3 cpu operation, 1 timing generator and bus cycle, 2 instruction fetch and execution – Epson S1C63000 User Manual
Page 28: 3 cpu o, Chapter, Peration
22
EPSON
S1C63000 CORE CPU MANUAL
CHAPTER 3: CPU OPERATION
CHAPTER
3 CPU O
PERATION
This section explains the CPU operations and the operation timings.
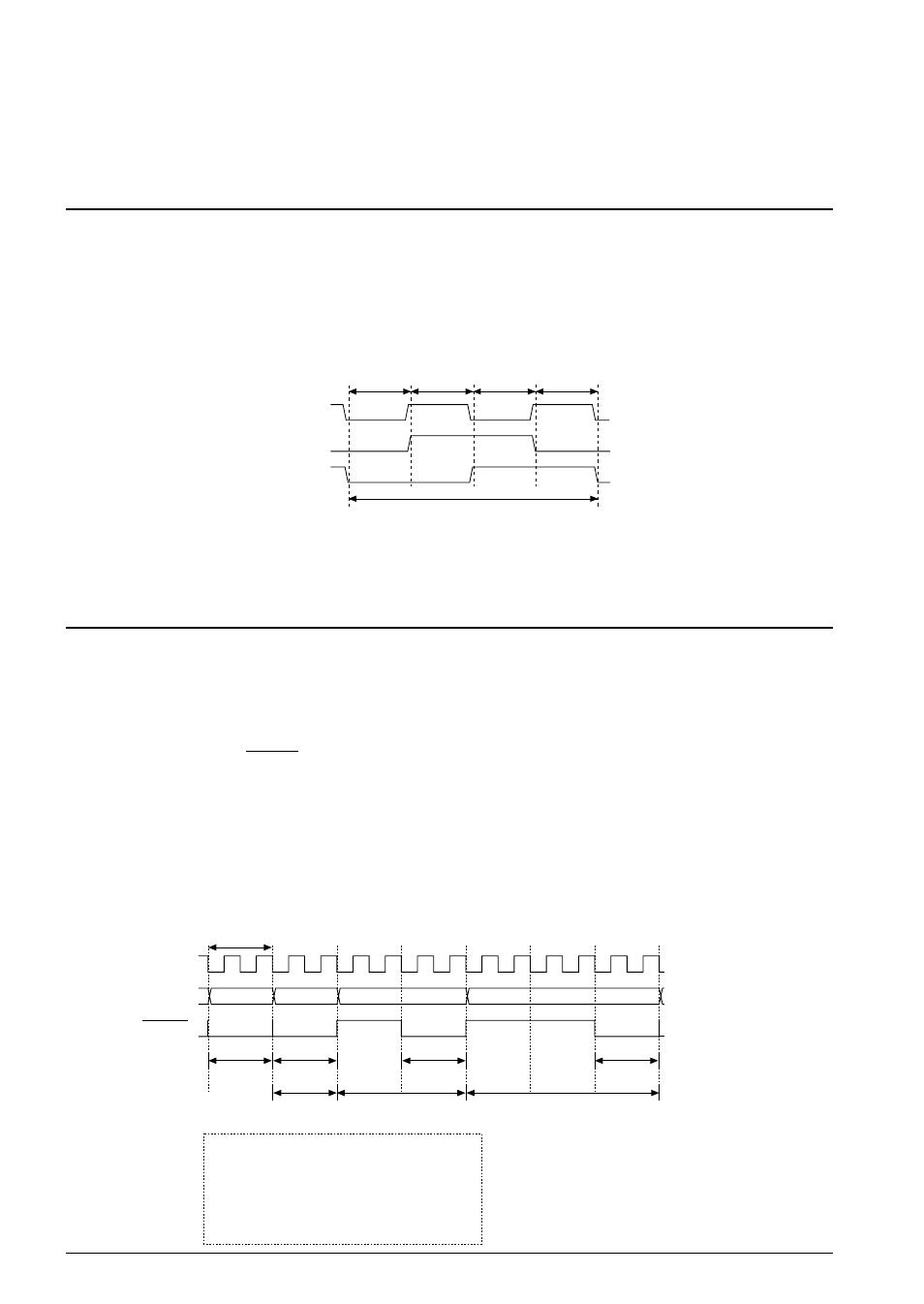
3.1 Timing Generator and Bus Cycle
The S1C63000 has a built-in timing generator. The timing generator of the S1C63000 generates the two-
phase divided signals PK and PL based on the clock (CLK) input externally (
∗
) to make states. One state
is a 1/2 cycle of the CLK and the one bus cycle that becomes the instruction execution unit is composed
of four states.
∗
The clock that is input to the S1C63000 is generated by an oscillation circuit provided outside of the
CPU. The S1C63 Family models have a built-in oscillation circuit.
Fig. 3.2.1 Fetch cycle and execution cycle
CLK
ROM address (PC)
FETCH
Fetch cycle
Execution cycle
One bus cycle
T1 T2 T3 T4
(PC)
(PC+1)
(PC+2)
inst. 1
inst. 2
inst. 3
inst. 1
inst. 2
inst. 3
PC
PC+1
PC+2
PC+3
(PC+3)
inst. 4
one-cycle
instruction
two-cycle
instruction
three-cycle
instruction
ROM address
:
PC
PC+1
PC+2
PC+3
:
Instruction
:
:
inst. 1 (one-cycle instruction)
inst. 2 (two-cycle instruction)
inst. 3 (three-cycle instruction)
inst. 4 (one-cycle instruction)
Fig. 3.1.1 State and bus cycle
The number of cycles which is stated in the instruction list indicates the number of bus cycles.
3.2 Instruction Fetch and Execution
The S1C63000 executes the instructions indicated with the PC (program counter) one by one. That
operation for an instruction is divided into two stages; one is a fetch cycle to read an instruction, and
another is an execution cycle to execute the instruction that has been read.
All the S1C63000 instructions are composed of one step (word), and are fetched in one bus cycle. An
instruction code that is written in the ROM is read out during the fetch cycle and is analyzed by the
instruction decoder. The FETCH signal goes to a low level during that time. In addition, the PC is
incremented at the end of each fetch.
The analyzed instruction is executed from the next bus cycle. The number of execution cycles is shown in
the instruction list and it is one, two or three bus cycles depending on the instruction.
The S1C63000 contains two different buses for the program memory and the data memory. Consequently,
a fetch cycle for the next instruction can be executed to overlap with the last execution cycle, and it
increases the processing speed. In the one-cycle instructions, the next instruction is fetched at the same
time an instruction is executed.
CLK
PK
PL
T1
T2
T3
T4
Bus cycle
State
State
State
State
