Order of transmission – Altera 40-Gbps Ethernet MAC and PHY MegaCore Function User Manual
Page 63
For example,
din_start
might be set to 5’b11000, indicating the start of a new packet in two successive
words. In this case,
din_end_pos
could equal 40’h0101000000, indicating two packets of eight bytes. Each
8-byte packet is padded with zeros to create a 64-byte packet.
Order of Transmission
The IP core transmits bytes on the Ethernet link starting with the preamble and ending with the FCS in
accordance with the IEEE 802.3 standard. Transmit frames the IP core receives on the client interface are
big-endian. Frames the MAC sends to the PHY on the XGMII/CGMII between the MAC and the PHY are
little-endian; the MAC TX transmits frames on this interface beginning with the least significant byte.
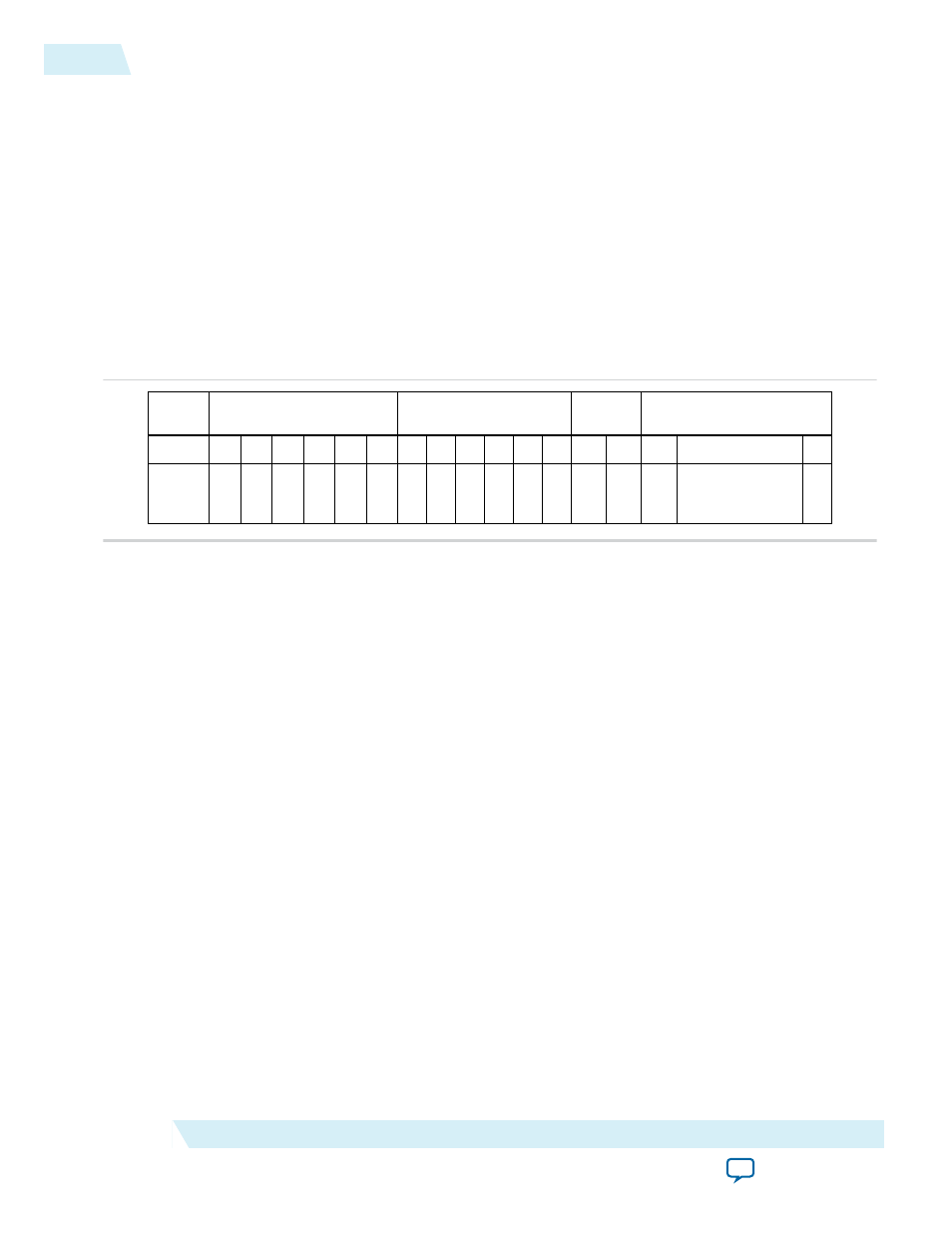
Figure 3-14: Byte Order on the Client Interface Lanes Without Preamble Pass‑Through
Describes the byte order on the Avalon-ST interface when the preamble pass-through feature is turned
off. Destination Address[40] is the broadcast/multicast bit (a type bit), and Destination Address[41] is a
locally administered address bit.
Destination Address (DA)
Source Address (SA)
Data (D)
Type/
Length
Octet
5
4
3
1
2
0
5
4
3
0
1
2
1
0
00
...
NN
Bit
[47
:40]
[39
:32]
[31
:24]
[23
:16]
[15
:8]
[7:
0]
[47
:40]
[39
:32]
[31
:24]
[23
:16]
[15
:8]
[7:
0]
[15
:8]
[7:
0]
MSB[7
:0]
...
LSB[
7:0]
For example, the destination MAC address includes the following six octets AC-DE-48-00-00-80. The first
octet transmitted (octet 0 of the MAC address described in the 802.3 standard) is AC and the last octet
transmitted (octet 7 of the MAC address) is 80. The first bit transmitted is the low-order bit of AC, a zero.
The last bit transmitted is the high order bit of 80, a one.
The preceding table and the following figure show that in this example, 0xAC is driven on
DA5
(DA[47:40])
and 0x80 is driven on
DA0
(DA[7:0])
.
3-16
Order of Transmission
UG-01088
2014.12.15
Altera Corporation
Functional Description
