pressure) and Qa (air consumption).
3) Graph 3 shows correlation between P (drive pressure) and Pg (suction pressure; when the
sample gas inlet of the ejector is closed).
4) Graph 4 shows correlation between P (drive pressure) and Qg (suction flow) for each gas
pressure.
Qa
L
200
100
0
5
10
15
P= 0.5
0
40
30
40
60
80
Po (kPa)
Qa (l/min)
0
-1.0
-0.5
40
60
80
Pg (kPa)
0
8
4
40
60
80
Qg (l/min)
L (m)
P (kPa)
P (kPa)
P (kPa)
Po (kPa) : Pressure setting
P (kPa) : Drive pressure (at the ejector entrance)
Pg (kPa) : Suction pressure
Qa (l/min) : Air consumption
Qg (l/min) : Suction flow
L (m) : Distance between the ejector and the pressure
gauge
Needle
valve
Pressure gauge
Ejector
Po
Air
source
Gas
Pg
Qg
Gas pressure : -15 Pa
Air consumption characteristics
Pressure setting characteristics
Suction pressure characteristics
Suction flow characteristics
F2-9E.ai
Gas Pressure:
0 kPa
1)
2)
3)
4)
Needle valve
<1>
<2>
Pressure gauge
Pressure gauge assembly
Nozzle (Note1)
R1/2
Ejector
Detector
<1> Rc1/4 or 1/4 FNPT
<2> Ш6/Ш4 or 1/4 inch copper tube (stainless)
with ejector to connect
<3> R1/4 or 1/4 NPT
40
20
Tee
Blow Rc1/4
Ø43
Approx. 67
Approx. 88
39
Approx. 70 38
Full open height
(Note1) The connecter of ejector assembly is a
dedicated connecter with nozzle function.
Instrument air inlet
<3>
