Port modes – H3C Technologies H3C S5830V2 Series Switches User Manual
Page 14
3
shows the structure of an FC address. The FC address is 24 bits long and contains the following
8-bit fields:
•
Domain_ID—A domain represents a switch and all N_Ports connected to the switch. For more
information about N_Ports, see "
." A Domain_ID, which is in the range of 1 to 239,
uniquely identifies an FC switch. Different FC switches in the same fabric have different
Domain_IDs.
•
Area_ID—One or more N_Ports on the same node can be assigned to an area, which is identified
by an Area_ID.
•
Port_ID—The Port_ID field identifies an N_Port.
Figure 2 Structure of an FC address
An FC address can uniquely identify an N_Port on a node. Different N_Ports on the same node have
different FC addresses. FC switches use Domain_IDs to route messages between each other.
The FC protocol standardizes the FC address usage. For more information, see "
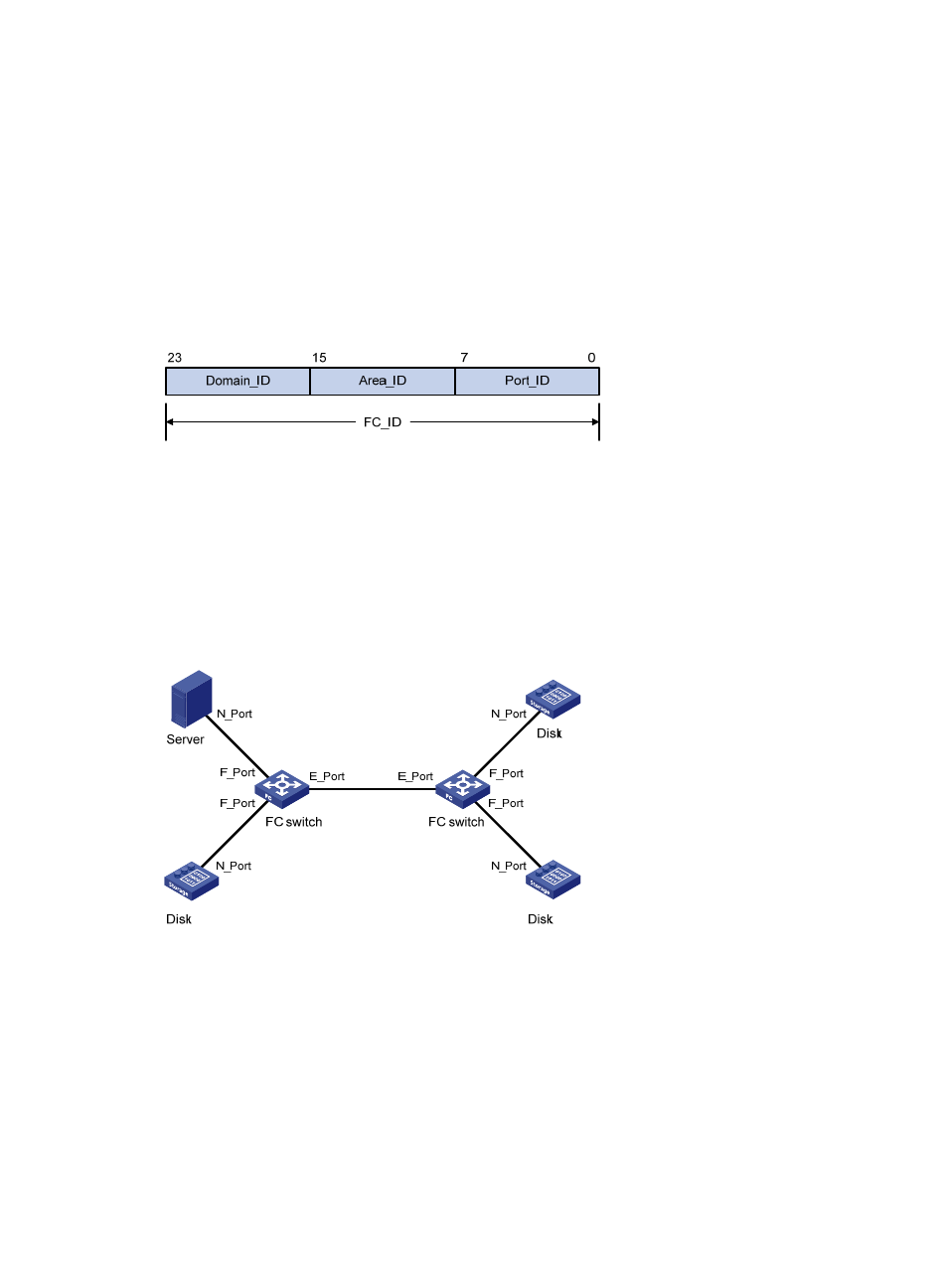
Port modes
In a switched fabric, nodes and FC switches communicate through interfaces operating in different
modes.
Figure 3 Port modes
A node supports the following port modes:
•
N_Port—Directly connects to a fabric.
•
NL_Port—Connects to a fabric through an arbitrated loop.
An FC switch provides the following port modes:
•
E_Port—Connects to an E_Port on another FC switch.
•
F_Port—Connects to an N_Port on a node or an NP_Port on another FC switch.
•
G_Port—Operates in auto mode to negotiate the operating mode with its peer:
{
If the peer is an E_Port, the G_Port works as an E_Port.
