Scada interface, Client-server environment, Scada interface client-server environment – Motorola 68P02958C00-B User Manual
Page 27
System Overview
2-7
SCADA Central
IP Gateway
ToolBox
(over IP)
Ethernet
IP Gateway
with
Reflector
LINE 1
RS232
Private DataTAC Radio
MOSCAD
RTU
MOSCAD
Programming
ToolBox
(over IP)
RS232
MOSCAD-L
RTU
IP Cloud
RS232
RS232
Private DataTAC Radio
Host
Computer
RF System
RNC
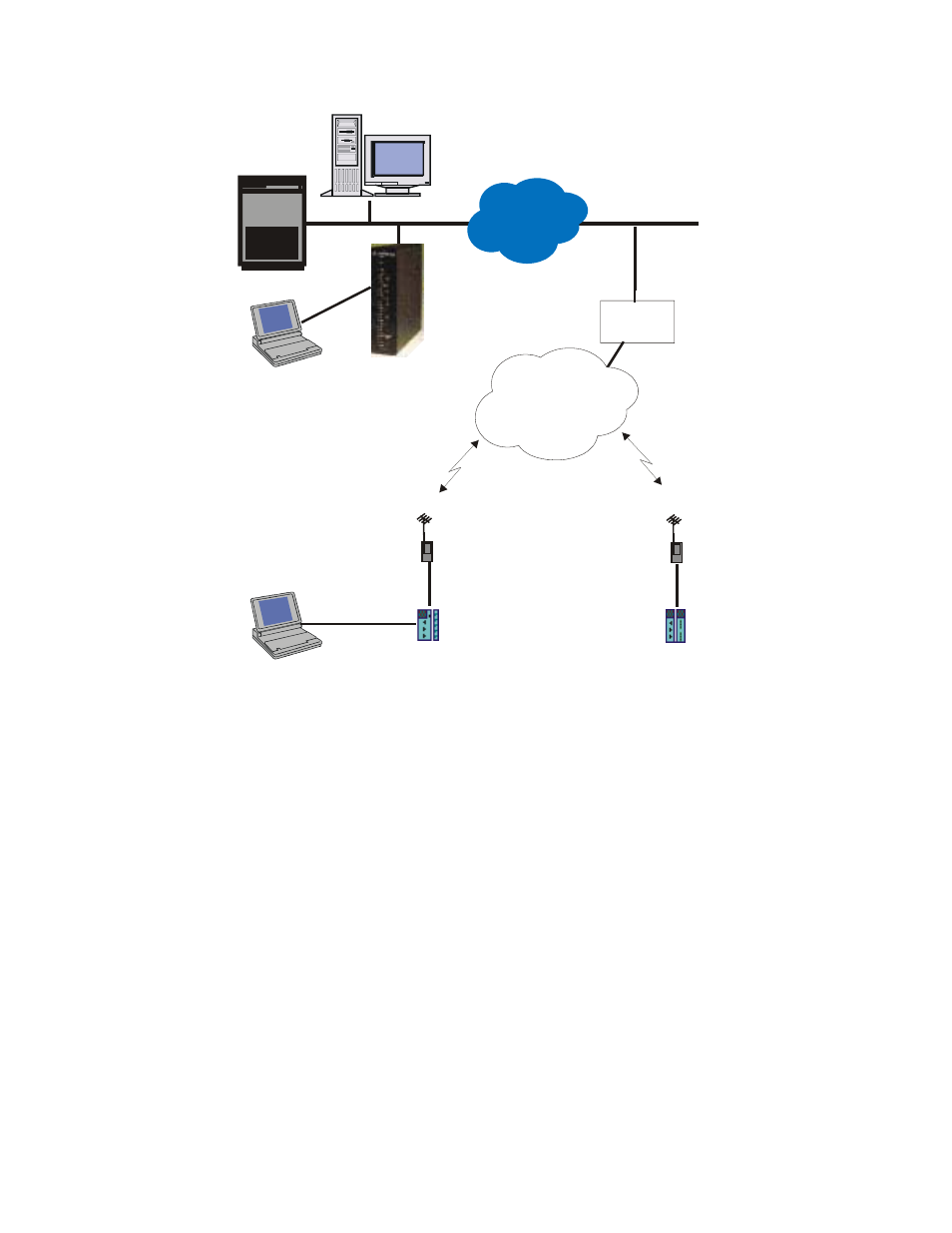
Figure 2-5: Typical Configuration, MDLC via Private DataTac radios.
The picture above shows a typical system which supports MDLC communication over RDLAP
(DataTac) radios. Note that the IP Gateway is configured as RDLAP (DataTac) reflector. A
host computer attached to the Ethernet can receive TCP/IP applications from non-MOSCAD
terminals on existing RDLAP (DataTac) systems, if required. A MOSCAD Programming
ToolBox can be connected to one of the RTUs, and can access another RTU by using its Site
ID and Link ID. ToolBox can also be attached to one of the serial ports of the IP Gateway.
SCADA Interface
Client-Server environment
The SCADA application for the IP Gateway is based on a client-server approach.
The IP Gateway application acts as a server while the SCADA Interface acts as a client. In
such a relationship, the SCADA Interface must establish the connections with the IP Gateway
needed for communicating with the MOSCAD RTUs.
After the connections have been established, the SCADA Interface can send data, commands,
and polling requests to the field RTUs. It can also establish a special connection that enables
