IAI America ERC User Manual
Page 86
66
20
30
40
50
60
70
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
20
30
40
50
60
70
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
20
30
40
50
60
70
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
20
30
40
50
60
70
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
20
30
40
50
60
70
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
20
30
40
50
60
70
0
50
100
150
200
250
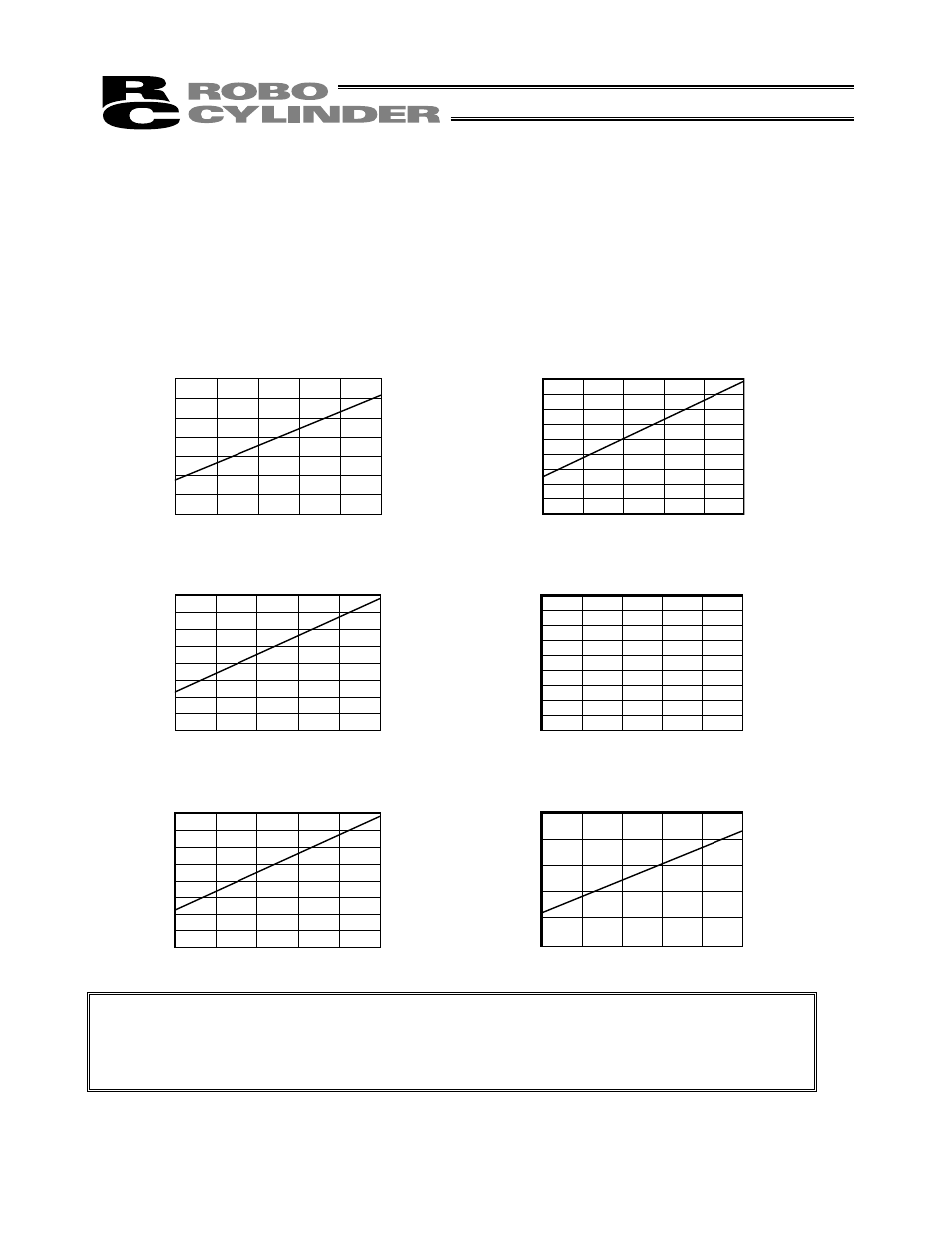
5.1.1 Relationship of Push Force at Standstill and Current-Limiting Value
When performing operation in the push & hold mode, enter the current-limiting value (%) in the push column of
the position-data table.
Determine the current-limiting value (%) from the push force to be applied to the load at standstill.
The graphs below illustrate the relationship of push force at standstill and current-limiting value for each actuator
type:
● Slider type
(1) SA6 type
(2) SA7 type
Low-speed type
Low-speed type
(Lead: 3 mm)
(Lead: 4 mm)
Current-limiting value (%)
Current-limiting value (%)
Current-limiting value (%)
Current-limiting value (%)
Current-limiting value (%)
Current-limiting value (%)
Note: The accuracy of push force at standstill is not guaranteed. The above graphs are provided for
reference purposes only. If the push force is too small, malfunction may occur during push &
hold operation due to slide resistance, etc., so exercise caution.
The maximum current-limiting value is shown in the above graphs. The minimum value is 20%.
Push force (N)
Push force (N)
Push force (N)
Push force (N)
Push force (N)
Push force (N)
Medium-speed type
(Lead: 6 mm)
Medium-speed type
(Lead: 8 mm)
High-speed type
(Lead: 12 mm)
High-speed type
(Lead: 16 mm)
