NEC NEAX NDA-24349 User Manual
Page 61
Chapter 3 System Highlights
NEAX2000 IPS
Request For Proposal (RFP) Reference Guide
Page 3-9
NDA-24349 Issue 4
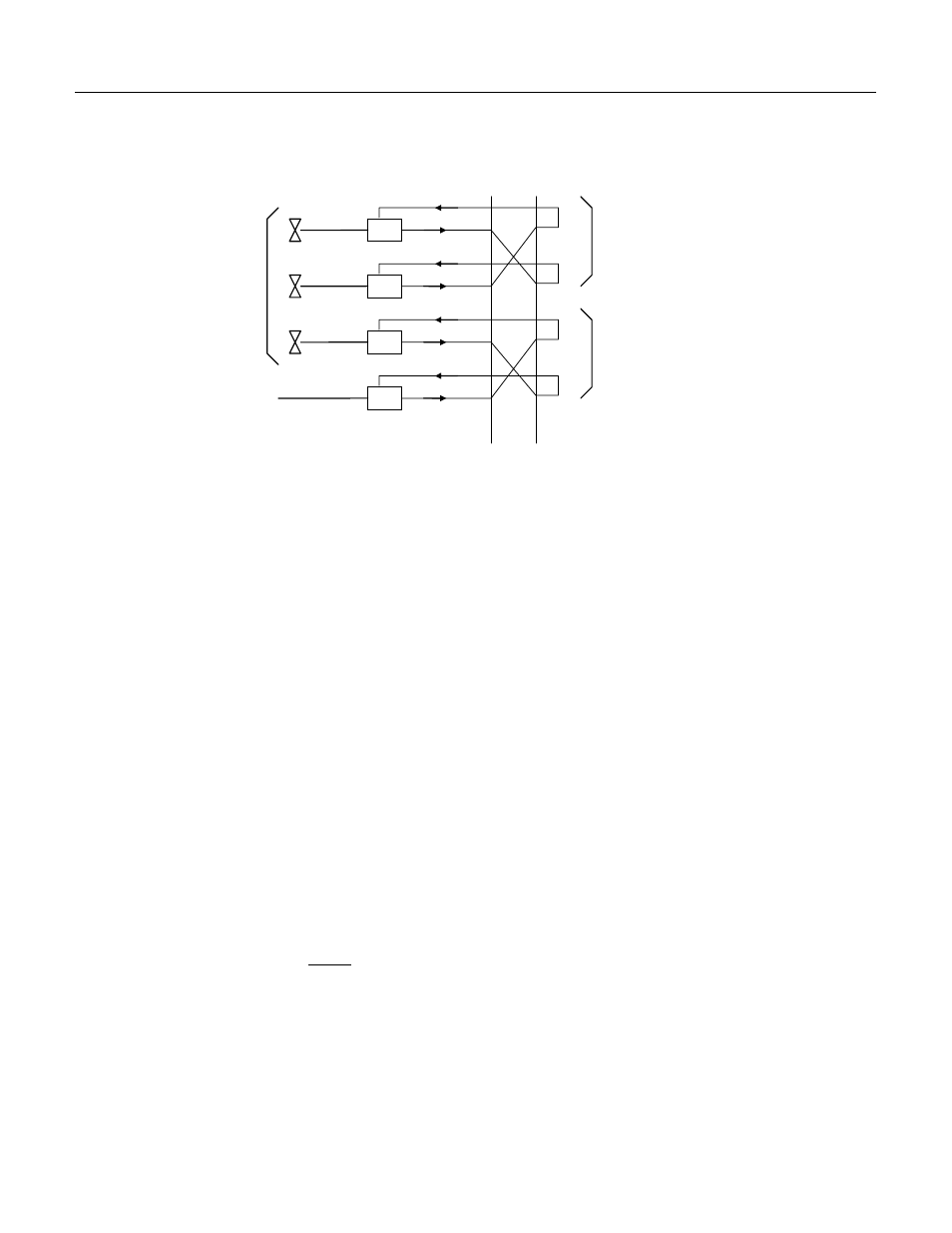
Traffic Capacity In Erlang (For TDM Circuits)
Calculation Procedure
TDSW
LC
Internal Traffic
(I-erl)
LC
STA
LC
External Traffic
COT
(E-erl)
C.O.
Total system traffic capacity (T-erl) is obtainable by the following formula.
T (erl) = I (erl) + E (erl)
In the NEAX 2000 IPS, external traffic capacity is obtained from the Central Office Trunk (COT) quantity
by employing the “Erlang B Table”. There is no limitation for the internal traffic capacity. The time slot is
assigned for individual station and the connection between stations can be made without limitation
through TDSW (Time Division Switch). Consequently, when describing the traffic capacity in erlang, it is
meaningless unless specifying the ratio of the internal and external traffic. From the above idea, total
system traffic capacity (T-erl) is actually obtained by the following formula:
T (erl) = Internal Traffic (I-erl) + External Traffic (E-erl)
= E (erl)
÷ (Ratio of external traffic)
When assuming the external and internal traffic is even.
T(erl)
=
E(erl)+
0.5
For example:
System configuration
:
• 384 Lines
• 64 C. O. Trunks
• External traffic: Internal traffic: = 7:4
In this system, external traffic capacity is obtained from “Erlang B” table. That is, 64 C. O. Trunks at
grade of service of 0.01 can carry 50.6 erl. Total traffic capacity of this system is obtained from above
50.6 erl and ratio of external traffic as shown below:
T (erl) = E (erl) ÷
(Ratio of external traffic)
= 50.6 ч
7__
7
ч
3
= 72.3 erl
Traffic capacity per station line
= 72.3erl ÷ 384
lines
= 0.19 erl/L
