Guralp Systems CMG-DCM build <10,000 User Manual
Page 75
Acquisition Modules and Platinum Firmware
Networking Configuration
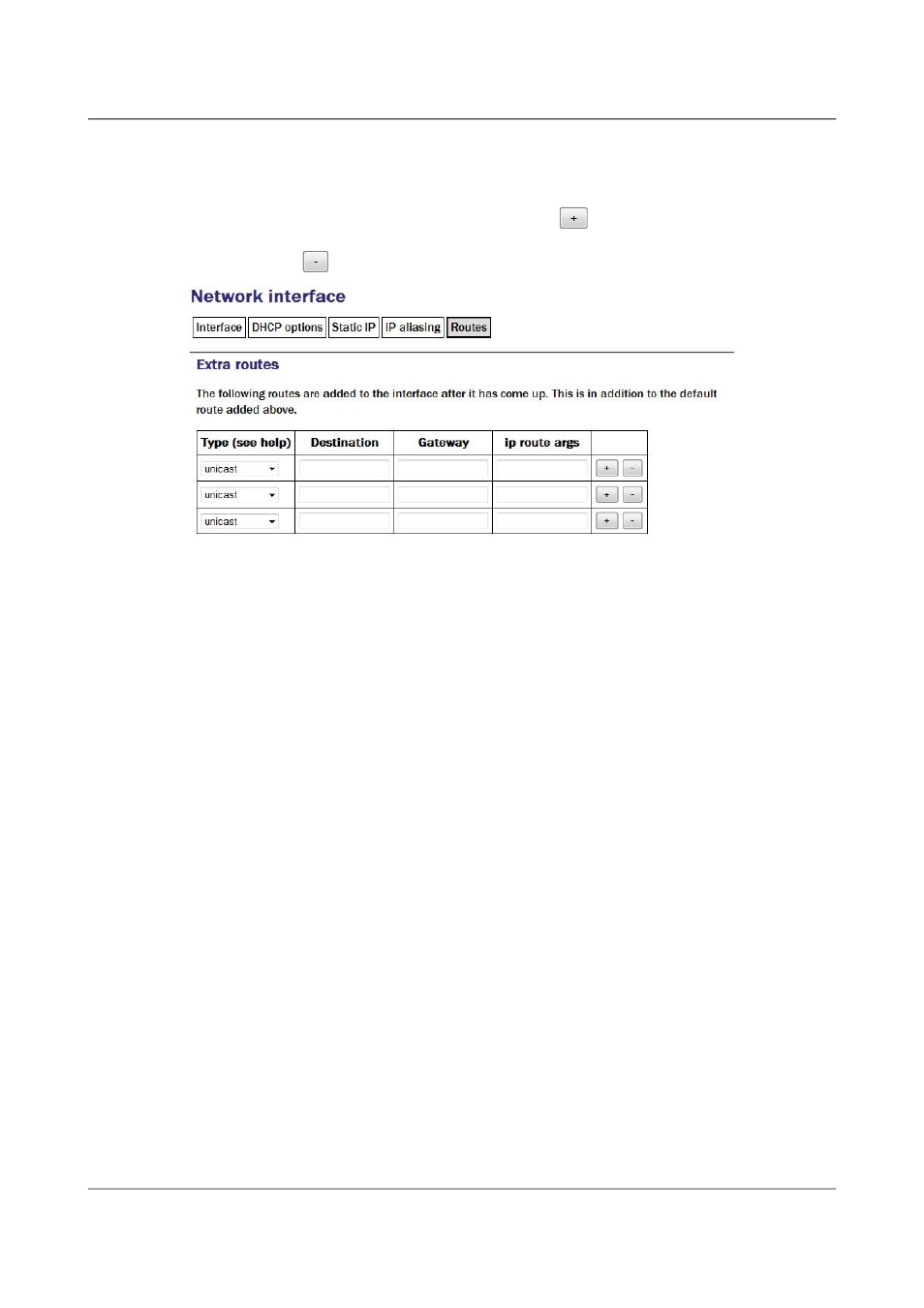
or to force packets to traverse a particular route despite the default router
setting. By default, the table displays three blank rows but, should you need
more, complete the first three and submit the form: it will be redrawn with
extra blank rows. Alternatively, clicking the
button on any row will open
a new row. In the same way, rows can be deleted by clicking the
corresponding
button.
Type: This drop-down menu offers the following choices:
•
unicast - This is the normal setting for a host or network route. The
route entry describes real paths to the destinations specified in the
Destination column.
•
unreachable - these destinations are unreachable. Packets are discarded
and the ICMP message host unreachable is generated. An
EHOSTUNREACH error may appear in /var/log/messages.
•
blackhole - these destinations are unreachable. Packets are discarded
silently. An EINVAL error may appear in /var/log/messages.
•
prohibit - these destinations are unreachable. Packets are discarded and
the ICMP message communication administratively prohibited is
generated. An EACCES error may appear in /var/log/messages.
•
local - the destinations are assigned to this host. The packets are looped
back and delivered locally.
•
broadcast - the destinations are broadcast addresses. The packets are
sent as link broadcasts.
Destination: The host or network to which this route offers access should be
entered here in CIDR format, where the address is followed by a slash and
then the number of bits defining the netmask, e.g. 192.168.0.1/24 for IPV4
or 2001:db8:/32 for IPV6.
Gateway: The IP address of the host which serves as the gateway to the
specified destination.
75
Issue E - February 2014
