P410 (p), Minimum frequency analog input 1/2, P411 (p) – NORD Drivesystems BU0700 User Manual
Page 79: Maximum frequency analog input 1/2, P412 (p), Nominal value process controller, P413 (p), Pid control p-component, P414 (p), Pid control i-component
BU 0700 GB-1411
Subject to technical alterations
79
Parameter
Setting value / Description / Note
Available with option
P410 (P)
Minimum frequency analog input 1/2
always visible
0.0 ... 400.0 Hz
[ 0.0 ]
The minimum frequency that can act on the setpoint via the auxiliary setpoints.
Auxiliary setpoints are all frequencies that have also been entered into the inverter for additional
functions. Actual frequency PID
Frequency addition
Frequency subtraction
Auxiliary setpoints via BUS
Minimum frequency above analog setpoint (potentiometer) Process controller
P411 (P)
Maximum frequency analog input 1/2
always visible
0.0 ... 400.0 Hz
[ 50.0 ]
The maximum frequency that can act on the setpoint via the auxiliary setpoints.
Auxiliary setpoints are all frequencies that have also been entered into the inverter for additional
functions. Actual frequency PID
Frequency addition
Frequency subtraction
Auxiliary setpoints via BUS
Maximum frequency above analog setpoint (potentiometer) Process controller
P412 (P)
Nominal value process controller
always visible
0.0 ... 10.0 V
[ 5.0 ]
Fixed specification of a setpoint for the process controller that will only occasionally be altered.
Only with P400 = 14 ... 16 (process controller). Further details can be found in Chap. 8.2
P413 (P)
PID control P-component
always visible
0 ... 400.0 %
[ 10.0 ]
Only effective if the function Actual frequency PID is selected.
The P-component of the PID controller determines the frequency jump if there is a rule deviation based
on the rule difference.
For example: At a setting of P413 = 10% and a rule difference of 50%, 5% is added to the actual
setpoint.
P414 (P)
PID control I-component
always visible
0 ... 300.0
‰ / ms
[ 1.0 ]
Only effective if the function Actual frequency PID is selected.
The I-component of the PID controller determines the frequency change, dependent on time.
P415 (P)
PID control D-component
always visible
0 ... 400.0 %ms
[ 1.0 ]
Only effective if the function Actual frequency PID is selected.
If there is a rule deviation, the D-component of the PID controller determines the frequency change
multiplied by time.
P416 (P)
Ramptime PID setpoint
always visible
0 ... 99.99s
[ 2.00 ]
Only effective when the function Actual frequency PID is selected.
Ramp for PID setpoint
PID controller
P413 (P-component)
P414 ( I-component)
P415 (D-component)
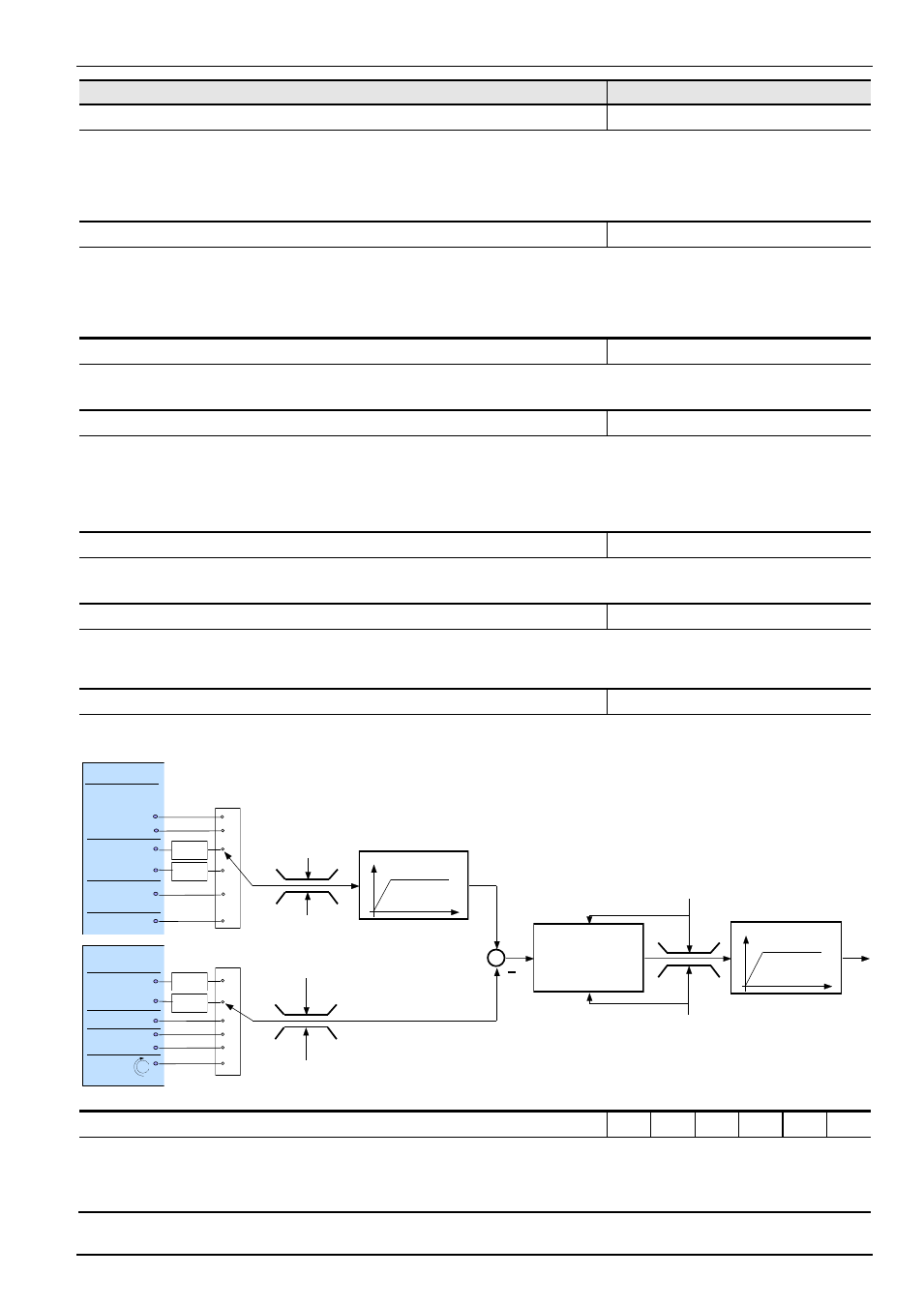
Frequency ramp
P102, P103
Ramp setpoint
P416
Maximum frequency P105
(monitored, limited)
Maximum frequency P105
(unlimited)
Minimum frequency P104
(monitored, limited)
- Maximum frequency P105
(unlimited)
Maximum
frequency P105
Minimum
frequency P104
Maximum frequency
auxiliary setpoint P410
Minimum frequency
auxiliary setpoint P411
Analog input 1
Analog input 2
Bus setpoint 3
Bus setpoint 2
Inc
Auxiliary
setpoint sources
PotentiometerBox
P400-P404
Scaling
P405-P409
Scaling
Analog input 1
Analog input 2
Bus setpoint 1,2,3
Main
setpoint sources
Fixed frequency 1-5
Controlbox /
PotentiometerBox
Jog frequency
P400-P404
Scaling
P405-P409
Scaling
Also in
combination, se e
se tpoint adjustme nt
P417 (P)
Offset analog output 1
STD MLT
-10.0 ... +10.0 V
[ 0.0 ]
In the analog output function an offset can be entered to simplify the processing of the analog signal in
other equipment.
If the analog output has been programmed with a digital function, then the difference between the
switch-on point and the switch-off point can be set in this parameter (hysteresis).
