Fip protocol, Fcoe frames, How fcoe works – H3C Technologies H3C S5830V2 Series Switches User Manual
Page 18
7
To use a VFC interface, bind it to a physical Ethernet interface.
You can connect either an ENode or an FCF switch to a VFC interface.
VFC interfaces support E mode, F mode (default), and NP mode.
The virtual node (VN) interface is a logical interface on an ENode to simulate the function of a physical
FC interface.
FIP protocol
FCoE initialization protocol (FIP) is an FCoE control protocol that establishes and maintains virtual links.
FIP establishes a virtual link between the VFC interface of an FCF switch and the VN interface of an
ENode or between VFC interfaces of two FCF switches to provide a physical infrastructure for
transmitting FC frames over Ethernet.
FCoE frames
To transmit an FC frame over an Ethernet link, FCoE must encapsulate the FC frame in an FCoE frame by
adding an Ethernet frame header to the FC frame.
An FCoE frame uses Ethernet II encapsulation, which has the following fields in the Ethernet header:
•
EtherType 0x8906.
•
Destination MAC address/source MAC address—The meanings of this field are different for
switches and nodes.
{
For a switch, this field is the FCoE MAC address of the switch (which can be displayed by using
the display fcoe command).
{
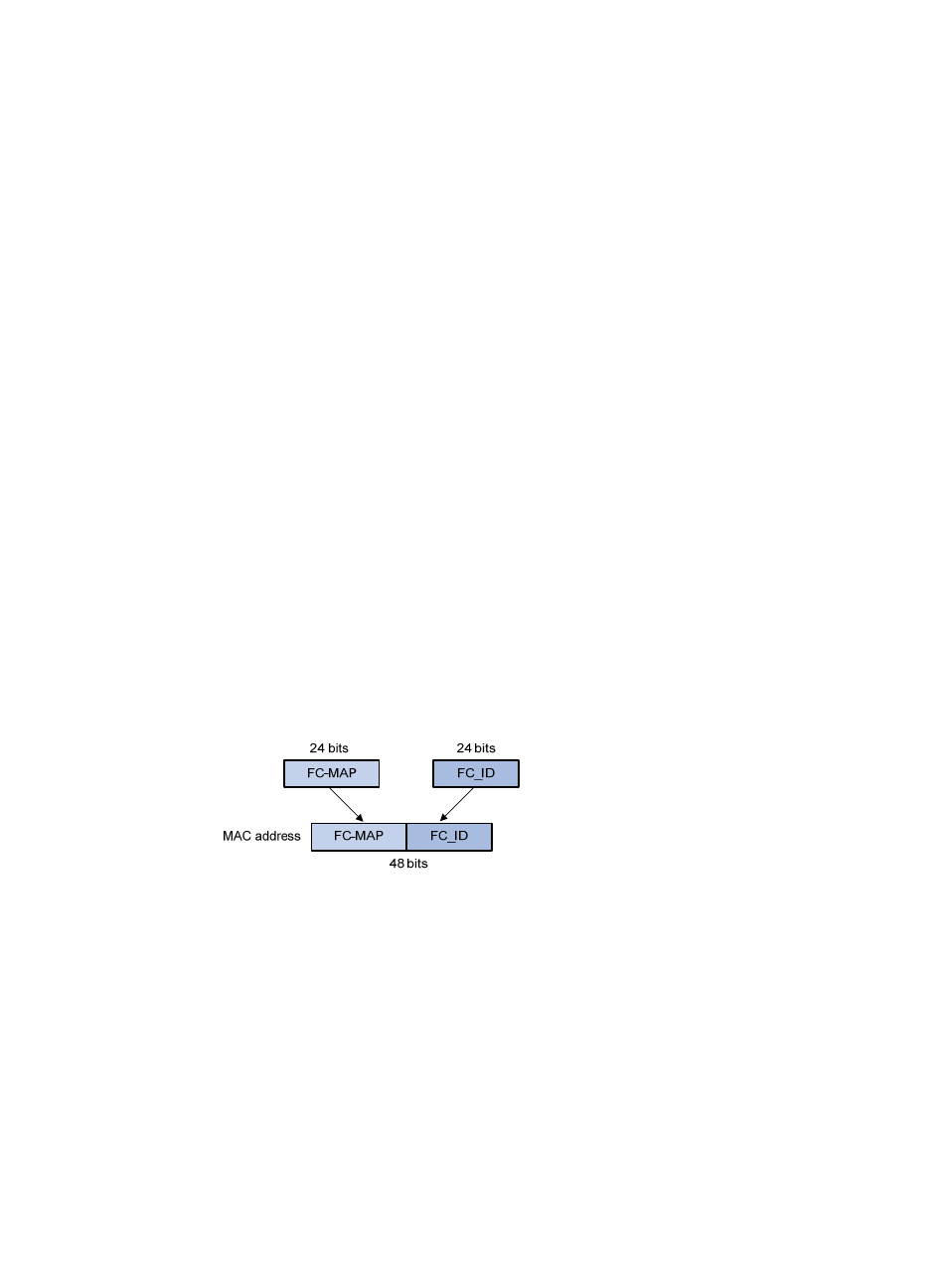
For a node, this field is the fabric provided MAC address (FPMA) of the node. As shown
in
, an FPMA is composed of the FC-MAP as the 24 most significant bits and the FC ID
of the VN interface as the 24 least significant bits. The FC-MAP takes the value of the switch
FC-MAP, 0x0EFC00 by default and configurable by using the fcoe fcmap command.
Figure 7 FPMA composition
How FCoE works
This section describes how FCoE works only on the FCF switch, rather than on the ENode.
