0x53c), 0x5bc) – Texas Instruments TMS320C645X User Manual
Page 49
www.ti.com
31
0
1
2
15
23
7
27
11
19
3
29
O
W
N
E
R
S
H
I
P
T
E
A
R
D
O
W
N
E
O
P
E
O
Q
S
O
P
3
Reserved
Retry_count
cc
Message Length
13
21
5
25
9
17
1
30
14
22
6
26
10
18
2
28
12
20
4
24
8
16
0
Bit Fields
Next Descriptor Pointer
Buffer Pointer
Dest_ID
PRI
tt
SSIZE
Mailbox
Port_ID
Word
Offset
SRIO Functional Description
2.3.4.2
TX Operation
Outgoing messages are handled similarly, with buffer descriptor queues that are assigned by the CPUs.
The queues are configured and initialized upon reset. When a CPU wants to send a message to an
external RapidIO device, it writes the buffer descriptor information via the configuration bus into the
SRAM. Again, there is a single buffer descriptor per RapidIO message. Upon completion of writing the
buffer descriptor, the OWNERSHIP bit is set to give control to the peripheral. The CPU then writes the TX
DMA State HDP register to initiate the queue transmit. For TX operation, PortID is specified to direct the
outgoing packet to the appropriate port.
and
show the TX DMA state registers.
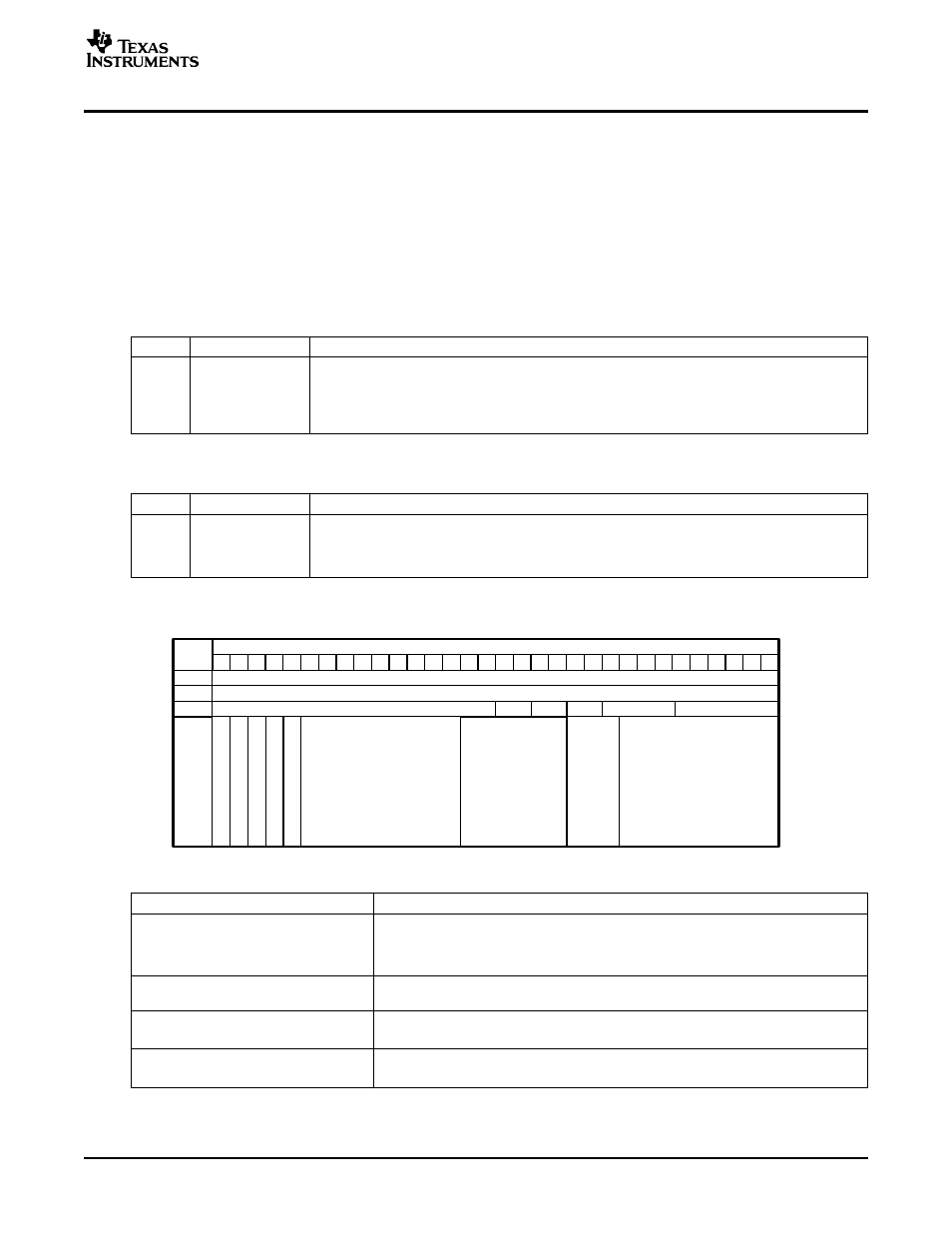
shows the TX buffer descriptor fields. A TX buffer descriptor is a contiguous block of four 32-bit
data words aligned on a 32-bit boundary.
Table 18. TX DMA State Head Descriptor Pointer (HDP) (Address Offset 0x500 – 0x53C)
Bit
Name
Description
31:0
TX Queue Head
Tx Queue Head Descriptor Pointer: This field is the host memory address for the first buffer
Descriptor Pointer
descriptor in the transmit queue. This field is written by the host to initiate queue transmit
operations and is zeroed by the port when all packets in the queue have been transmitted. An error
condition results if the host writes this field when the current field value is nonzero. The address
must be 32-bit word aligned.
Table 19. TX DMA State Completion Pointer (CP) (Address Offset 0x580 – 0x5BC)
Bit
Name
Description
31:0
TX Queue
Tx Queue Completion Pointer: This field is the host memory address for the transmit queue
Completion Pointer
completion pointer. This register is written by the host with the buffer descriptor address for the last
buffer processed by the host during interrupt processing. The port uses the value written to
determine if the interrupt should be deasserted.
Figure 22. TX Buffer Descriptor Fields
Table 20. TX Buffer Descriptor Field Definitions
Field
Description
next_descriptor_pointer
Next Descriptor Pointer: The 32-bit word aligned memory address of the next buffer
descriptor in the TX queue. This is the mechanism used to reference the next buffer
descriptor from the current buffer descriptor. If the value of this pointer is zero then the
current buffer is the last buffer in the queue. The host sets the next_descriptor_pointer.
buffer_pointer
Buffer Pointer: The byte aligned memory address of the buffer associated with the
buffer descriptor. The host sets the buffer_pointer.
sop = 1
Start of Message: Indicates that the descriptor buffer is the first buffer in the message.
•
This bit will always be set as this device only supports one buffer per message.
eop = 1
End of Message: Indicates that the descriptor buffer is the last buffer in the message.
•
This bit will always be set as this device only supports one buffer per message.
SPRU976 – March 2006
Serial RapidIO (SRIO)
49
