Fig. 2.2.3.2 operation of call instructions – Epson S1C63000 User Manual
Page 21
S1C63000 CORE CPU MANUAL
EPSON
15
CHAPTER 2: ARCHITECTURE
This instruction permits the extended addressing with the E flag, and the 8-bit relative address can
be extended into 16 bits (the contents of the EXT register becomes the high-order 8 bits). In this
case, the range that can be branched is from the next instruction address -32768 to +32767. Conse-
quently, in the extended addressing mode this instruction can call subroutines over a 64K program
memory.
Examples:
CALR -50
...Calls the subroutine 49 steps before
LDB
%EXT,50
...(50
×
256) = 17800
CALR 50
...Calls the subroutine 17851 steps after
(2) Instruction with a data memory address within 0000H to 003FH in which the content specifies a 4-bit
relative address
CALR [addr6]
This instruction branches the program sequence with the content of the data memory specified by
the [addr6] as an unsigned 4-bit relative address. The operand [addr6] can specify a data memory
address within 0000H to 003FH. The range that can be branched is from the next instruction
address +0 to +15. Same with the "JR [addr6]", this call instruction can be used as a conditional
call according to the flags that are set in the memory specified with [addr6].
Example:
When the content of the address 0010H is 4 (0100B).
SET
[0x0010],0
...Sets the bit 0 in the address 0010H to "1" ([0010H] = 5)
CALR [0x0010]
...Calls the subroutine 6 steps after
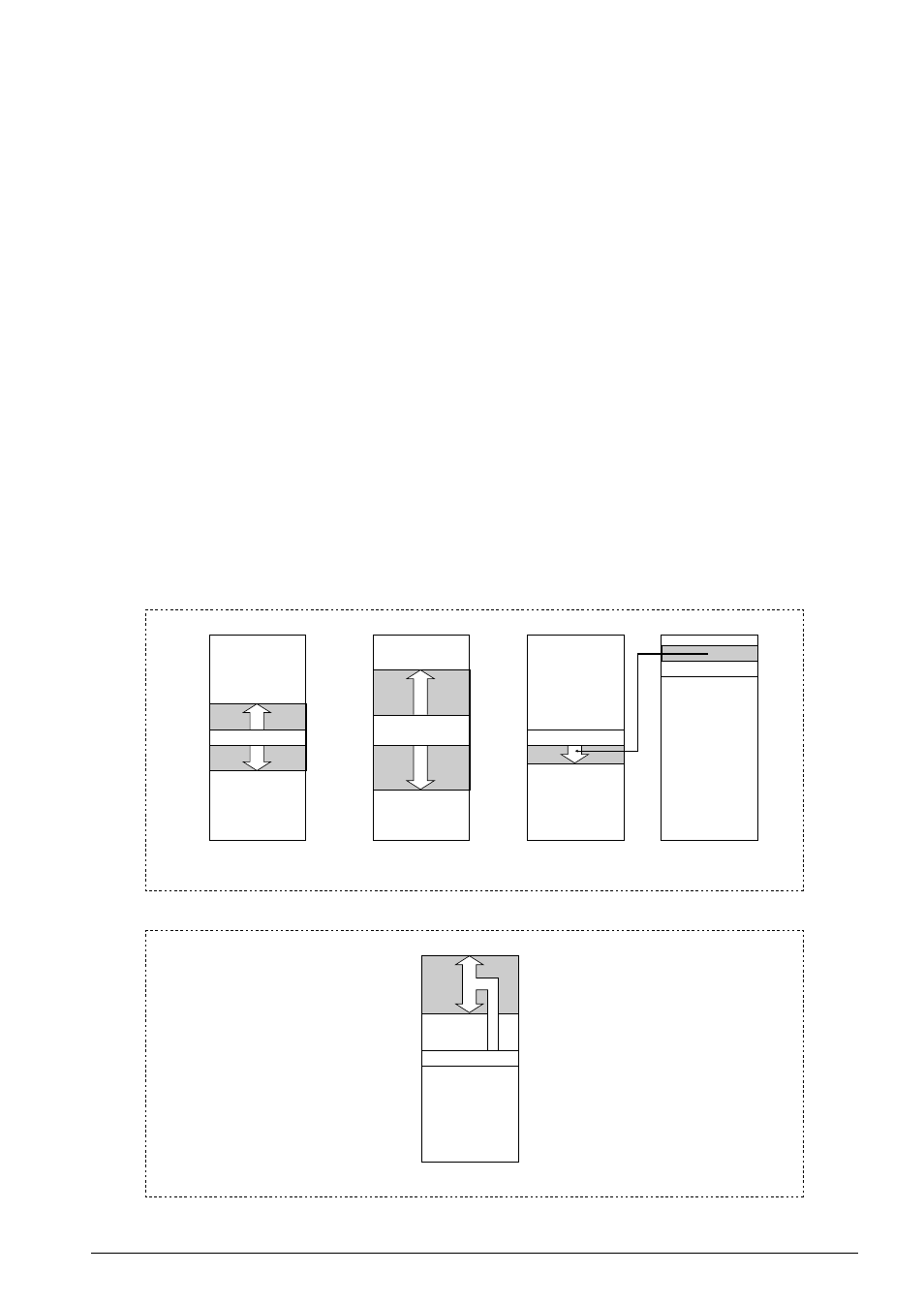
Figure 2.2.3.2 shows the operation of the call instructions and the branch range.
PC relative call instructions
Program memory
0000H
FFFFH
xxxxH
xxxxH-127
CALR sign8
xxxxH+128
0000H
FFFFH
CALZ imm8
imm
→
Branch destination
absolute address
FFFFH
xxxxH CALR [addr6]
xxxxH+16
[addr6]=0
→
xxxxH+1
:
[addr6]=15
→
xxxxH+16
Absolute call instruction
00FFH
0000H
FFFFH
xxxxH-1
xxxxH
xxxxH-32767
LDB %EXT,imm8
CALR sign8
xxxxH+32768
0000H
FFFFH
003FH
addr6
Program memory
Program memory
Program memory
Data memory
∗
In the extended addressing mode,
this instruction can call subroutines
over a 64K program memory.
∗
∗
Fig. 2.2.3.2 Operation of call instructions
