Application, Features, E1 interface – RAD Data comm IPmux-11 User Manual
Page 16: T1 interface, Ethernet interface
Chapter 1 Introduction
Installation and Operation Manual
1-2
Overview
IPmux-11 Ver. 2.00
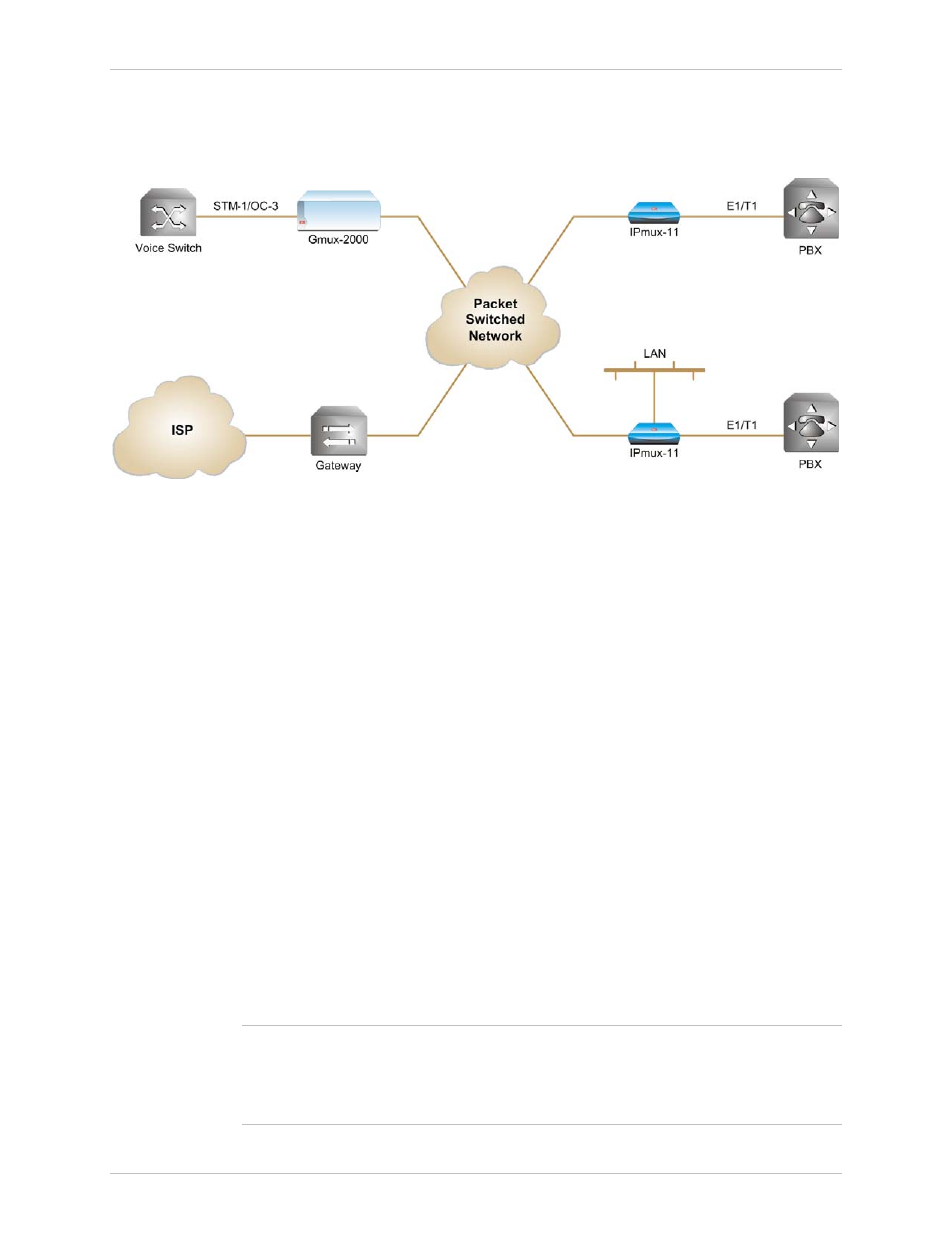
Application
illustrates
a typical IPmux-11 multiplexing voice and Ethernet traffic over
an IP link.
Figure 1-1. Multiplexing Voice and Ethernet over a Packet-Switched Network
Features
E1 Interface
The E1 port complies with G.703, G.704, and G.823 standards. The E1 port
supports unframed, framed and multiframed operation with or without CRC-4.
The E1 port supports long haul and short haul input signals and can be monitored
for alarms and error statistics.
T1 Interface
The T1 port complies with ANSI T1.403, G.703, and G.704 standards. T1 jitter
performance is according to G.824 and TR-62411. The T1 port supports
unframed, SF, ESF and Robbed Bit signaling. The T1 port supports long haul and
short haul input/output signals and can be monitored for alarms and error statistics.
FDL and transmit performance monitoring for T1/ESF are also supported.
Ethernet Interface
IPmux-11 is available with three Ethernet ports (two user and one network port).
The Ethernet ports work in the following switch modes:
• Transparent
• Tagged
• Untagged
• Double Tagged.
Half-duplex operation in the IPmux-11 network port is not recommended when
transmitting small-size packets, because collisions and backoffs cause large delay
variation and may exceed the delay variation buffer tolerance at the receiving end,
resulting in buffer underflows and errors.
Note
