Pitney Bowes MapXtreme User Manual
Page 383
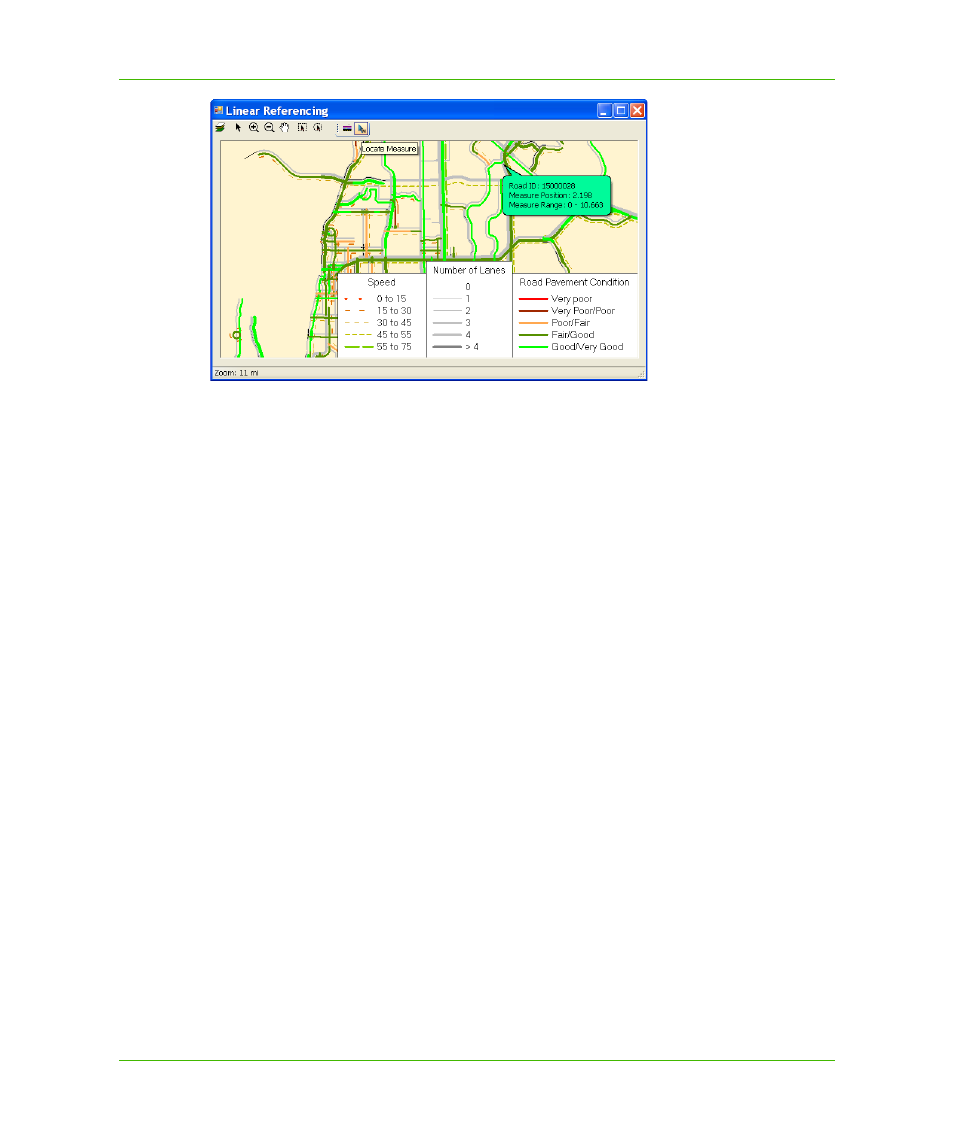
Chapter 21: Linear Referencing
Using M values for Linear Referencing
MapXtreme v7.1
390
Developer Guide
Linear Referencing Sample Application provided in MapXtreme
The linear referencing methods follow the OGC Simple Feature Specification as it applies to one
dimensional MultiCurve geometries. MultiCurves can consist of several disjointed curves. That is,
two Curves can be contained within the MultiCurve for which the end of one Curve does not match
the beginning of the other Curve. The operations, however, may be given a start and end measure
with the expectation that the measure is applied across the entire MultiCurve. In this and similar
scenarios, we assume that even though the actual location data differs (X, Y) between the end of
one curve and the start of another curve, MapXtreme assumes the measure values are the same.
Consider as an example, a highway network in which some highways cross but do not intersect
because one highway runs over the other on a bridge. In those cases, the highway underneath may
actually have the linear representation show a physical break before and after the other highway.
The methods provided in the LinearReferencingOperations class can be organized into three
categories:
•
Measure value determination methods
•
Linear referencing operations
•
Dynamic Segmentation operation (PerpendicularOffset)
The following sections provide a brief introduction to these operations. See also
MapInfo.LinearReferencing namespace for compete details.
