2 principle of measurement – K-Patents PR-23 User Manual
Page 10
2
PR-23 instruction manual
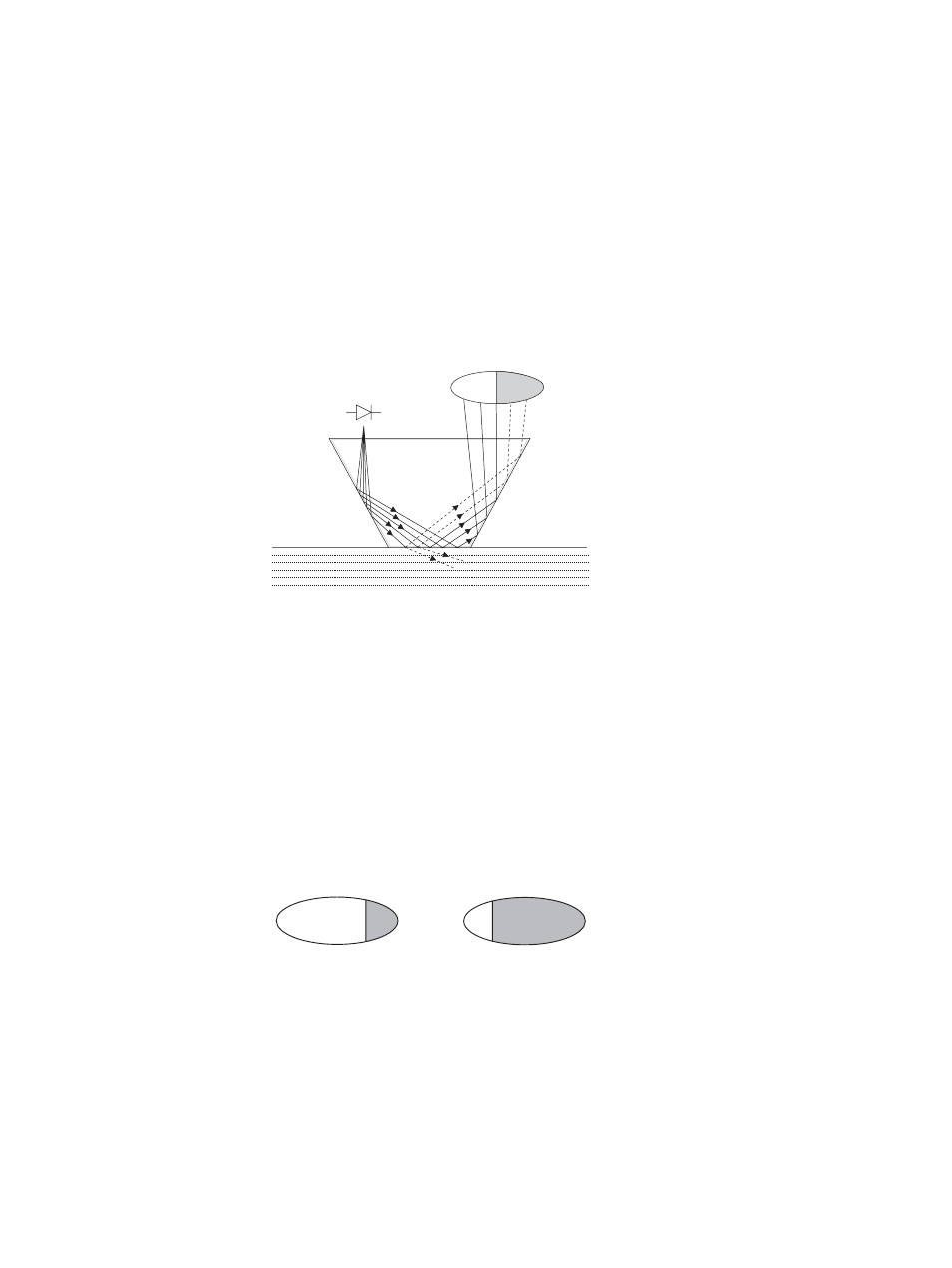
1.2 Principle of measurement
The K-Patents inline refractometer sensor determines the refractive index n
D
of the
process solution. It measures the critical angle of refraction using a yellow LED light
source with the same wavelength (580 nm) as the sodium D line (hence n
D
). Light
from the light source (L) in Figure 1.2 is directed to the interface between the prism
(P) and the process medium (S). Two of the prism surfaces (M) act as mirrors bending
the light rays so that they meet the interface at different angles.
L
P
M
M
S
A
C
B
Figure 1.2
Refractometer principle
The reflected rays of light form an image (ACB), where (C) is the position of the critical
angle ray. The rays at (A) are totally internally reflected at the process interface, the
rays at (B) are partially reflected and partially refracted into the process solution. In
this way the optical image is divided into a light area (A) and a dark area (B). The
position of the shadow edge (C) indicates the value of the critical angle. The refractive
index n
D
can then be determined from this position.
The refractive index n
D
changes with the process solution concentration and tempera-
ture. When the concentration changes, the refractive index normally increases when
the concentration increases. At higher temperatures the refractive index is smaller
than at lower temperatures. From this follows that the optical image changes with
the process solution concentration as shown in Figure 1.3. The color of the solution,
gas bubbles or undissolved particles do not affect the position of the shadow edge (C).
B
B
C
C
A
A
Low concentration
High concentration
Figure 1.3
Optical images
