Technical data, 1 measuring principle, 2 transit time measuring principle – KROHNE ALTOSONIC V12 EN User Manual
Page 98
9
TECHNICAL DATA
98
ALTOSONIC V12
www.krohne.com
04/2013 - 4002643502 - MA ALTOSONIC V12 R02 en
9.1 Measuring principle
The ultrasonic gas flowmeter operates according to the principle of measuring the transit time
of an ultrasonic sound wave. A gas velocity is derived from the difference in transit time of a
sound wave travelling in a direction with the flow direction and the sound wave travelling in the
opposite direction.
The trajectory of the sound wave is called the acoustic path. A chord is the direct path crossing
the pipe from one side to the opposite side. Using reflection, an acoustic path can consist of two
or more chords. The name ALTOSONIC V12 is related to its design where 12 chords build 6
acoustic paths.
9.2 Transit time measuring principle
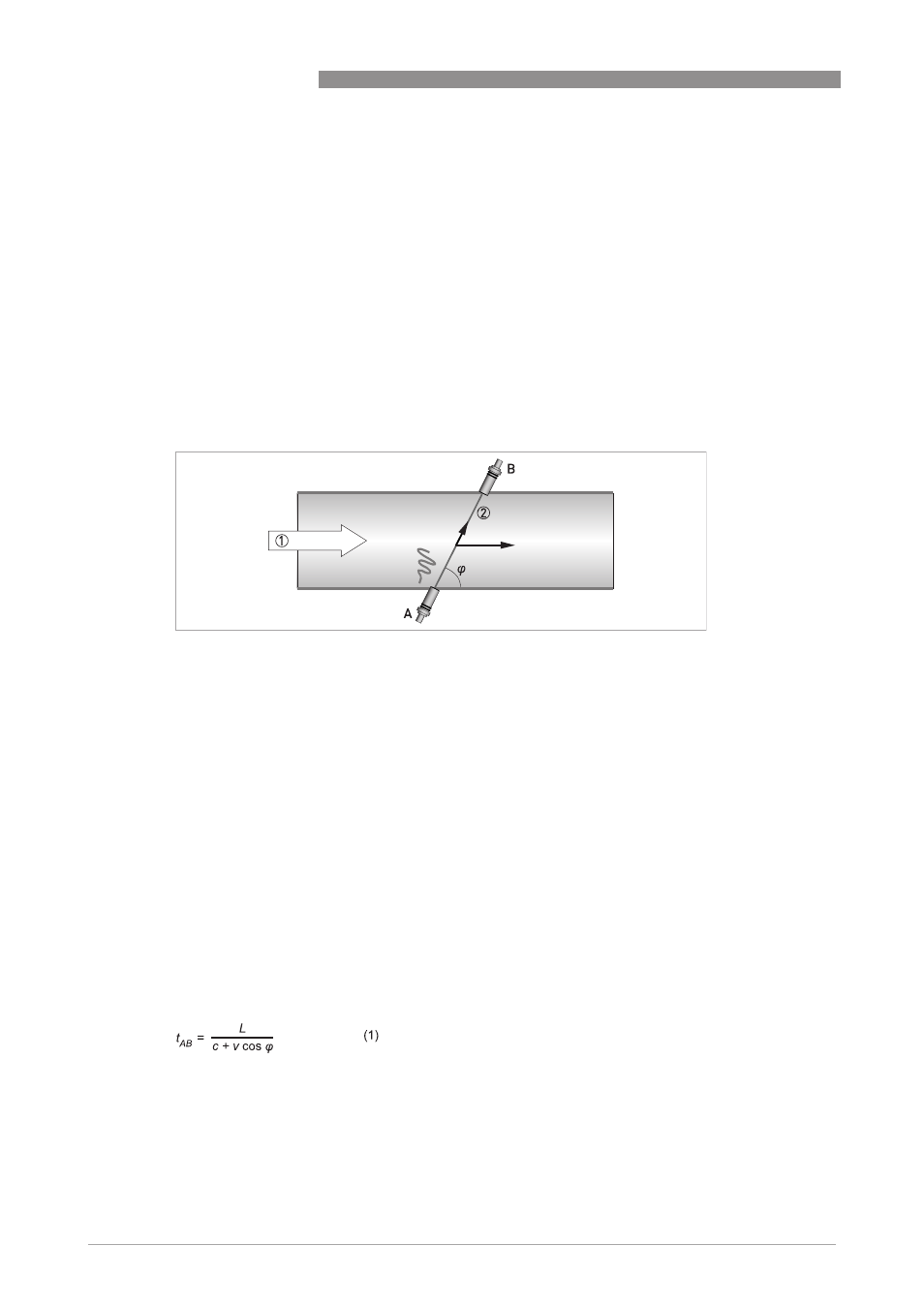
In a pipe section two transducers A and B create an acoustic path, which in the above figure, is a
single chord. This chord is the distance between transducer A and B and has a length L. The
chord intersects with the centre line of the pipe at an angle ϕ.
Both transducers are capable to transmit and receive an ultrasonic signal. First, one transducer
acts as a transmitter and the other as receiver, then the other way around. The transit time of an
ultrasonic signal along a measuring chord is influenced by the velocity of the gas flow (v). If the
gas flow is zero the transit time from transducer A to B is exactly the same as the transit time
from transducer B to A (determinded by the speed of sound in the gas).
When the gas flows with a velocity v and with c being the speed of sound in the gas:
v.cos(ϕ) is the component of velocity in the direction of the measurement chord.
This component increases or decreases the travel time (time of flight of an acoustic waveform)
as it moves from one transducer to the other transducer. The transit time from transducer A to B
(t
AB
) is:
In opposite direction from transducer B to A the transit time (t
BA
) is:
Figure 9-1: Transit time measuring principle
1 Direction of gas flow
2 Component of velocity in the direction of the chord
