Wireless distribution system (wds) – Proxim ORiNOCO AP-700 User Manual
Page 50
Performing Advanced Configuration
AP-700 User Guide
Interfaces
50
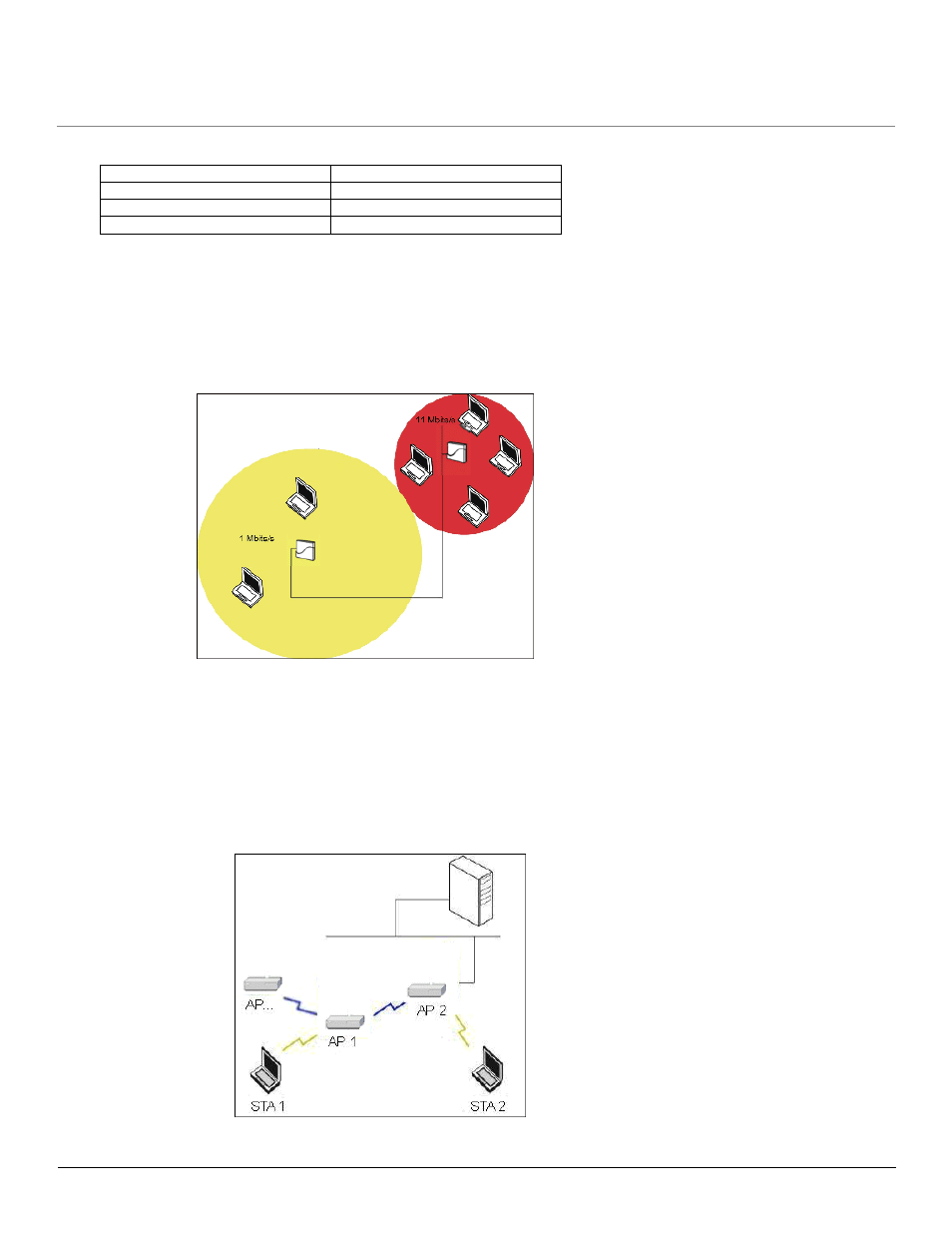
Cell capacities are compared in the following table, which shows that small cells suit most offices and large cells suit most warehouses:
Coverage
The number of Access Points in a set area determines the network coverage for that area. A large number of Access Points covering a small
area is a high-density cell. A few Access Points, or even a single unit, covering the same small area would result in a low-density cell, even
though in both cases the actual area did not change — only the number of Access Points covering the area changed.
In a typical office, a high density area consists of a number of Access Points installed every 20 feet and each Access Point generates a small
radio cell with a diameter of about 10 feet. In contrast, a typical warehouse might have a low density area consisting of large cells (with a
diameter of about 90 feet) and Access Points installed every 200 feet.
Figure 4-11 1 Mbits/s and 11 Mbits/s Multicast Rates
Wireless Distribution System (WDS)
A Wireless Distribution System (WDS) creates a link between two 802.11a, 802.11b, or 802.11b/g APs over their radio interfaces. This link
relays traffic from one AP that does not have Ethernet connectivity to a second AP that has Ethernet connectivity. WDS allows you to
configure up to six (6) ports per radio
In the WDS example below, AP 1 and AP 2 communicate over a WDS link (represented by the blue line). This link provides Client 1 with
access to network resources even though AP 1 is not directly connected to the Ethernet network. Packets destined for or sent by the client
are relayed between the Access Points over the WDS link.
Figure 4-12 WDS Example
Small Cell
Large Cell
Physically accommodates few stations
Physically accommodates many stations
High cell bandwidth per station
Lower cell bandwidth per station
High transmit rate
Lower transmit rate
