3 token passing, Calculating the transmission distance – Yaskawa MP920 Communications Module User Manual
Page 75
5 215IF Module
5.4.3 Token Passing
5-14
Calculating the Transmission Distance
The panel-to-panel transmission distance for the CP-215 communications system depends
on the baud rate, the number of stations connected, the number of JC215-01 and JC215-02
Junction Boxes connected, and the length of the transmission cables inside the control pan-
els. In general, the maximum transmission distances of the cables between control panels are
as follows:
• Maximum transmission distance with 4 Mbps = 520 - 4.5N - 3.0L
1
- 5.0M (m)
• Maximum transmission distance with 2 Mbps = 727 - 8.48N - 2.58L
1
- 6.06M (m)
• Maximum transmission distance with 1 Mbps = 1041 - 14.0N - 2.08L
1
- 8.33M (m)
Note: N: Number of stations and Repeaters connected
L1: Cable length inside the control panels (m)
M: Number of JC215-01 and JC215-02 Junction Boxes connected.
(The input side and output side of the JC215-01 may be counted
together as one Junction Box.)
5.4.3
Token Passing
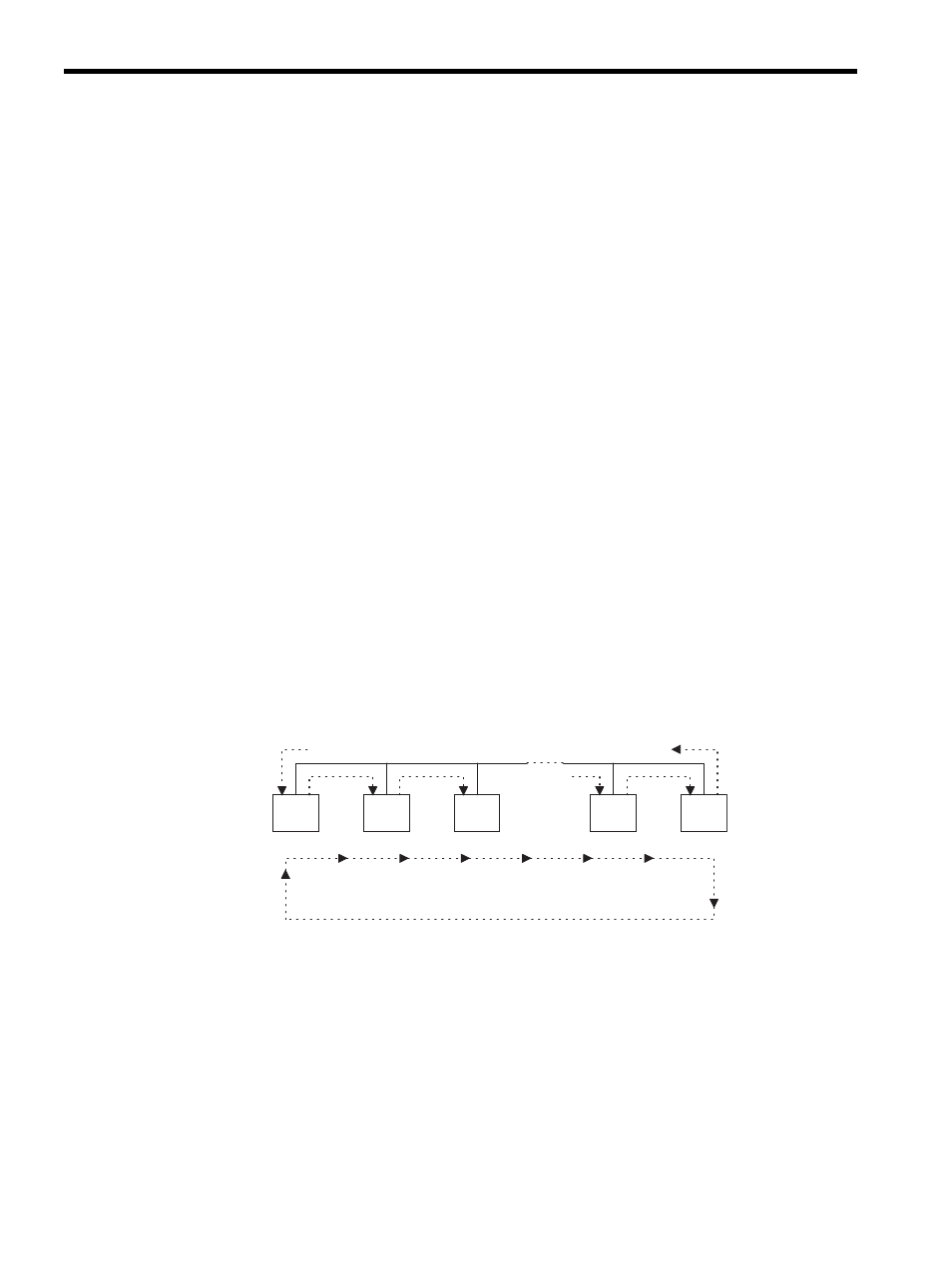
The CP-215 transmission access method known as token passing is explained below.
In token passing, data of a specific pattern, called a token, circulates continuously on the
transmission line. The token represents the right to send, and the station that has this token
has the right to send data.
As shown in the following diagram, the token is circulated from the lowest to the highest
station address (ST#). The stations need not be physically installed in numerical order.
Fig. 5.1 Token Passing
Each time a station with transmission data obtains the token, it transmits the data within the
token holding time. The token holding time is specified in the 215IF parameter settings. A
station with no transmission data immediately passes the token to the next station.
ST#1
ST#2
ST#3
ST#9
ST#10
