Scanning the adc, Atmega169v/l – Rainbow Electronics Atmega169L User Manual
Page 240
240
ATmega169V/L
2514A–AVR–08/02
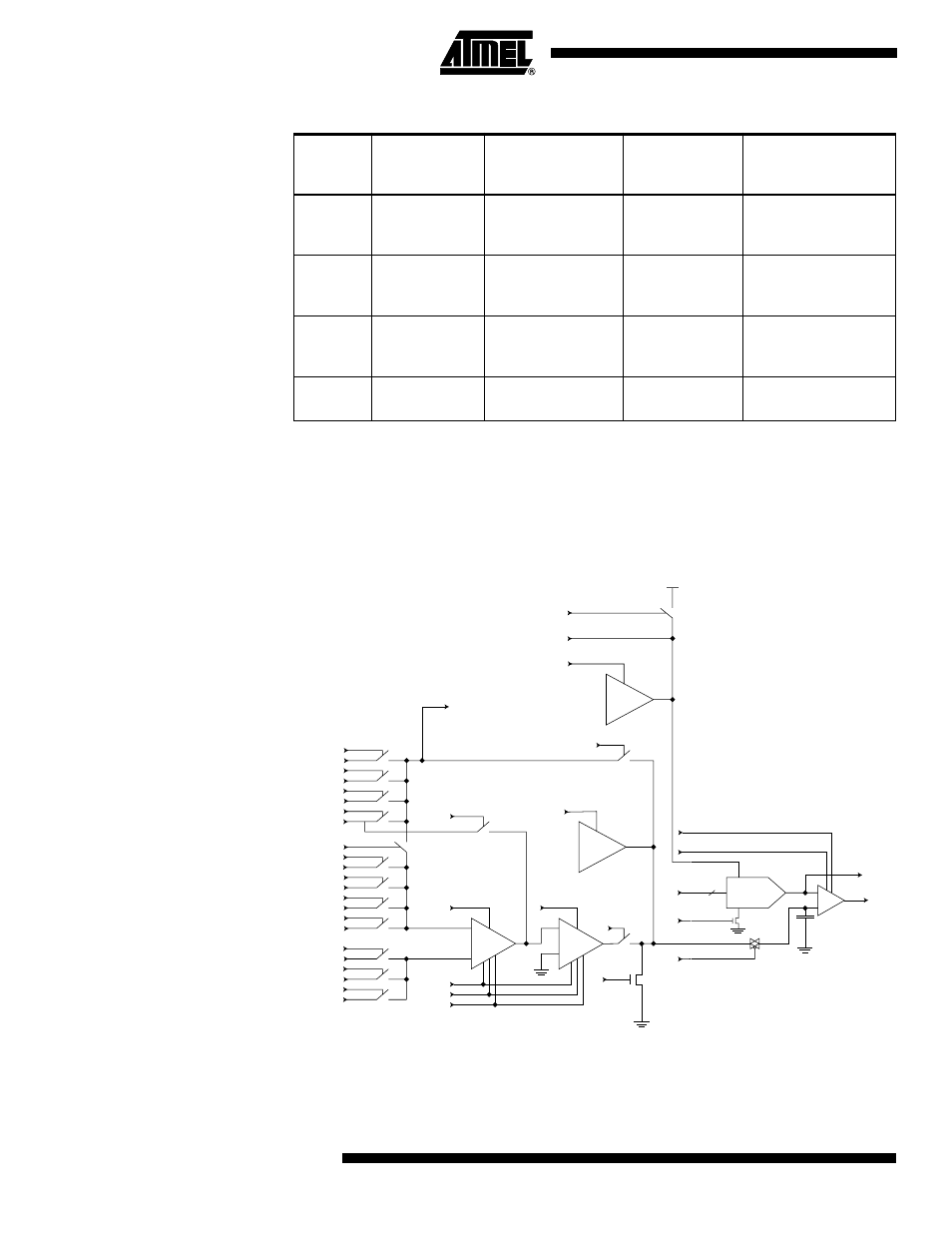
Scanning the ADC
Figure 114 shows a block diagram of the ADC with all relevant control and observe sig-
nals. The Boundary-scan cell from Figure 110 is attached to each of these signals. The
ADC need not be used for pure connectivity testing, since all analog inputs are shared
with a digital port pin as well.
Figure 114. Analog to Digital Converter
The signals are described briefly in Table 105.
Table 104. Boundary-scan Signals for the Analog Comparator
Signal
Name
Direction as
Seen from the
Comparator
Description
Recommended
Input when Not
in Use
Output Values when
Recommended
Inputs are Used
AC_IDLE
input
Turns off Analog
Comparator when
true
1
Depends upon µC
code being executed
ACO
output
Analog
Comparator Output
Will become
input to µC code
being executed
0
ACME
input
Uses output signal
from ADC mux
when true
0
Depends upon µC
code being executed
ACBG
input
Bandgap
Reference enable
0
Depends upon µC
code being executed
10-bit DAC
+
-
AREF
PRECH
DACOUT
COMP
MUXEN_7
ADC_7
MUXEN_6
ADC_6
MUXEN_5
ADC_5
MUXEN_4
ADC_4
MUXEN_3
ADC_3
MUXEN_2
ADC_2
MUXEN_1
ADC_1
MUXEN_0
ADC_0
NEGSEL_2
ADC_2
NEGSEL_1
ADC_1
NEGSEL_0
ADC_0
EXTCH
+
-
+
-
10x
20x
G10
G20
ST
ACLK
AMPEN
2.56V
ref
IREFEN
AREF
VCCREN
DAC_9..0
ADCEN
HOLD
PRECH
GNDEN
PASSEN
ACTEN
COMP
SCTEST
ADCBGEN
To Comparator
1.22V
ref
AREF
ADHSM
ADHSM
